ASTM D1343-95(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Viscosity of Cellulose Derivatives by Ball-Drop Method
Standard Test Method for Viscosity of Cellulose Derivatives by Ball-Drop Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test provides an easy method of determining the viscosity of cellulose derivatives in a given solvent. The answers are in units commonly used in industrial practice. Such information is needed for cellulose derivatives that are to be extruded, molded, sprayed, or brushed as is or in solution.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the apparatus and general procedure for making ball-drop viscosity measurements on solutions of various cellulose derivatives. Instructions for sample preparation, solution concentration, and other details are discussed in the ASTM methods for the respective cellulose derivatives.
1.2 This test method is applicable to solutions of various cellulose derivatives having viscosities greater than 10 P, by using balls of various diameters and densities. Viscosity results are expressed preferably in poises.
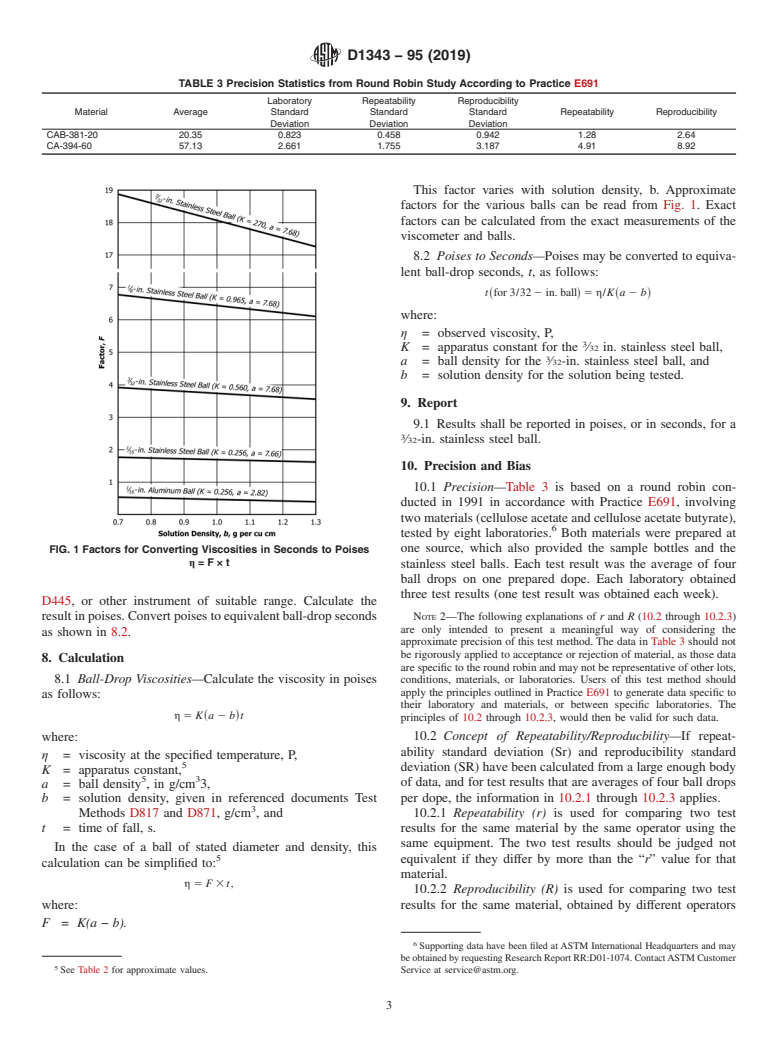
1.3 In commercial practice, viscosities are often expressed in seconds using 2.38-mm (3/32-in.) stainless steel balls.2 When the viscosity is outside the practical range for these balls (75 to 300 P), the measurement can be made using a calibrated pipet viscometer or a different ball and calculating the observed viscosity to the corresponding time for a 2.38-mm (3/32-in.) ball, even though it is a small fraction of a second.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1343 − 95 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
1
Viscosity of Cellulose Derivatives by Ball-Drop Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
3
1.1 This test method describes the apparatus and general 2.1 ASTM Standards:
procedure for making ball-drop viscosity measurements on D301 Test Methods for Soluble Cellulose Nitrate (With-
4
solutions of various cellulose derivatives. Instructions for drawn 2011)
sample preparation, solution concentration, and other details D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
arediscussedintheASTMmethodsfortherespectivecellulose and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
derivatives. ity)
D817 Test Methods of Testing Cellulose Acetate Propionate
1.2 This test method is applicable to solutions of various
and Cellulose Acetate Butyrate
cellulose derivatives having viscosities greater than 10 P, by
D871 Test Methods of Testing Cellulose Acetate
using balls of various diameters and densities.Viscosity results
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
are expressed preferably in poises.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.3 In commercial practice, viscosities are often expressed
2
3
in seconds using 2.38-mm ( ⁄32-in.) stainless steel balls. When
3. Summary of Test Method
the viscosity is outside the practical range for these balls (75 to
3.1 A solution of the cellulose derivative is made in a
300 P), the measurement can be made using a calibrated pipet
suitable solvent and allowed to equilibrate at a chosen tem-
viscometer or a different ball and calculating the observed
perature.Astainless steel or aluminum ball is dropped into the
3
viscosity to the corresponding time for a 2.38-mm ( ⁄32-in.)
solution, and the time required for it to cover a measured
ball, even though it is a small fraction of a second.
distance in its fall is recorded.The viscosity of the solution can
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
then be calculated in poise or recorded in seconds.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
NOTE 1—The choice of solvent has significant influence on viscosity.
only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Significance and Use
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 This test provides an easy method of determining the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
viscosity of cellulose derivatives in a given solvent. The
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
answers are in units commonly used in industrial practice.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Such information is needed for cellulose derivatives that are to
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
be extruded, molded, sprayed, or brushed as is or in solution.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
5. Apparatus
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5.1 Constant-Temperature Water Bath, glass-walled.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5.1.1 For routine testing, an aquarium viscometer is recom-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
mended. This viscometer is a rectangular glass enclosure with
front and rear walls that have etched horizontal parallel lines
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
50.8 mm (2.00 6 0.02 in.) apart. The bottles containing the
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.36 on Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally
3
approved in 1954. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D1343 – 95 (2011). For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/D1343-95R19. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2 3
When a ⁄32-in. stainless steel ball is used, the viscosities in seconds should be Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
practically the same as those obtained using the apparatus described in Section 11 the ASTM website.
4
of Te
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.