ASTM A893/A893M-03(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Complex Dielectric Constant of Nonmetallic Magnetic Materials at Microwave Frequencies
Standard Test Method for Complex Dielectric Constant of Nonmetallic Magnetic Materials at Microwave Frequencies
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method can be used to evaluate batch type or continuous production of material for use in microwave applications. It may be used to determine the loss factors of microwave ferrites or help evaluate absorption materials for use in microwave ovens and other shielding applications.
3.2 The values obtained by use of this practice can be used as quality assurance information for process control, or both, when correlated to the chemistry or process for manufacturing the material.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the complex dielectric constant of isotropic ferrites for extremely high-frequency applications.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. Within this standard, SI units are shown in brackets.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A893/A893M − 03 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Complex Dielectric Constant of Nonmetallic Magnetic
Materials at Microwave Frequencies
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA893/A893M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
k = dielectric constant. If the medium is subjected to an
alternatingelectricfield,theelectricdisplacementisnot
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the com-
necessarily in phase with the field. This fact may be
plex dielectric constant of isotropic ferrites for extremely
expressed mathematically by taking k as a complex
high-frequency applications.
quantity.Ifwewrite k= k'− jk",theimaginarypart, k",
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
determines the dissipation in the medium.
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
2.2 This test method uses a cavity perturbation technique as
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
a means of separating electric from magnetic effects. Quanti-
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
ties that must be measured are the resonance frequency, f,of
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
the cavity with and without the sample, the loaded Q of the
with the standard. Within this standard, SI units are shown in
cavity with and without the specimen, and the cavity and
brackets.
specimen dimensions.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.3 The specimen is in the form of a rod and is placed
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
parallel to the microwave electric field in a region of substan-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
tially uniform electric and zero microwave magnetic fields.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
The perturbation theory requires that the diameter of the
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
samplerodbesmallcomparedtoonequarterofthewavelength
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
of the microwave radiation in the specimen. Estimation of this
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
wavelengthrequiresknowledgeofthepermittivity,ε= kε ,and
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
permeability, µ, of the specimen under the conditions of
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
measurement. The wavelength, λ, in the specimen is given by
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the equation:
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1/2
λ 51/f' µε (2)
~ !
2. Summary of Test Method
For many ferrites, µ may be taken equal to µ , the perme-
ability of empty space, without serious error. The permittivity,
2.1 In an isotropic dielectric medium with a steady electric
ε, is determined by measurement as described below; after
field, E, the electric displacement, D, is given by the equation:
obtaining a value of ε, it is necessary to ascertain with the aid
D 5 kε E (1)
of Eq 1 that the sample diameter is sufficiently small.
where:
2.4 This test method is not suitable for materials with loss
ε = permittivity of free space and tangents ≥0.1, with the loss tangent defined as tan δ= k"⁄k'.
2.5 Theresultsoftheperturbationtheorycalculationmaybe
expressed in the form:
o i o 2
δf/f 5 2 k 2 1 ?Miv E E dv /2?Miv E dv (3)
@ ~ ! # ~ !
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
s c
MagneticPropertiesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA06.01onTest
where:
Methods.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published November 2022. Originally
f = f'+jf'⁄2Q;
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as A893/A893M–03
Q = loaded Q of the cavity;
(2015). DOI: 10.1520/A0893_A0893M-03R22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A893/A893M − 03 (2022)
4. Apparatus
v = specimen volume contained within the cavity,
s
3 3
in. [mm ];
4.1 Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the equipment required
3 3
v = cavity volume, in. [mm ]; and
c for the measurement. Power from a suitable unmodulated or
E = microwave electric field strength.
amplitude modulated microwave source, A, is run through a
The superscript o refers to fields in the empty cavity and the variable attenuator, D, and kept at a constant level throughout
superscript i refers to fields inside the specimen.
the measurement with the aid of a directional coupler, E,a
crystaldetector,andapower-indicatingmeter, F.Thisconstant
2.6 Aspecific cavity suitable for this test method is a TE
10n
power is run through a precision variable attenuator, G,tothe
rectangular cavity, where n is odd. With the rod running
cavity, H,andthecavityoutputpowerisdetectedandindicated
completely across the cavity at the center, Eq 2 for δf/f can be
on a suitable meter, I.
reduced to the following:
δf'/f'522~k'21!~v /v !;δ ~1/Q! 5 4k"~v /v ! (4)
s c s c
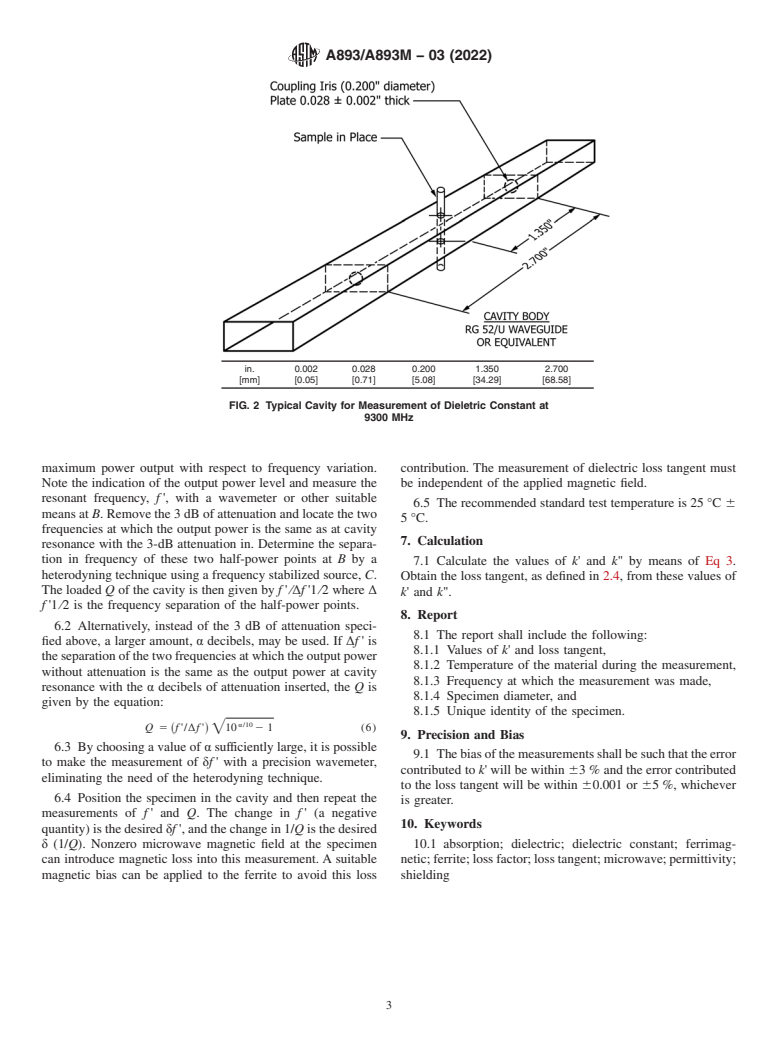
5. Test Specimen and Cavity
δf and δ(1/Q) are, respectively, the difference in the cavity
5.1 The specimen shall be in the form of a rod. It is inserted
resonant frequency with and without the specimen and the
inatransmission-typecavitysothattheaxisoftherodisalong
differenceinthereciprocal Qofthecavitywithandwithoutthe
a line of constant microwave electric field and zero microwave
specimen, and f' is the resonant frequency of the empty cavity.
magnetic field. The ends of the rod shall pass through holes in
both cavity walls.
2.7 Inmanycasesitisconvenienttodescribethedissipative
properties of the med
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.