ASTM C502-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Wedging of Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
Standard Test Method for Wedging of Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Tile are normally pressed in dies having true 90° angle construction. However, minor variations in die fill, compacting pressure, and heat treatment can result in finished tile with acute and obtuse angles. This out-of-squareness results in a difference in length of opposite sides, and the tile may have the appearance of a keystone or wedge.
4.2 Excessive wedging presents difficulties in the installation of tile. This test method provides a means for determining the degree of wedging.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wedging or deviation from rectangularity of flat, rectangular wall and floor tile. The test method covers tile as defined in Terminology C242.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C502 − 16
Standard Test Method for
1
Wedging of Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C502; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope pressure, and heat treatment can result in finished tile with
acute and obtuse angles. This out-of-squareness results in a
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wedg-
difference in length of opposite sides, and the tile may have the
ing or deviation from rectangularity of flat, rectangular wall
appearance of a keystone or wedge.
and floor tile. The test method covers tile as defined in
Terminology C242. 4.2 Excessive wedging presents difficulties in the installa-
tion of tile. This test method provides a means for determining
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
the degree of wedging.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
5. Apparatus
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 An apparatus as shown in Fig. 1 or other suitable
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
apparatus. The dial gauge (B) is used for measuring rectangu-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
larity.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. 5.2 A calibrating plate made of steel or aluminum of
accurate dimensions and with straight, flat sides.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6. Test Specimens
C242 Terminology of Ceramic Whitewares and Related
6.1 At least ten tile specimens shall be selected at random
Products
from the lot to be tested. The specimens shall be brushed to
C499 Test Method for Facial Dimensions and Thickness of
remove all adhering particles of clay and sand.
Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
7. Procedure
3. Terminology
7.1 Select an apparatus of the appropriate dimensions so
3.1 Definitions:
that, when a tile is placed in the apparatus, the locating studs
3.1.1 wedging of tile—the difference between two spaced
are 5 mm from each corner of the side adjacent to the side
measurements of the length or width of a tile, expressed as a
being measured. The plunger of the gauge (B) shall also be 5
percentage of the distance between points of measurements.
mm from the corner of the tile on the side being measured.
3.2 For the definition of major and minor facial dimensions
7.2 Fit the appropriate calibrating plate exactly into position
see Test Method C499.
on the instrument and adjust the gauge reading to a suitable
4. Significance and Use
known value.
4.1 Tile are normally pressed in dies having true 90° angle
7.3 Removethecalibratingplate,placethepropersurfaceof
construction. However, minor variations in die fill, compacting
the tile on the locating studs in the apparatus, and record the
gauge reading 5 mm from the corner. Rotate the tile, if square,
1
This method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C21 on Ceramic
to obtain four measurements. Repeat this procedure for each
Whitewares and Related Productsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
tile. In the case of oblong tiles, use separate instruments of the
C21.06 on Ceramic Tile.
appropriate dimensions to measure lengths and widths. Mea-
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2016. Published November 2016. Originally
approved 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C502 – 09. DOI:
sure to an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
10.1520/C0502-16.
2
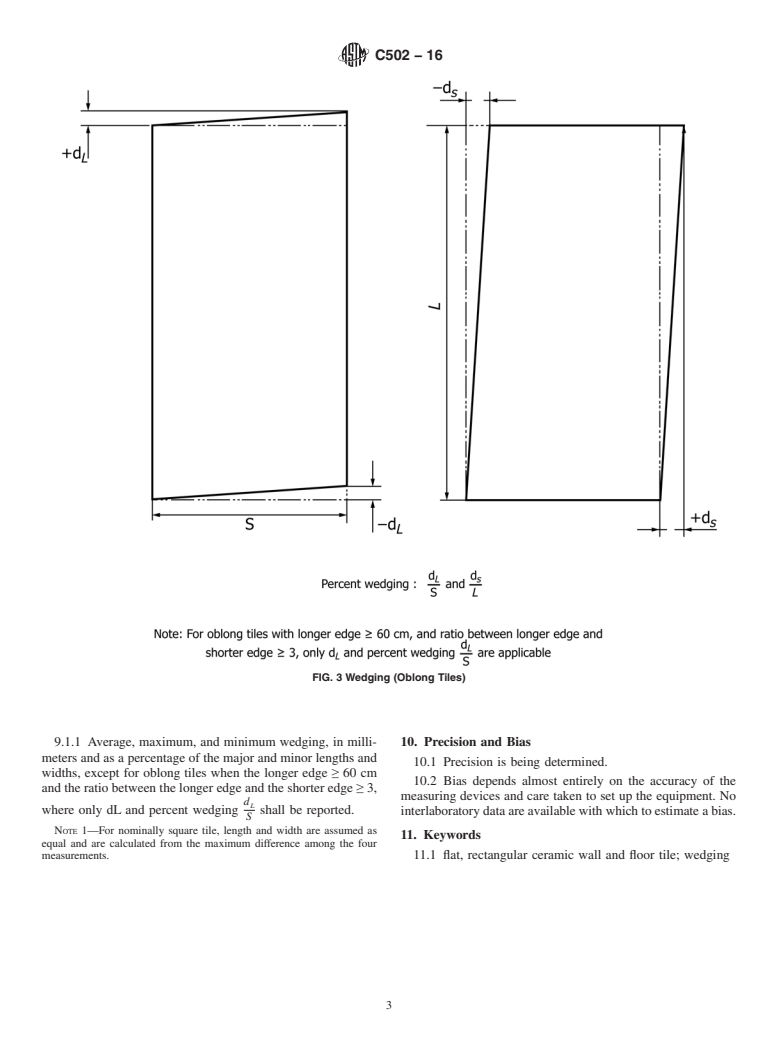
7.4 For oblong tiles with longer edge ≥ 60 cm, and ratio
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
between longer edge and shorter edge≥ 3, only d and percent
L
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
d
L
the ASTM website. wedging shall be determined (see Fig. 3).
S
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C502 − 16
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Measurement of Straightness of Sides and Rectangularity
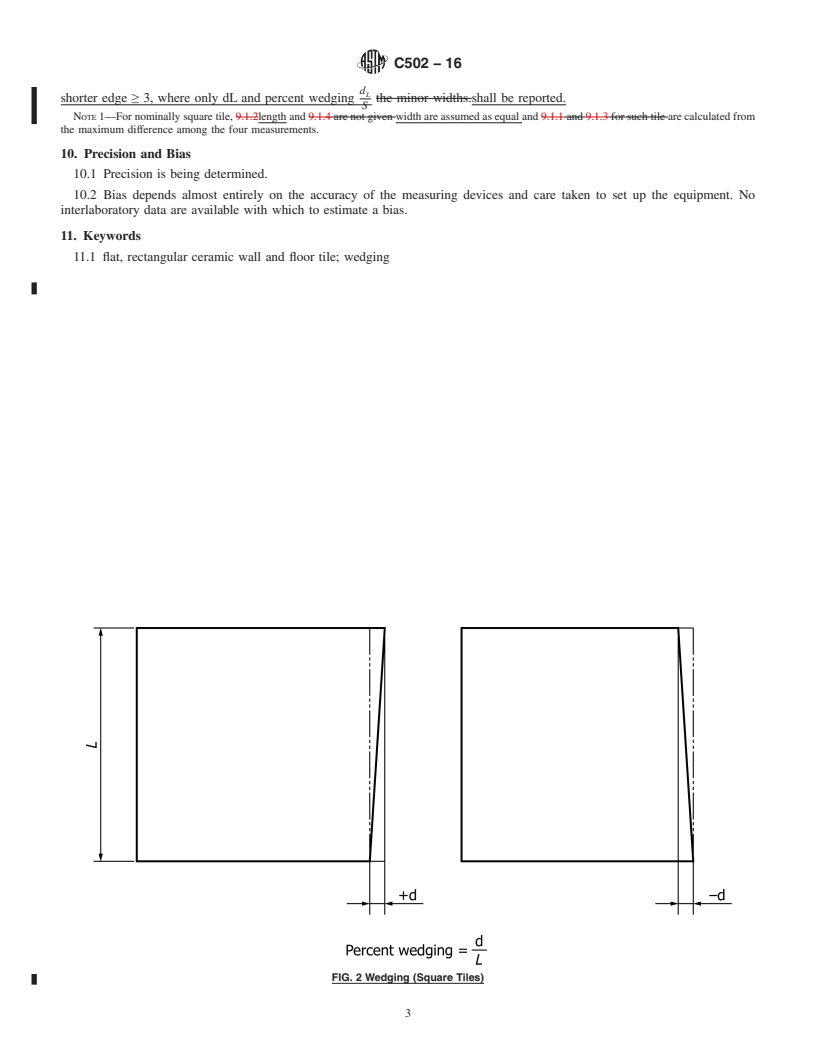
FIG. 2 Wedging (Square Tiles)
8. Calculation
L and S = length of the sides of the tile in accordance with
Figs. 2 and 3,
8.1 Wedging is expressed as:
d = deviation of the outer corner of the side of the tile
8.1.1 In millimeters, d, for square tiles (see Fig. 2) and
(measured 5 mm
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C502 − 09 C502 − 16
Standard Test Method for
1
Wedging of Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C502; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wedging or deviation from rectangularity of flat, rectangular wall and floor
tile. The test method covers tile as defined in Terminology C242.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C242 Terminology of Ceramic Whitewares and Related Products
C499 Test Method for Facial Dimensions and Thickness of Flat, Rectangular Ceramic Wall and Floor Tile
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 wedging of tile—the difference between two spaced measurements of the length or width of a tile, expressed as a
percentage of the distance between points of measurements.
3.2 For the definition of major and minor facial dimensions see Test Method C499.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Tile are normally pressed in dies having true 90° angle construction. However, minor variations in die fill, compacting
pressure, and heat treatment can result in finished tile with acute and obtuse angles. This out-of-squareness results in a difference
in length of opposite sides, and the tile may have the appearance of a keystone or wedge.
4.2 Excessive wedging presents difficulties in the installation of tile. This test method provides a means for determining the
degree of wedging.
5. Apparatus
5.1 An apparatus as shown in Fig. 1 or other suitable apparatus. The dial gage (B) is used for measuring rectangularity.
5.2 A calibrating plate made of steel or aluminum of accurate dimensions and with straight, flat sides.
6. Test Specimens
6.1 At least ten tile specimens shall be selected at random from the lot to be tested. The specimens shall be brushed to remove
all adhering particles of clay and sand.
7. Procedure
7.1 Select an apparatus of the appropriate dimensions so that, when a tile is placed in the apparatus, the locating studs are 5 mm
from each corner of the side adjacent to the side being measured. The plunger of the gage (B) shall also be 5 mm from the corner
of the tile on the side being measured.
1
This method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C21 on Ceramic Whitewares and Related Productsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C21.06
on Ceramic Tile.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2009Nov. 1, 2016. Published January 2009November 2016. Originally approved 1962. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
C502 – 04.C502 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/C0502-09.10.1520/C0502-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C502 − 16
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Measurement of Straightness of Sides and Rectangularity
7.2 Fit the appropriate calibrating plate exactly into position on the instrument and adjust the gauge reading to a suitable known
value.
7.3 Remove the calibrating plate, place the proper surface of the tile on the locating studs in the apparatus, and record the gage
reading 5 mm from the corner. Rotate the tile, if square, to obtain four measurements. Repeat this procedure for each tile. In the
case of oblong tiles, use separate instruments of the appropriate dimensions to measure lengths and widths. Measure to an accuracy
of 0.1 mm.
7.4 For oblong tiles with longer edge ≥ 60 cm, and ratio between longer edge and shorter edge ≥ 3, only d and percent wedging
L
d
L
shall be determined (see Fig. 3).
S
8. Calculation
8.1 Calculate the percentage of wedging or deviation from rectangularity as follows:W
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.