ASTM D1916-93(1997)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Penetration of Adhesives (Withdrawn 2005)
Standard Test Method for Penetration of Adhesives (Withdrawn 2005)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the penetration under pressure of adhesives used in systems where at least one of the adherends is porous.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the determination of the penetration under pressure of adhesives used in systems where at least one of the adherends is porous.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D14 on Adhesives, this test method was withdrawn in April 2005. This standard is being withdrawn without replacement due to its limited use by industry.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1916–93 (Reapproved 1997)
Standard Test Method for
Penetration of Adhesives
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1916; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the pen-
etration under pressure of adhesives used in systems where at
least one of the adherends is porous.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 907 Terminology of Adhesives
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Many terms in this test method are de-
fined in Terminology D 907.
3.1.1 adhesive penetration, n—the entering of an adhesive
into a porous adherend.
4. Significance and Use
Metric Equivalents
in. 1 1 ⁄16 231
4.1 This test method is useful in selecting adhesive systems
mm 25 27 51 787 (0.8 m)
for a particular application, and in modifying adhesive systems
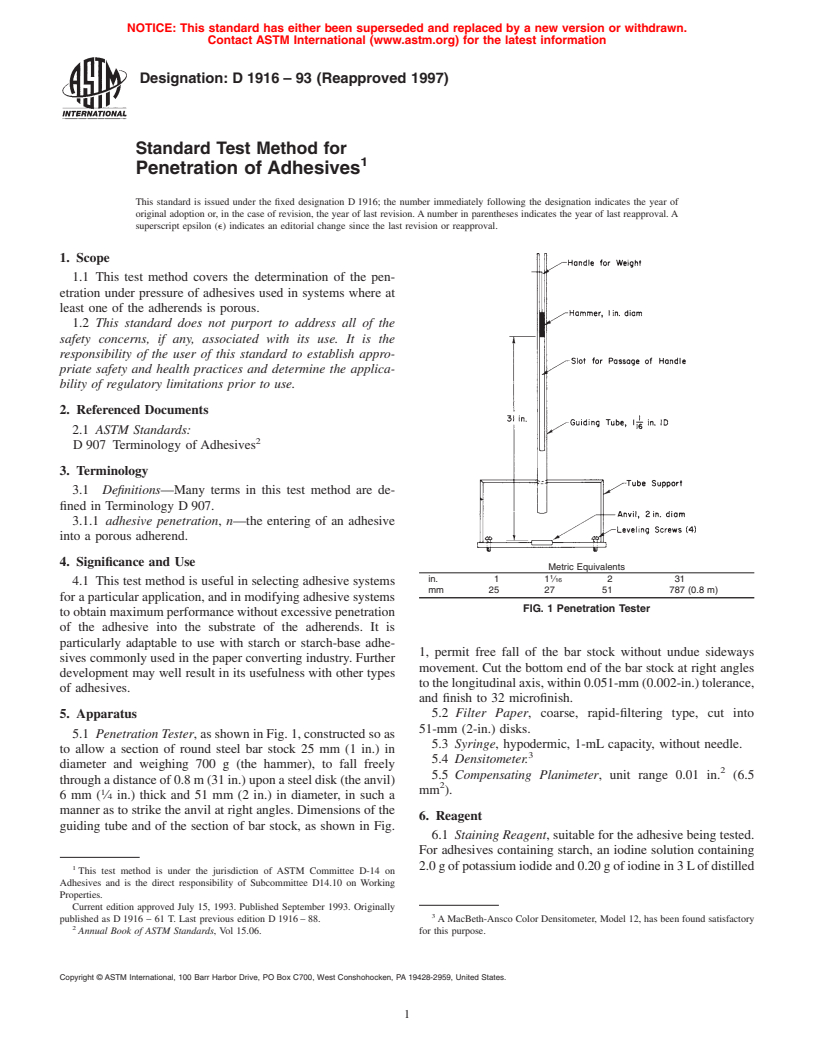
FIG. 1 Penetration Tester
to obtain maximum performance without excessive penetration
of the adhesive into the substrate of the adherends. It is
particularly adaptable to use with starch or starch-base adhe-
1, permit free fall of the bar stock without undue sideways
sives commonly used in the paper converting industry. Further
movement. Cut the bottom end of the bar stock at right angles
development may well result in its usefulness with other types
to the longitudinal axis, within 0.051-mm (0.002-in.) tolerance,
of adhesives.
and finish to 32 microfinish.
5. Apparatus 5.2 Filter Paper, coarse, rapid-filtering type, cut into
51-mm (2-in.) disks.
5.1 Penetration Tester, as shown in Fig. 1, constructed so as
5.3 Syringe, hypodermic, 1-mL capacity, without needle.
to allow a section of round steel bar stock 25 mm (1 in.) in
5.4 Densitometer.
diameter and weighing 700 g (the hammer), to fall freely
5.5 Compensating Planimeter, unit range 0.01 in. (6.5
through a distance of 0.8 m (31 in.) upon a steel disk (the anvil)
mm ).
6mm( ⁄4 in.) thick and 51 mm (2 in.) in diameter, in such a
manner as to strike the anvil at right angles. Dimensions of the
6. Reagent
guiding tube and of the section of bar stock, as shown in Fig.
6.1 Staining Reagent, suitable for the adhesive being tested.
For adhesives containing starch, an iodine solution containing
1 2.0gofpotassiumiodideand0.20gofiodinein3Lofdistilled
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-14 on
Adhesives and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.10 on Working
Properties.
Current edition approved July 15, 1993. Published September 1993. Originally
published as D 1916 – 61 T. Last previous edition D 1916 – 88. A MacBeth-Ansco Color Densitometer, Model 12, has been found satisfactory
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.06. for this purpose.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1916
water is appropriate. Some adhesives that are basic in pH must 7.8 Measure the stained area of each level with the com-
be stained with phenolphthalein or other suitable indicator pensating planimeter.
solution.
8. Calculation
7. Procedure
8.1 Calculate the corrected densitometer readings of Level
7.1 Place five disks of filter paper, stacked one on top of
one, M , as follows:
another, upon the anvil at the bottom of the tube.Apply 0.1 mL
M 5 K 2 L (1)
1 2 1
of the adhesive to be tested to the center of the bottom end of
the hammer (bar stock) using the 1-mLsyringe (Note 1). If the
where:
hammer has been inverted for this purpose, reinvert the K 5 averaged densitometer readings of the colored areas
hammer so that the adhesive is now on the bottom and place in of Level one, and
the testing apparatus with the handle of the hammer resting in L 5 averaged densitometer readings of the unstained
areas of Level one.
the notch provided for it (Note 2).
8.2 Calculate the corrected density times area at Level one,
NOTE 1—The hammer may be inverted for this purpose.
J , as follows:
NOTE 2—Inversion of the hammer without loss of adhesive may require
some practice. If any adhesive is lost during this step, restar
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.