ASTM D4438-24
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Electronic Counting
Standard Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers by Electronic Counting
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method can be used to determine particle size distributions for material specifications, manufacturing control, and research and development work in the particle size range usually encountered in fluidizable cracking catalysts.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of particle size distribution of catalyst and catalyst carrier (see Terminology D3766) particles using an electroconductive sensing method and is one of several valuable methods for the measurement of particle size.
1.2 The range of particle sizes investigated was 20 μm to 150 μm (see IEEE/ASTM SI 10) equivalent spherical diameter. The technique is capable of measuring particles above and below this range. The instrument used for this method is an electric current path of small dimensions that is modulated by individual particle passage through an aperture, and produces individual pulses of amplitude proportional to the particle volume.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4438 − 24
Standard Test Method for
Particle Size Distribution of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers
1
by Electronic Counting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4438; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
1.1 This test method covers the determination of particle
Lot or Process
size distribution of catalyst and catalyst carrier (see Terminol-
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ogy D3766) particles using an electroconductive sensing
ASTM Test Methods
method and is one of several valuable methods for the
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
measurement of particle size.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.2 The range of particle sizes investigated was 20 μm to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
150 μm (see IEEE/ASTM SI 10) equivalent spherical diameter.
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylin-
The technique is capable of measuring particles above and
ders
below this range. The instrument used for this method is an
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International
electric current path of small dimensions that is modulated by
System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
individual particle passage through an aperture, and produces
individual pulses of amplitude proportional to the particle
3. Summary of Test Method
volume.
3.1 A carefully dispersed, dilute suspension of the represen-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tative sample in a beaker filled with an electrolyte is placed in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the counting position on the instrument sample stand. The
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
suspension is forced through a restricting aperture. Each
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
passing particle is recorded on an electronic counter, and the
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
data are accumulated according to selected particle size inter-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
vals for subsequent processing.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2 The instrument response is proportional to liquid dis-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
placement by the particle volume. Equivalent spherical diam-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
eter is commonly used to express the particle size.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents 4.1 This test method can be used to determine particle size
distributions for material specifications, manufacturing control,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and research and development work in the particle size range
B215 Practices for Sampling Metal Powders
usually encountered in fluidizable cracking catalysts.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D3766 Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
3
5. Apparatus
E105 Guide for Probability Sampling of Materials
5.1 Electronic Particle Counter, with sample stand and
stirring motor.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
5.2 Aperture Tubes, with varying diameters. The diameter
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.02 on Physical-
required is dependent upon the particle size distribution of the
Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved March 15, 2024. Published March 2024. Originally
sample. Generally, any given tube will cover a particle size
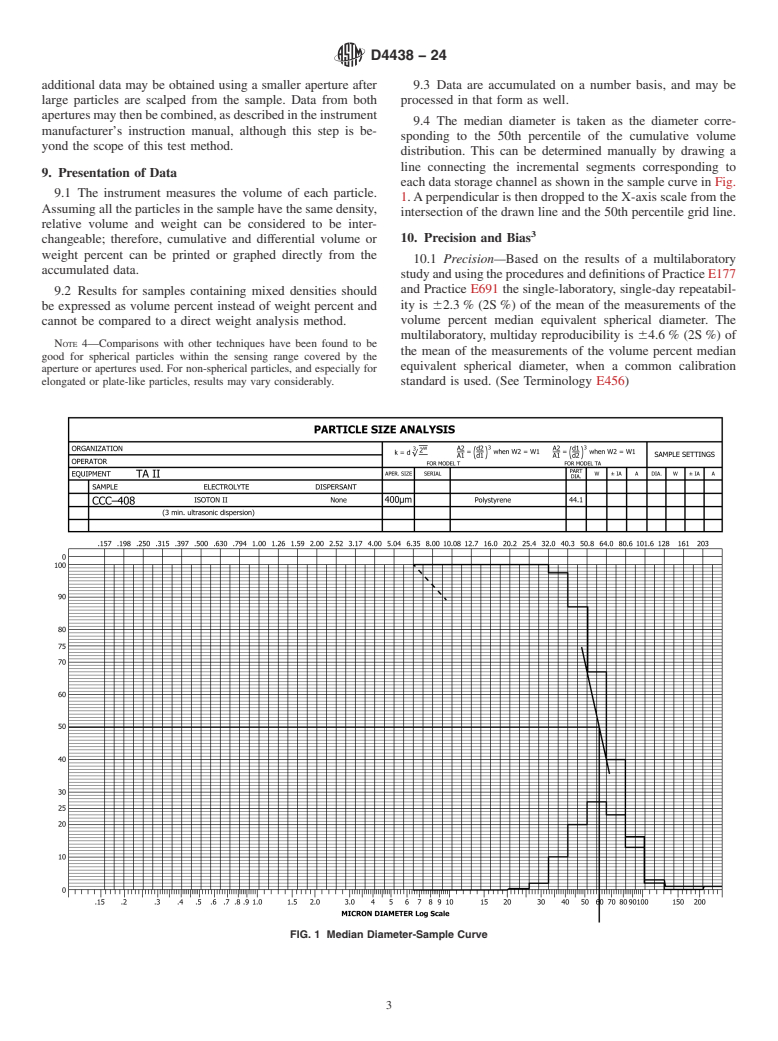
ɛ1
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D4438 – 13 (2018) .
range from 2 % to 40 % of its aperture diameter.
DOI: 10.1520/D4438-24.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may
the ASTM website. be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D32-1011.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4438 − 24
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D4438 − 13 (Reapproved 2018) D4438 − 24
Standard Test Method for
Particle Size Distribution of Catalysts and Catalyst Carriers
1
by Electronic Counting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4438; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Keywords revised editorially in May 2018.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of particle size distribution of catalyst and catalyst carrier (see Terminology D3766)
particles using an electroconductive sensing method and is one of several valuable methods for the measurement of particle size.
1.2 The range of particle sizes investigated was 20 to 150 μm 20 μm to 150 μm (see IEEE/ASTM SI 10) equivalent spherical
diameter. The technique is capable of measuring particles above and below this range. The instrument used for this method is an
electric current path of small dimensions that is modulated by individual particle passage through an aperture, and produces
individual pulses of amplitude proportional to the particle volume.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B215 Practices for Sampling Metal Powders
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D3766 Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
E105 Guide for Probability Sampling of Materials
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a Lot or
Process
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylinders
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.02 on Physical-Mechanical
Properties.
Current edition approved May 1, 2018March 15, 2024. Published June 2018March 2024. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 20132018 as
ɛ1
D4438 – 13.D4438 – 13 (2018) . DOI: 10.1520/D4438-13R18E01.10.1520/D4438-24.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4438 − 24
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A carefully dispersed, dilute suspension of the representative sample in a beaker filled with an electrolyte is placed in the
counting position on the instrument sample stand. The suspension is forced through a restricting aperture. Each passing particle
is recorded on an electronic counter, and the data are accumulated according to selected particle size intervals for subsequent
processing.
3.2 The instrument response is proportional to liquid displacement by the particle volume. Equivalent spherical diameter is
commonly used to express the particle size.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method can be used to determine particle size distributions for material specifications, manufacturing control, and
research and development work in the particle size range usually encountered in fluidizable cracking catalysts.
3
5. Apparatus
5.1 Electronic Particle Counter, with sample stand and stirring motor.
5.2 Aperture Tubes, with varying diameters. The diameter required is dependent upon the particle size distribu
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.