ASTM D4529-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Estimation of Net Heat of Combustion of Aviation Fuels
Standard Test Method for Estimation of Net Heat of Combustion of Aviation Fuels
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the net heat of combustion at constant pressure in metric (SI) units, megajoules per kilogram.
1.2 This test method is purely empirical, and it is applicable only to liquid hydrocarbon fuels derived by normal refining processes from conventional crude oil which conform to the requirements of specifications for aviation gasolines or aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels of limited boiling ranges and compositions as described in Note 1.
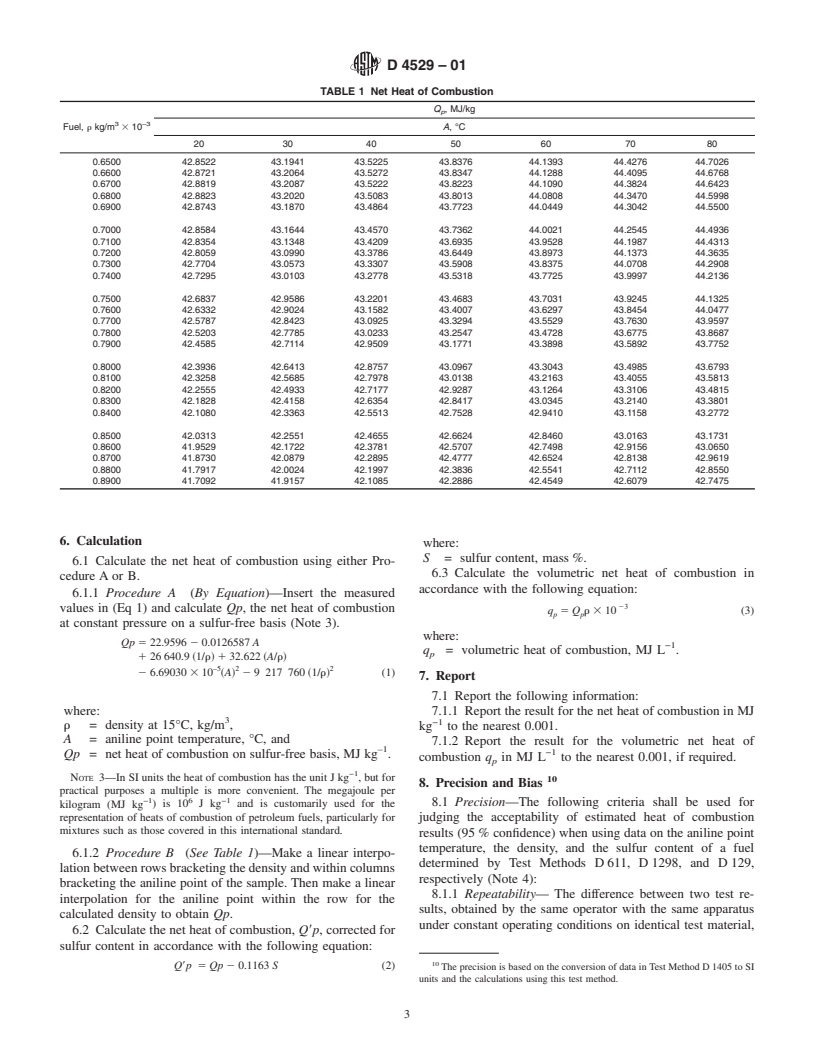
Note 1--The estimation of the net heat of combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel from its aniline point temperature and density is justifiable only when the fuel belongs to a well-defined class for which a relationship between these quantities has been derived from accurate experimental measurements on representative samples of that class. Even in this class, the possibility that the estimates can be in error by large amounts for individual fuels should be recognized. The JP-8 fuel, although not experimentally tested, has properties similar to JP-5 and Jet A fuels and can be considered in the same class. The classes of fuels used to establish the correlation presented in this test method are represented by the following applications:Fuel SpecificationAviation gasoline fuels:Specification D 910Grades 80, 82, 100/130, and 115/145Specification D 6227 DEF STAN 91-90 NATO Code F-18Aviation turbine fuels: MIL-DTL-5624JP-4, Avtag/FSIIDEF STAN 91-88 NATO Code F-40JP-5, Avcat/FSIIMIL-DTL-5624 DEF STAN 91-86 NATO Code F-44JP-8, Avtur/FSIIMIL-DTL-83133 DEF STAN 91-87 NATO Code F-34Jet A, Jet A-1, AvturSpecification D 1655 DEF STAN 91-91 NATO Code F-35
1.3 The net heat of combustion can also be estimated by Test Method D1405. Test Method D1405 requires calculation of one of four equations dependent on the fuel type with the precision equivalent to that of this test method.
1.4 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D4529–01
Designation: 381/97
Standard Test Method for
1
Estimation of Net Heat of Combustion of Aviation Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4529; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
JP-8, Avtur/FSII MIL-DTL-83133
DEF STAN 91–87
1.1 Thistestmethodcoverstheestimationofthenetheatof
NATO Code F-34
combustion at constant pressure in metric (SI) units, mega-
Jet A, Jet A-1, Avtur Specification D 1655
joules per kilogram.
DEF STAN 91–91
1.2 Thistestmethodispurelyempirical,anditisapplicable
NATO Code F-35
only to liquid hydrocarbon fuels derived by normal refining
1.3 The net heat of combustion can also be estimated by
processes from conventional crude oil which conform to the
Test Method D1405.Test Method D1405 requires calculation
requirements of specifications for aviation gasolines or aircraft
of one of four equations dependent on the fuel type with the
turbine and jet engine fuels of limited boiling ranges and
precision equivalent to that of this test method.
compositions as described in Note 1.
1.4 The values stated in acceptable metric units are to be
NOTE 1—The estimation of the net heat of combustion of a hydrocar-
regarded as the standard.
bon fuel from its aniline point temperature and density is justifiable only
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
when the fuel belongs to a well-defined class for which a relationship
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
between these quantities has been derived from accurate experimental
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
measurements on representative samples of that class. Even in this class,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the possibility that the estimates can be in error by large amounts for
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
individual fuels should be recognized. The JP-8 fuel, although not
experimentally tested, has properties similar to JP-5 and Jet A fuels and
2. Referenced Documents
can be considered in the same class.The classes of fuels used to establish
the correlation presented in this test method are represented by the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
following applications:
D129 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products (Gen-
Fuel Specification 2
eral Bomb Method)
D240 Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid
Aviation gasoline fuels: Specification D 910
2
Grades 80, 82, 100/130, and 115/145 Specification D 6227 Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter
DEF STAN 91–90
D611 Test Methods for Aniline Point and Mixed Aniline
NATO Code F-18
2
Point of Petroleum Products and Hydrocarbon Solvents
2
Aviation turbine fuels: MIL-DTL-5624
D910 Specification for Aviation Gasolines
JP-4, Avtag/FSII DEF STAN 91–88
D941 Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Spe-
NATO Code F-40
cific Gravity) of Liquids by Lipkin Bicapillary Pycnom-
2
JP-5, Avcat/FSII MIL-DTL-5624
eter
DEF STAN 91–86
D1217 Test Method for Density and Relative Density
NATO Code F-44
2
(Specific Gravity) of Liquids by Bingham Pycnometer
2
D1250 Guide for Petroleum Measurement Tables
D1266 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products
2
(Lamp Method)
1
D1298 TestMethodforDensity,RelativeDensity(Specific
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee Gravity) or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid
2
D02.05 on Petroleum, Coke, and Carbon Materials.
Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2001. Published March 2001. Originally
D1405 Test Method for Estimation of Net Heat of Com-
published as D4529–85. Last previous edition D4529–95.
2
bustion of Aviation Fuels
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4529–01
2
D1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels 4. Significance and Use
D2622 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by
4.1 This test method is intended for use as a guide in cases
2
X-Ray Spectrometry
where an experimental determination of heat of combustion is
D3120 Test Method forTrace Quantities of Sulfur in Light
not available and cannot be made conveniently, and where an
Liquid Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Oxidative Microcou-
estimate is considered satisfactory. It is not intended as a
2
lometry
substitute for experimental measurements of heat of combus-
D4052 Test Method for Density and Relative Den
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.