ASTM F736-17(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Impact Resistance of Monolithic Polycarbonate Sheet by Means of a Falling Weight
Standard Test Method for Impact Resistance of Monolithic Polycarbonate Sheet by Means of a Falling Weight
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is applicable for qualitatively evaluating coated and uncoated monolithic polycarbonate sheet material, for monitoring process control, for screening studies, and as an aid in the prediction of hardware performance when exposed to impact service conditions.
5.2 A limitation of Type A specimen testing is that a thick sheet may not fail since the available impact energy is limited by the maximum drop height and falling weight capacity of the test apparatus. Use Specimen Type A for material less than 12.7 mm (0.50 in.) thick.
5.3 Within the range of drop heights of this system, tests employing different velocities are not expected to produce different results. However, for a given series of tests, the drop height should be held constant so that velocity of impact (strain rate) will not be a variable.
5.4 As the polycarbonate specimen undergoes large plastic deformation under impact, the down (opposite impact) side is under tensile loading and most influential in initiating failure. For that reason, polycarbonate sheet coated on one side should be tested with the coated side down.
5.5 Direct comparison of specimen Type A and specimen Type B test results should not be attempted. For test programs that will require the comparison of interlaboratory test results the specimen type and the approximate drop height must be specified.
5.6 Monolithic polycarbonate sheet is notch sensitive. Data obtained from other test methods, particularly notched Izod/Charpy test results, and extremely high- or low-strain rate test results, should not be compared directly to data obtained from this method. It is noted that Type A specimens, free of flaws, have not experienced the characteristic ductile-to-brittle transition between thin, less than 3.18 mm (1/8 in.), and thick, greater than 7.94 mm (5/16 in.), sheet as reflected by other test methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the energy required to initiate failure in monolithic polycarbonate sheet material under specified conditions of impact using a free falling weight.
1.2 Two specimen types are defined as follows:
1.2.1 Type A consists of a flat plate test specimen and employs a clamped ring support.
1.2.2 Type B consists of a simply supported three-point loaded beam specimen (Fig. 1) for use with material which can not be failed using the Type A specimen. For a maximum drop height of 6.096 m (20 ft) and a maximum drop weight of 22.68 kg (50 lb), virgin polycarbonate greater than 12.70 mm (1/2 in.) thick will require use of the Type B specimen.
Note 1: See also ASTM Methods: D1709, D2444 and D3029.
FIG. 1 Type B Specimen Geometry and Loading
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 Exception—The inch-pound units in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statement, See Section 7.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F736 − 17 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Method for
Impact Resistance of Monolithic Polycarbonate Sheet by
Means of a Falling Weight
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF736;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the energy
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
required to initiate failure in monolithic polycarbonate sheet
D790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
material under specified conditions of impact using a free
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
falling weight.
als
1.2 Two specimen types are defined as follows:
1.2.1 Type A consists of a flat plate test specimen and 3. Terminology
employs a clamped ring support.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2.2 Type B consists of a simply supported three-point
3.1.1 failure (of test specimen)—failure is signified by the
loaded beam specimen (Fig. 1) for use with material which can
presence of any crack or split in the impact-deformed area that
not be failed using the TypeAspecimen. For a maximum drop was created by the impact of the falling weight and that can be
height of 6.096 m (20 ft) and a maximum drop weight of
seen by the naked eye.
22.68 kg (50 lb), virgin polycarbonate greater than 12.70 mm
4. Summary of Test Method
( ⁄2 in.) thick will require use of the Type B specimen.
4.1 The test procedure to cause failure covers a range of
NOTE 1—See also ASTM Methods: D1709, D2444 and D3029.
impact energies and differs with respect to geometry and
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
support of test specimen Type A and test specimen Type B.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Guidelines are established to control drop heights, impact
standard.
velocity, drop weights, impactor heads, impactor release,
1.3.1 Exception—The inch-pound units in parentheses are impactorrebound,impactlocation,andspecimenconfiguration
which are applicable to a falling weight impact tester designed
provided for information only.
to accommodate Type A or Type B test specimens, or both,
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
fabricated from monolithic polycarbonate sheet material.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
5.1 This test method is applicable for qualitatively evaluat-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ing coated and uncoated monolithic polycarbonate sheet
For specific hazard statement, See Section 7.
material, for monitoring process control, for screening studies,
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
and as an aid in the prediction of hardware performance when
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
exposed to impact service conditions.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
5.2 A limitation of Type A specimen testing is that a thick
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sheet may not fail since the available impact energy is limited
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
by the maximum drop height and falling weight capacity of the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
test apparatus. Use Specimen Type A for material less than
12.7 mm (0.50 in.) thick.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on
Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on
Transparent Enclosures and Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2023. Published January 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as F736 – 17. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/F0736-17R23. theASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F736 − 17 (2023)
FIG. 1 Type B Specimen Geometry and Loading
5.3 Within the range of drop heights of this system, tests 6.1.2 Drop Weight—Thefallingweightsshallbedetachable,
employing different velocities are not expected to produce
interchangeable, and variable in small known increments from
different results. However, for a given series of tests, the drop a total of 0.45 kg (1 lb) to a maximum drop weight of 50 kg
heightshouldbeheldconstantsothatvelocityofimpact(strain
(110 lb).
rate) will not be a variable.
6.1.3 Impactor—The loading nose to be used with Type A
5.4 As the polycarbonate specimen undergoes large plastic specimens is shown inFig. 3; withType Bspecimens as shown
deformation under impact, the down (opposite impact) side is
in Fig. 4. The impactor surface shall be free of nicks or other
under tensile loading and most influential in initiating failure.
surface irregularities. The impactor geometry for Type B
For that reason, polycarbonate sheet coated on one side should
specimens corresponds to Test Method D790.
be tested with the coated side down.
6.1.4 Impact Location—The center of mass of the falling
5.5 Direct comparison of specimen Type A and specimen weight shall be guided by a two cable system or other suitable
Type B test results should not be attempted. For test programs means to repeatedly strike within 2.54 mm (0.10 in.) of the
that will require the comparison of interlaboratory test results
center of the specimen support fixture as measured in the plane
the specimen type and the approximate drop height must be
of the specimen, in order to assure uniform, reproducible
specified.
drops. Friction retarding the falling weight shall be minimal so
that the impact velocity approaches
5.6 Monolithic polycarbonate sheet is notch sensitive. Data
obtained from other test methods, particularly notched Izod/
=
2gh
Charpy test results, and extremely high- or low-strain rate test
results, should not be compared directly to data obtained from where:
this method. It is noted that Type A specimens, free of flaws,
g = acceleration of gravity, and
have not experienced the characteristic ductile-to-brittle tran-
h = drop height.
sition between thin, less than 3.18 mm ( ⁄8 in.), and thick,
6.1.5 Supports—Clamp and support rings as shown inFig. 5
greater than 7.94 mm ( ⁄16 in.), sheet as reflected by other test
and Table 1 shall be used to accommodate Type A plate
methods.
specimens. Adjustable D790–Test Method 1 supports shall be
used to accommodate the Type B simply supported beam
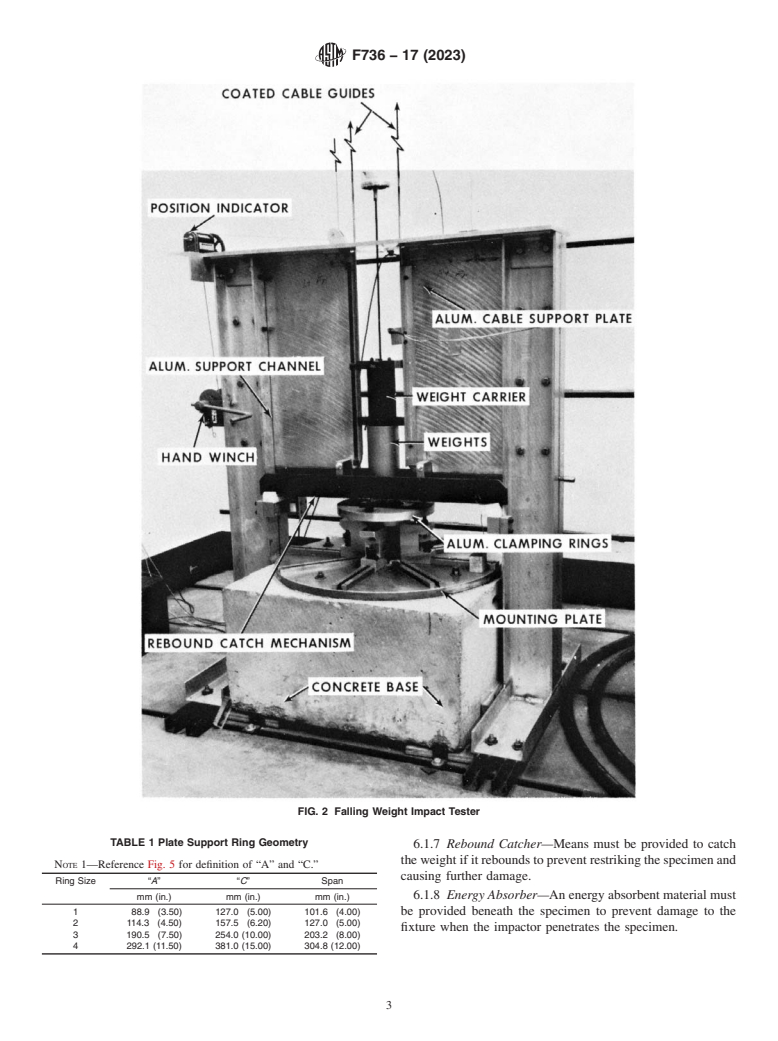
6. Apparatus
specimens of 6 + 1 span-to-depth ratio. Specimens shall be
6.1 Impact Tester—The apparatus shall be constructed as
supported so that the surface to be impacted is horizontal and
shown in Fig. 2. Although not specified, materials called out
at an angle of 90 (6 1)° (π/2 radians) with respect to the falling
have been found to be satisfactory.
weight guides.
6.1.1 Drop Height—A lifting carrier shall be provided to
6.1.6 Release—An electromagnetic or mechanical releasing
raise or lower the falling weight impactor that will be adjust-
mechanism, capable of supporting the maximum falling
ablewithintherangeof0.305m(1ft)tomaximumdropheight
and measurable to the nearest 25.40 mm (1 in.). weight,shallbeusedtoassureuniformandreproducibledrops.
F736 − 17 (2023)
FIG. 2 F
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.