ASTM D5236-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Distillation of Heavy Hydrocarbon Mixtures (Vacuum Potstill Method)
Standard Test Method for Distillation of Heavy Hydrocarbon Mixtures (Vacuum Potstill Method)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the procedure for distillation of heavy hydrocarbon mixtures having initial boiling points greater than 150°C (300°F), such as heavy crude oils, petroleum distillates, residues, and synthetic mixtures. It employs a potstill with a low pressure drop entrainment separator operated under total takeoff conditions. Distillation conditions and equipment performance criteria are specified and typical apparatus is illustrated.
1.2 This test method details the procedures for the production of distillate fractions of standardized quality in the gas oil and lubricating oil range as well as the production of standard residua. In addition, it provides for the determination of standard distillation curves to the highest atmospheric equivalent temperature possible by conventional distillation.
1.3 The maximum achievable atmospheric equivalent temperature (AET) is dependent upon the heat tolerance of the charge. For most samples, a temperature up to 565°C (10570°F) can be attained. This maximum will be significantly lower for heat sensitive samples (for example, heavy residues) and might be somewhat higher for nonheat sensitive samples.
1.4 The recommended distillation method for crude oils up to cutpoint 400°C (752°F) AET is Test Method D 2892. This test method can be used for heavy crude oils with initial boiling points greater than 150—C (302°F). However, distillation curves and fraction qualities obtained by these methods are not comparable.
1.5 This test method contains the following annexes:
1.5.1 Annex A1—Test Method for Determination of the Temperature Response Time,
1.5.2 Annex A2—Practice for Calibration of Sensors,
1.5.3 Annex A3—Test Method for Dehydration of a Wet Sample of Oil,
1.5.4 Annex A4—Practice for Conversion of Observed Vapor Temperature to Atmospheric Equivalent Temperature (AET), and
1.5.5 Annex A5—Test Method for Determination of Wettage.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warnings see 6.5.4.2, 6.5.6.3, 6.9.3, 9.5, 9.6 and A2.3.1.3.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: D 5236 – 02
Standard Test Method for
Distillation of Heavy Hydrocarbon Mixtures (Vacuum Potstill
1
Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5236; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5.5 Annex A5—Test Method for Determination of Wet-
tage.
1.1 This test method covers the procedure for distillation of
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
heavy hydrocarbon mixtures having initial boiling points
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are
greater than 150°C (300°F), such as heavy crude oils, petro-
provided for information purposes only.
leum distillates, residues, and synthetic mixtures. It employs a
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
potstill with a low pressure drop entrainment separator oper-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ated under total takeoff conditions. Distillation conditions and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
equipment performance criteria are specified and typical appa-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ratus is illustrated.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
1.2 This test method details the procedures for the produc-
warnings see 6.5.4.2, 6.5.6.3, 6.9.3, 9.5, 9.7, and A2.3.1.3.
tion of distillate fractions of standardized quality in the gas oil
and lubricating oil range as well as the production of standard
2. Referenced Documents
residue. In addition, it provides for the determination of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
standard distillation curves to the highest atmospheric equiva-
D 941 Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Spe-
lent temperature possible by conventional distillation.
cific Gravity) of Liquids by Lipkin Bicapillary Pycnom-
1.3 The maximum achievable atmospheric equivalent tem-
2
eter
perature (AET) is dependent upon the heat tolerance of the
D 1160 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products
charge. For most samples, a temperature up to 565°C
3
at Reduced Pressure
(10570°F) can be attained. This maximum will be significantly
D 1217 Test Method for Density and Relative Density
lower for heat sensitive samples (for example, heavy residues)
3
(Specific Gravity) of Liquids by Bingham Pycnometer
and might be somewhat higher for nonheat sensitive samples.
3,4
D 1250 Guide for Petroleum Measurement Tables
1.4 The recommended distillation method for crude oils up
D 1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific
to cutpoint 400°C (752°F) AET is Test Method D 2892. This
Gravity), or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid
test method can be used for heavy crude oils with initial boiling
3
Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method
points greater than 150°C (302°F). However, distillation curves
D 1480 Test Method for Density and Relative Density
and fraction qualities obtained by these methods are not
(Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Bingham Pyc-
comparable.
3
nometer
1.5 This test method contains the following annexes:
D 2892 Test Method for Distillation of Crude Petroleum
1.5.1 Annex A1—Test Method for Determination of Tem-
5
(15-Theoretical Plate Column)
perature Response Time,
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
1.5.2 Annex A2—Practice for Calibration of Sensors,
5
Petroleum Products
1.5.3 Annex A3—Test Method for Dehydration of a Wet
D 4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
Sample of Oil,
5
Petroleum Products
1.5.4 Annex A4—Practice for Conversion of Observed Va-
D 5002 Test Method for Density and Relative Density of
por Temperature to Atmospheric Equivalent Temperature
6
Crude Oils by Digital Density Analyzer
(AET), and
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Discontinued; see 1993 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3
Petroleum Products and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
4
D02.08.0Con Crude Distillation. Description only. Tables are published separately in 12 volumes.
5
Current edition approved April 10, 2002. Published July 2002. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
6
published as D 5236–92. Last previous edition D 5236–01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM
...







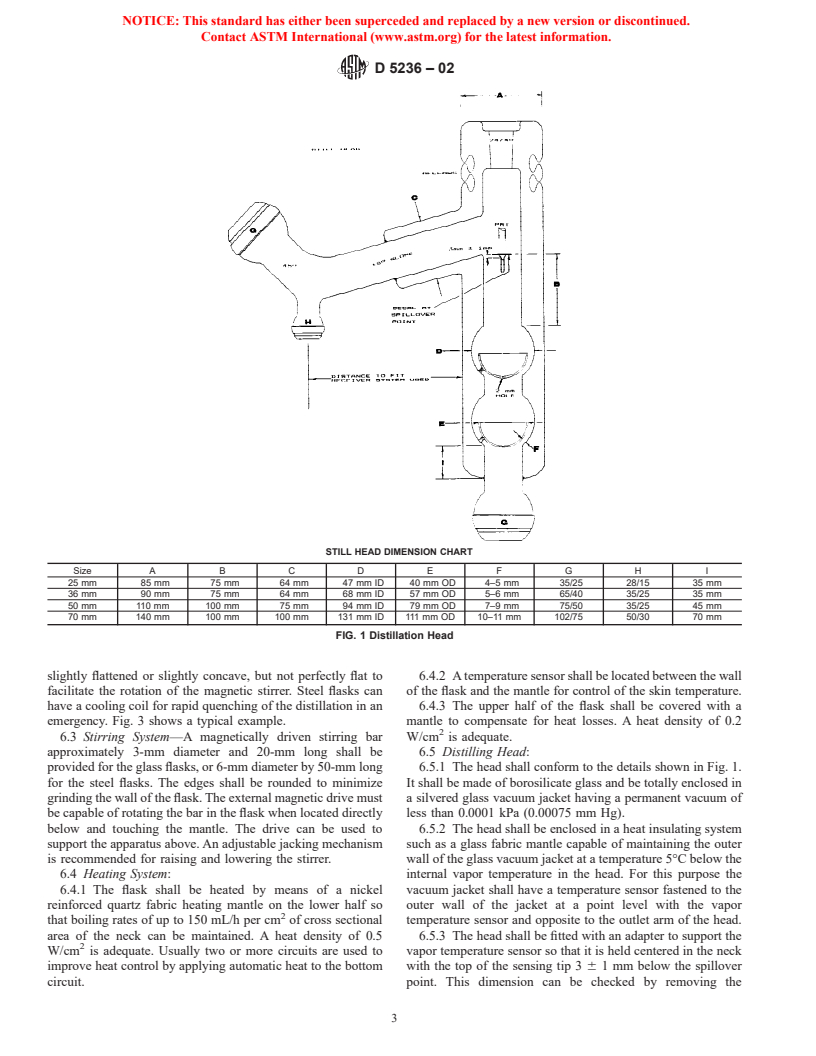
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.