ASTM E490-00a(2006)
(Guide)Standard Solar Constant and Zero Air Mass Solar Spectral Irradiance Tables
Standard Solar Constant and Zero Air Mass Solar Spectral Irradiance Tables
SCOPE
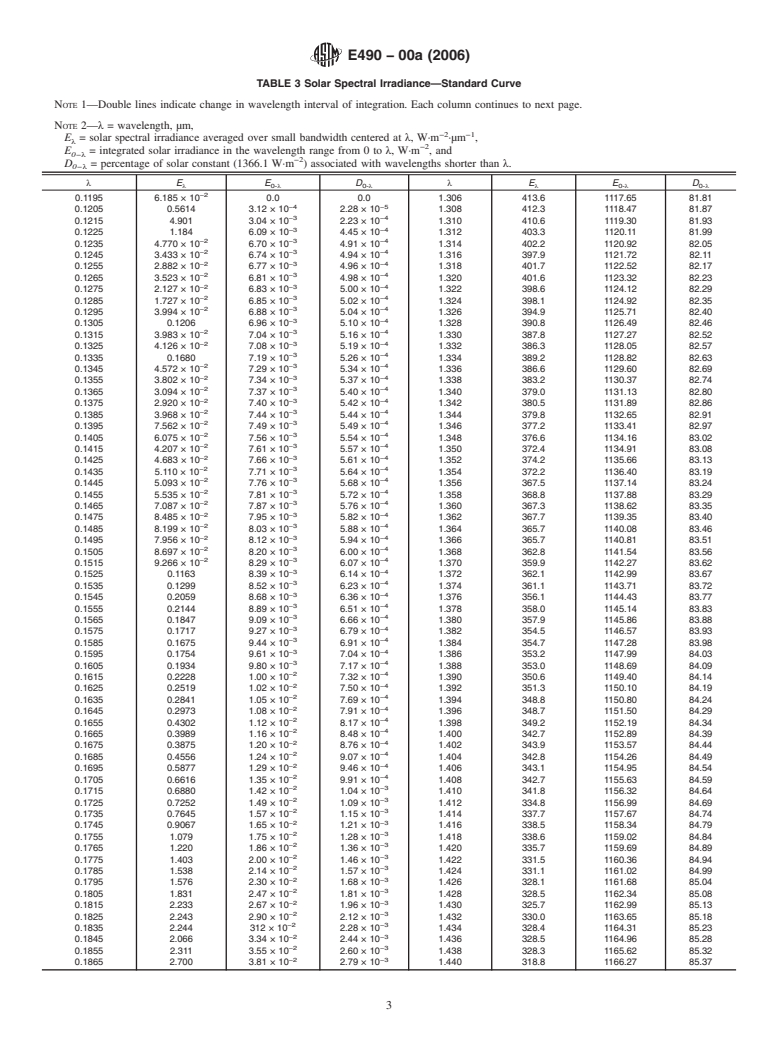
1.1 These tables define the solar constant and zero air mass solar spectral irradiance for use in thermal analysis, thermal balance testing, and other tests of spacecraft and spacecraft components and materials. Typical applications include the calculation of solar absorptance from spectral reflectance data and the specification of solar UV exposure of materials during simulated space radiation testing.
1.2 These tables are based upon data from experimental measurements made from high-altitude aircraft, spacecraft, and the earth's surface and from solar spectral irradiance models.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Other units of measurement are included for information purposes only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E490 − 00a(Reapproved 2006)
Standard
Solar Constant and Zero Air Mass Solar Spectral Irradiance
1
Tables
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E490; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope AM 5 l /l>secZ , for Z#62° (1)
m z
1.1 These tables define the solar constant and zero air mass
Symbol: AM1 (air mass one), AM2 (air mass two)
solar spectral irradiance for use in thermal analysis, thermal
3.2 astronomical unit (AU),n—a unit of length defined as
balance testing, and other tests of spacecraft and spacecraft
the mean distance between the earth and the sun, that is,
components and materials. Typical applications include the
149597890 6 500 km.
calculation of solar absorptance from spectral reflectance data
3.3 integrated irradiance, n—spectral irradiance integrated
and the specification of solar UV exposure of materials during
over a specific wavelength interval from λ to λ , measured in
1 2
simulated space radiation testing.
−2
W·m , Symbol:
1.2 These tables are based upon data from experimental
λ2
E 5 E dλ (2)
*
measurementsmadefromhigh-altitudeaircraft,spacecraft,and
λ12λ2 λ
λ1
the earth’s surface and from solar spectral irradiance models.
3.4 irradiance at a point on a surface (E) , n—quotient of
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the radiant flux incident on an element of the surface contain-
−2
standard. Other units of measurement are included for infor- ing the point, by the area of that element, measured in W·m .
mation purposes only.
3.5 irradiance, spectral (E), n—the irradiance per unit
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the wavelength interval at a specific wavelength, or as a function
−2 −1
of wavelength measured in W·m ·µm .
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.6 solar constant, n—the total solar irradiance at normal
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
incidence on a surface in free space at the earth’s mean
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
distance from the sun (1 AU).
3.7 zero air mass (AMO),n—the absence of atmospheric
2. Referenced Documents
attenuation of the solar irradiance at one astronomical unit
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
from the sun.
E349Terminology Relating to Space Simulation
3.8 Additional definitions will be found in Terminology
E349.
3. Terminology
3.1 air mass (optical air mass) (AM),n—the ratio of the 4. Solar Constant
−2
path length or radiation through the atmosphere (l )atany
m
4.1 The solar constant is 1366.1 W·m . This value is the
given angle, Z degrees, to the sea level path length toward the
mean of daily averages from six different satellites over the
zenith (l ).
z
1978 to 1998 time period, all measured with absolute cavity
3
radiometers, as reported by Fröhlich and Lean (1) . The
standard deviation of this mean value is 425 ppm, with a
−2
1
These tables are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E21 on Space 0.37% minimum-to-maximum range (1363 to 1368 W·m ).
Simulation and Applications of Space Technology and are the direct responsibility
4.2 Table 1 summarizes the results in different units, and
of Subcommittee E21.04 on Space Simulation Test Methods.
Table 2 presents the total solar irradiance at various planetary
Current edition approved April 1, 2006. Published April 2006. Originally
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as E49–00a. DOI:
distances from the sun.
10.1520/E0490-00AR06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Theboldfacenumbersinparenthesesrefertothelistofreferencesattheendof
the ASTM website. these tables.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E490 − 00a (2006)
TABLE 1 The Solar Constant in Alternative Units
−2
Solar constant = 1366.1 W·m [SI unit]
−2
= 0.136 61 W·cm
−2
= 136.61 m W·cm
6 −2 -1
=1.3661×10 erg·cm ·s
−2
= 126.9 W·ft
−2 −1
= 1.959 cal·cm ·min (±0.03
−2 −1
cal·cm ·min )
−2 −1
= 0.0326 cal·cm ·s
−2 −1
= 433.4 Btu·ft ·h
−2 −1
= 0.1202 Btu·ft ·s
−1
= 1.956 Langleys·min
The calorie is the thermochemical calorie-gram and is defined as 4.1840
absolute joules.
The Btu is the thermochemical British thermal unit and is d
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.