ASTM D7573-09(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Carbon and Organic Carbon in Water by High Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Infrared Detection
Standard Test Method for Total Carbon and Organic Carbon in Water by High Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Infrared Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used for determination of the carbon content of water from a variety of natural, domestic, and industrial sources. In its most common form, this test method is used to measure organic carbon as a means of monitoring organic pollutants in industrial wastewater. These measurements are also used in monitoring waste treatment processes.
5.2 The relationship of TOC to other water quality parameters such as chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total oxygen demand (TOD) is described in the literature.4
SCOPE
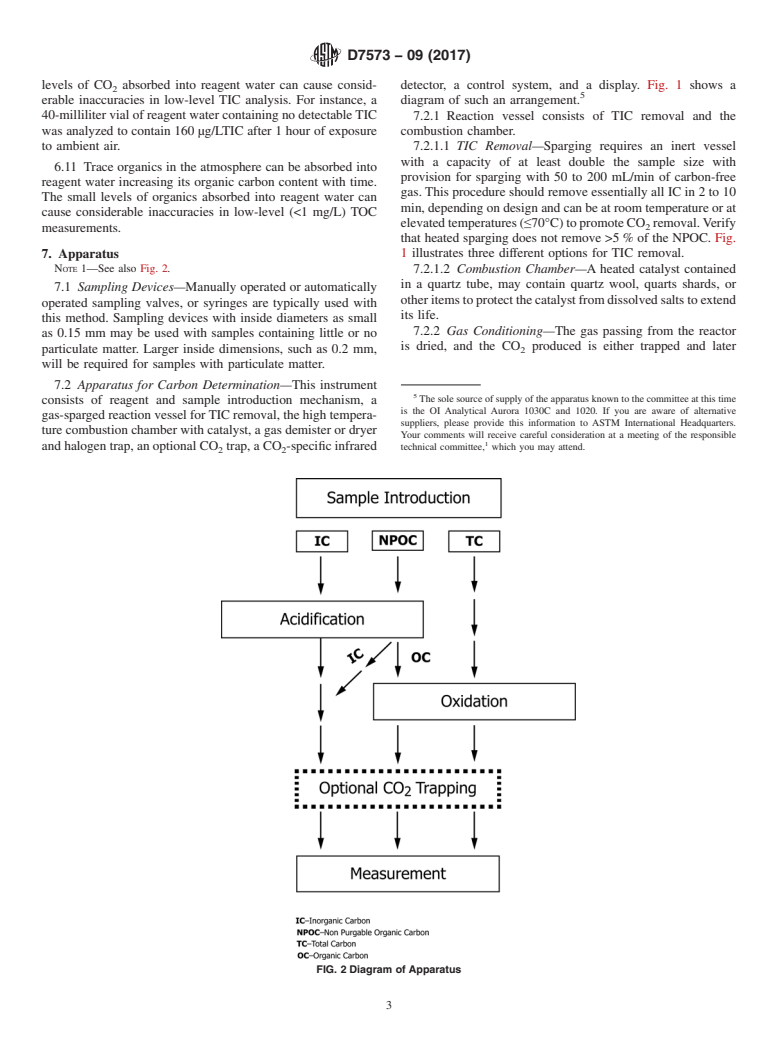
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total carbon (TC), inorganic carbon (IC), total organic carbon (TOC), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), and non-purgable organic carbon (NPOC) in water, wastewater, and seawater in the range from 0.5 mg/L to 4000 mg/L of carbon. Higher levels may be determined by sample dilution. The sample is injected onto a quartz bed heated at 680ºC. The sample converts into a gaseous phase and forced through a layer of catalyst ensuring conversion of all carbon containing compounds to CO2. A non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) detector measures the resulting CO2.
1.2 For TOC and DOC analysis a portion of the sample is injected to determine TC or dissolved carbon (DC). A portion of the sample is then acidified and purged to remove the IC. The purged inorganic carbon is measured as TIC, or DIC. TOC or DOC is calculated by subtracting the inorganic fraction from the total carbon:
1.3 For NPOC analysis a portion of sample is acidified and purged to remove IC. The purged sample is then injected to determine NPOC.
1.4 This test method was used successfully with reagent water spiked with potassium hydrogen phthalate, sucrose, nicotinic acid, benzoquinone, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, urea, acetic acid, and humic acid. It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
1.5 This test method is applicable only to carbonaceous matter in the sample that can be introduced into the reaction zone. The syringe needle or injector opening size generally limits the maximum size of particles that can be so introduced.
1.6 In addition to laboratory analyses, this test method may be applied to stream monitoring.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7573 − 09 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Total Carbon and Organic Carbon in Water by High
1
Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Infrared Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7573; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total
standard.
carbon (TC), inorganic carbon (IC), total organic carbon
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(TOC), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), and non-purgable
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
organic carbon (NPOC) in water, wastewater, and seawater in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
therangefrom0.5mg/Lto4000mg/Lofcarbon.Higherlevels
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
may be determined by sample dilution. The sample is injected
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
onto a quartz bed heated at 680ºC. The sample converts into a
gaseous phase and forced through a layer of catalyst ensuring
2. Referenced Documents
conversion of all carbon containing compounds to CO.A
2
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
non-dispersiveinfrared(NDIR)detectormeasurestheresulting
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
CO .
2
D1192 Guide for Equipment for Sampling Water and Steam
1.2 For TOC and DOC analysis a portion of the sample is
3
in Closed Conduits (Withdrawn 2003)
injected to determine TC or dissolved carbon (DC). A portion
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
of the sample is then acidified and purged to remove the IC.
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
The purged inorganic carbon is measured asTIC, or DIC.TOC
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
orDOCiscalculatedbysubtractingtheinorganicfractionfrom
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
the total carbon:
D4129 Test Method for Total and Organic Carbon in Water
TOC 5 TC 2 IC
by High Temperature Oxidation and by Coulometric
Detection
1.3 For NPOC analysis a portion of sample is acidified and
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
purged to remove IC. The purged sample is then injected to
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
determine NPOC.
1.4 This test method was used successfully with reagent 3. Terminology
water spiked with potassium hydrogen phthalate, sucrose,
3.1 Definitions:
nicotinic acid, benzoquinone, sodium dodecyl benzene
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
sulfonate, urea, acetic acid, and humic acid. It is the user’s
Terminology D1129.
responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
waters of untested matrices.
3.2.1 inorganic carbon (IC), n—carbon in the form of
1.5 This test method is applicable only to carbonaceous
carbon dioxide, carbonate ion, or bicarbonate ion.
matter in the sample that can be introduced into the reaction
3.2.2 total organic carbon (TOC), n—carbon in the form of
zone. The syringe needle or injector opening size generally
organic compounds.
limits the maximum size of particles that can be so introduced.
3.2.3 non-purgable organic carbon (NPOC), n—carbon
1.6 In addition to laboratory analyses, this test method may
measured in a sample after acidification and sparging to
be applied to stream monitoring.
remove inorganic carbon.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Organic Substances in Water. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2017. Published February 2017. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D7573 – 09. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D7573-09R17. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7573 − 09 (2017)
3.2.4 total carbon (TC), n—the sum of IC and TOC. 5.2 The relationship of TOC to other water quality param-
eterssuchaschemicaloxygendemand(COD)andtotaloxygen
3.2.5 dissolved organic carbon (DOC), n—carbon deter-
4
demand (TOD) is descr
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7573 − 09 D7573 − 09 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Total Carbon and Organic Carbon in Water by High
1
Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Infrared Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7573; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total carbon (TC), inorganic carbon (IC), total organic carbon (TOC), dissolved
organic carbon (DOC), and non-purgable organic carbon (NPOC) in water, wastewater, and seawater in the range from 0.5 mg/L
to 4000 mg/L of carbon. Higher levels may be determined by sample dilution. The sample is injected onto a quartz bed heated at
680ºC. The sample converts into a gaseous phase and forced through a layer of catalyst ensuring conversion of all carbon
containing compounds to CO . A non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) detector measures the resulting CO .
2 2
1.2 For TOC and DOC analysis a portion of the sample is injected to determine TC or dissolved carbon (DC). A portion of the
sample is then acidified and purged to remove the IC. The purged inorganic carbon is measured as TIC, or DIC. TOC or DOC is
calculated by subtracting the inorganic fraction from the total carbon. carbon:
TOC 5 TC 2 IC
TOC = TC – IC.
1.3 For NPOC analysis a portion of sample is acidified and purged to remove IC. The purged sample is then injected to
determine NPOC.
1.4 This test method was used successfully with reagent water spiked with potassium hydrogen phthalate, sucrose, nicotinic
acid, benzoquinone, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, urea, acetic acid, and humic acid. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure
the validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
1.5 This test method is applicable only to carbonaceous matter in the sample that can be introduced into the reaction zone. The
syringe needle or injector opening size generally limits the maximum size of particles that can be so introduced.
1.6 In addition to laboratory analyses, this test method may be applied to stream monitoring.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
3
D1192 Guide for Equipment for Sampling Water and Steam in Closed Conduits (Withdrawn 2003)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D4129 Test Method for Total and Organic Carbon in Water by High Temperature Oxidation and by Coulometric Detection
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis for
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009Feb. 1, 2017. Published November 2009February 2017. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as
D7573 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/D7573-09.10.1520/D7573-09R17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7573 − 09 (2017)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions: For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D1129.
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to Terminology D1129.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 inorganic carbon (IC), n—carbon in the form of carbon dioxide
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.