ASTM A139/A139M-04(2015)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Electric-Fusion (Arc)-Welded Steel Pipe (NPS 4 and Over)
Standard Specification for Electric-Fusion (Arc)-Welded Steel Pipe (NPS 4 and Over)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers five grades of electric-fusion(arc)-welded straight-seam or helical steel pipe including pipe of NPS 4 and over. The required chemical composition, tensile requirements of the steel, and the tensile requirements of the production welds are presented. Heat analysis of each heat of steel was made to determine the percentage of the elements as per chemical requirements. Tests to be performed shall include one longitudinal tension test for the steel, one reduced-section production weld test for the pipe, and hydrostatic test for each length of the pipe.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers five grades of electric-fusion (arc)-welded straight-seam or helical-seam steel pipe. Pipe of NPS 4 (Note 1) and larger with nominal (average) wall thickness of 1.0 in. [25.4 mm] and less are covered. Listing of standardized dimensions are for reference (Note 2). The grades of steel are pipe mill grades having mechanical properties which differ from standard plate grades. The pipe is intended for conveying liquid, gas, or vapor.
Note 1: The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as “nominal diameter,”“ size,” and “nominal size.”
Note 2: A comprehensive listing of standardized pipe dimensions is contained in ASME B36.10M.
Note 3: The suitability of pipe for various purposes is somewhat dependent on its dimensions, properties, and conditions of service. For example, for high-temperature service see applicable codes and Specification A691.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or in SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system is to be used independently of the other.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A139/A139M −04(Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
Electric-Fusion (Arc)-Welded Steel Pipe (NPS 4 and Over)
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA139/A139M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
2.2 American Welding Society Standard:
1.1 This specification covers five grades of electric-fusion
AWS B2.1 Standard for Welding Procedure and Perfor-
(arc)-welded straight-seam or helical-seam steel pipe. Pipe of
mance Qualifications Welding Handbook, Vol 1, 8th ed
NPS4(Note 1) and larger with nominal (average) wall
2.3 ASME Standards:
thickness of 1.0 in. [25.4 mm] and less are covered. Listing of
ASME B36.10M Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
standardized dimensions are for reference (Note 2).The grades
ASME B36.19M Stainless Steel Pipe
of steel are pipe mill grades having mechanical properties
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX
which differ from standard plate grades. The pipe is intended
for conveying liquid, gas, or vapor.
3. Ordering Information
NOTE 1—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should
been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as “nominal
include the following, as required, to describe the desired
diameter,”“ size,” and “nominal size.”
NOTE 2—A comprehensive listing of standardized pipe dimensions is material adequately:
contained in ASME B36.10M.
3.1.1 Quantity (feet, metres, or number of lengths),
NOTE 3—The suitability of pipe for various purposes is somewhat
3.1.2 Name of material (electric-fusion-(arc) welded steel
dependent on its dimensions, properties, and conditions of service. For
pipe),
example, for high-temperature service see applicable codes and Specifi-
3.1.3 Grade (Table 1),
cation A691.
3.1.4 Size (NPS, or outside diameter, and nominal wall
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or in SI
thickness, or schedule number),
units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text,
3.1.5 Lengths (specific or random, Section 17),
the SI units are shown in brackets. The values in each system
3.1.6 End finish (Section 18),
are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system is to be used
3.1.7 Hydrostatic test pressure (Section 16, Note 8, and
independently of the other.
Note 9),
3.1.8 ASTM specification designation, and
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.9 End use of material.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
4. Process
of Steel Products
4.1 The steel shall be made by one or more of the following
A691 Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Pipe,
processes: open-hearth, basic-oxygen, or electric-furnace.
Electric-Fusion-WeldedforHigh-PressureServiceatHigh
4.2 Steel may be cast in ingots or may be strand cast. When
Temperatures
steels of different grades are sequentially strand cast, identifi-
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
cation of the resultant transition material is required. The
cal Analysis of Steel Products
producer shall remove the transition material by any estab-
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
lished procedure that positively separates the grades.
NOTE 4—The term “basic-oxygen steelmaking” is used generically to
describe processes in which molten iron is refined to steel under a basic
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.09 on Carbon Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2015. Published September 2015. Originally The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
approved in 1932. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A139/A139M–04 www.astm.org.
(2010). DOI: 10.1520/A0139_A0139M-04R15. Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd.,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
the ASTM website. www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A139/A139M−04 (2015)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
5.2 All weld seams made in manufacturing pipe shall be
Element Composition, max, % made using complete joint penetration groove welds.
Grade A Grade B Grade C Grade D Grade E
Carbon 0.25 0.26 0.28 0.30 0.30 6. Chemical Composition
Manganese 1.00 1.00 1.20 1.30 1.40
Phosphorus 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035
6.1 The steel shall conform to the chemical requirements
Sulfur 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035
prescribed in Table 1 and the chemical analysis shall be in
accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology
A751.
slag in a cylindrical furnace lined with basic refractories, by directing a jet
of high-purity gaseous oxygen onto the surface of the hot metal bath.
7. Tensile Requirements for the Steel
7.1 Longitudinal tension test specimens taken from the steel
5. Manufacture
shall conform to the requirements as to tensile properties
5.1 The longitudinal edges of the steel shall be shaped to
prescribed in Table 2.At the manufacturer’s option, the tension
give the most satisfactory results by the particular welding
test specimen for sizes 8 ⁄8 in. [219.1 mm] in outside diameter
process employed. The weld shall be made by automatic (Note
and larger may be taken transversely as described in 19.4.
5) means (except tack welds if used) and shall be of reasonably
uniform width and height for the entire length of the pipe.
7.2 The yield point shall be determined by the drop of the
beam, by the halt in the gage of the testing machine, by the use
NOTE 5—Upon agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer,
of dividers, or by other approved methods. The yield strength
manual welding by qualified procedure and welders may be used as an
equal alternative under these specifications. correspondingtoapermanentoffsetof0.2 %ofthegagelength
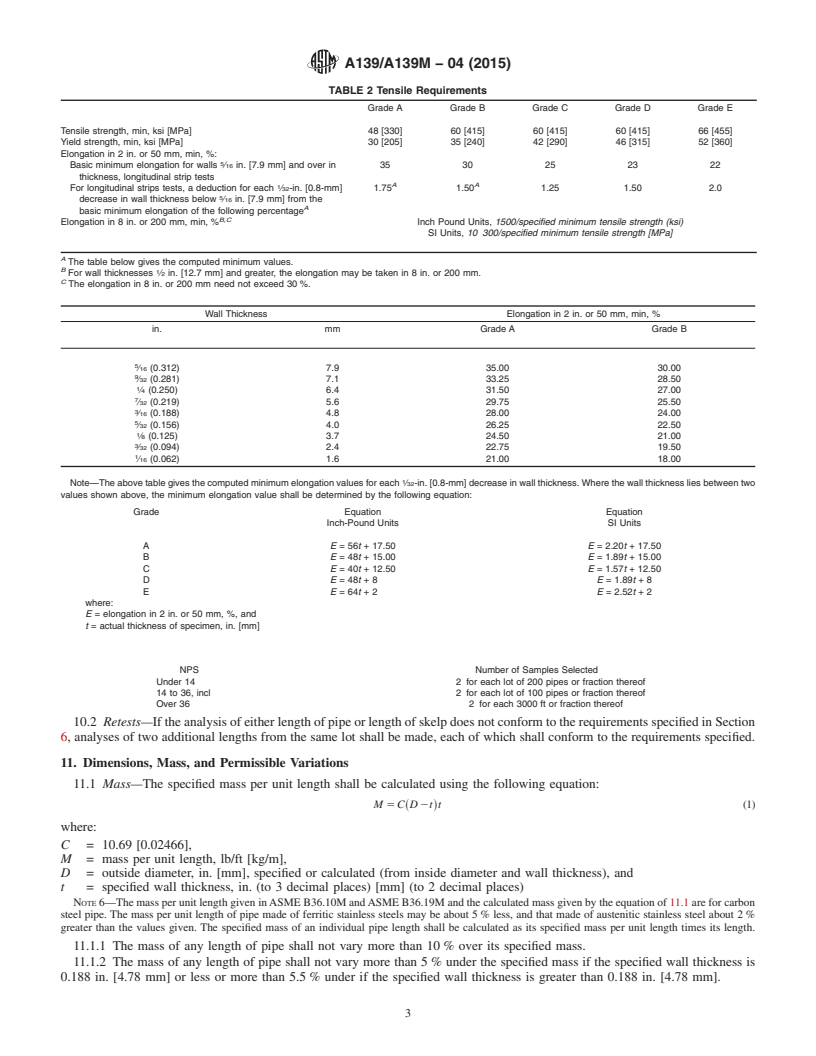
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements
Grade A Grade B Grade C Grade D Grade E
Tensile strength, min, ksi [MPa] 48 [330] 60 [415] 60 [415] 60 [415] 66 [455]
Yield strength, min, ksi [MPa] 30 [205] 35 [240] 42 [290] 46 [315] 52 [360]
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, min, %:
Basic minimum elongation for walls ⁄16 in. [7.9 mm] and over in 35 30 25 23 22
thickness, longitudinal strip tests
1 A A
For longitudinal strips tests, a deduction for each ⁄32-in. [0.8-mm] 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.50 2.0
decrease in wall thickness below ⁄16 in. [7.9 mm] from the
A
basic minimum elongation of the following percentage
B,C
Elongation in 8 in. or 200 mm, min, % Inch Pound Units, 1500/specified minimum tensile strength (ksi)
SI Units, 10 300/specified minimum tensile strength [MPa]
A
The table below gives the computed minimum values.
B
For wall thicknesses ⁄2 in. [12.7 mm] and greater, the elongation may be taken in 8 in. or 200 mm.
C
The elongation in 8 in. or 200 mm need not exceed 30 %.
Wall Thickness Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, min, %
in. mm Grade A Grade B
⁄16 (0.312) 7.9 35.00 30.00
⁄32 (0.281) 7.1 33.25 28.50
⁄4 (0.250) 6.4 31.50 27.00
⁄32 (0.219) 5.6 29.75 25.50
⁄16 (0.188) 4.8 28.00 24.00
⁄32 (0.156) 4.0 26.25 22.50
⁄8 (0.125) 3.7 24.50 21.00
⁄32 (0.094) 2.4 22.75 19.50
⁄16 (0.062) 1.6 21.00 18.00
Note—The above table gives the computed minimum elongation values for each ⁄32-in. [0.8-mm] decrease in wall thickness. Where the wall thickness lies between two
values shown above, the minimum elongation value shall be determined by the following equation:
Grade Equation Equation
Inch-Pound Units SI Units
A E=56t + 17.50 E = 2.20t + 17.50
B E=48t + 15.00 E = 1.89t + 15.00
C E=40t + 12.50 E = 1.57t + 12.50
D E=48t+8 E = 1.89t+8
E E=64t+2 E = 2.52t+2
where:
E = elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, %, and
t = actual thickness of specimen, in. [mm]
A139/A139M−04 (2015)
of the specimen, or to a total extension of 0.5 % of the gage 11.1.2 The mass of any length of pipe shall not vary more
length under load shall be determined. than 5 % under the specified mass if the specified wall
thickness is 0.188 in. [4.78 mm] or less or more than 5.5 %
8. Tensile Requirements of Production Welds
under if the specified wall thickness is greater than 0.188 in.
[4.78 mm].
8.1 Reduced-section tension test specimens taken perpen-
11.1.3 The mass of a carload lot shall not vary more than
dicularly across the weld in the pipe, with the weld reinforce-
1.75 % under the specified mass.Acarload lot is considered to
ment removed, shall show a tensile strength not less than 95 %
be a minimum of 40 000 lb [18 Mg] shipped on a conveyance.
of the minimum specified in Section 7. At the manufacturer’s
option, the test may be made without removing the weld 11.2 Thickness—The minimum wall thickness at any point
reinforcement, in which case the tensile strength shall be not
shallbenotmorethan12.5 %underthenominalwallthickness
less than that specified in Section 7. specified.
11.3 Circumference—The pipe shall be substantially round.
9. Heat Analysis
The outside circumference of the pipe shall not vary more than
9.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the 61.0 %, but not exceeding 6 ⁄4 in. [19.0 mm], from the
manufacturer to determine the percentages of the elements
nominal outside circumference based upon the diameter
specified in Section 6. This analysis shall be made from a test specified, except that the circumference at ends shall be sized,
ingot taken during the pouring of the heat. When requested by
if necessary, to meet the requirements of Section 18.
the purchaser, the chemical composition thus determined shall
11.4 Straightness—Finished pipe shall be commercially
be reported to the purchaser or his representative, and shall
straight. When specific straightness requirements are desired,
conform to the requirements specified in Section 6.
the order should so state, and the tolerance shall be a matter of
agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer.
10. Product Analysis
11.5 Ovality (Out-of-Roundness)—The pipe diameter,
10.1 An analysis may be made by the purchaser on samples
within 4.0 in. [100 mm] of ends, shall not vary more than 1 %
of pipe selected at random and shall conform to the require-
from the specified diameter as measured across any single
ments specified in Section 6. Samples for chemical analysis,
plane with a bar gage, caliper, or other instrument capable of
except for spectrochemical analysis, shall be taken in accor-
measuring actual diameter.
dance with Method E59. The number of samples shall be
determined as follows: 12. Finish
NPS Number of Samples Selected
12.1 Repair by Welding—The manual, or automatic arc,
Under 14 2 for each lot of 200 pipes or fraction thereof
welding of injurious defects in the pipe wall, provided their
14 to 36, incl 2 for each lot of 100 pipes or fraction thereof
Over 36 2 for each 3000 ft or fraction thereof depth does not exceed one third the specified wall thickness,
willbepermitted.Defectsinthewelds,suchassweatsorleaks,
10.2 Retests—If the analysis of either length of pipe or
shall be repaired or the piece rejected at the option of the
length of skelp does not conform to the requirements specified
manufacturer. Repairs of this nature shall be made by com-
in Section 6, analyses of two additional lengths from the same
pletely removing the defect, cleaning the cavity, and then
lot shall be made, each of which shall conform to the
welding.
requirements specified.
12.2 All repaired pipe shall be tested hydrostatically in
11. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
accordance with Section 16.
11.1 Mass—The specified mass per unit length shall be
13. Retests
calculated using the following equation:
13.1 If any specimen tested under Sections 8 or 15 fails to
M 5 C~D 2 t!t (1)
meet the requirements, retests of two additional specimens
fromthesamelotofpipeshallbemade,allofwhichshallmeet
where:
the specified requirements. If any of the retests fail to conform
C = 10.69 [0.02466],
to the requirements, test specimens may be taken from each
M = mass per unit length, lb/ft [kg/m],
untested pipe length, at the manufacturer’s option, and each
D = outside diameter, in. [mm], specified or calculated
specimen shall meet the requirements specified, or that pipe
(from inside diameter and wall thickness), and
shall be rejected.
t = specified wall thickness, in. (to 3 decimal places) [mm]
(to 2 decimal places)
14. Number of Production Test Specimens
NOTE 6—The mass per unit length given in ASME B36.10M and
ASMEB36.19Mandthecalculatedmassgivenbytheequationof11.1are 14.1 One longitudinal tension test specimen specified in
for carbon steel pipe. The mass per unit length of pipe made of ferritic
19.2 shall be made from the steel of each heat, or fraction
stainlesssteelsmaybeabout5 %less,andthatmadeofausteniticstainless
thereof, used in the manufacture of the pipe.
steel about 2 % greater than the values given. The specified mass of an
individual pipe length shall be calculated as its specified mass per unit
14.2 One reduced-section production weld test specimen
length times its length.
specified in 19.5 shall be taken from a length of pipe from each
11.1.1 The mass of any length of pipe shall not vary more lot of 3000 ft (914 m) of pipe, or fraction thereof, of each size
than 10 % over its specified mass. and wall thickness.
A139/A139M−04 (2015)
14.3 If any test specimen shows defective machining or
developsflawsnotassociatedwiththequalityofthesteelorthe
welding,itmaybediscardedandanotherspecimensubstituted.
14.4 Each length of pipe shall be subjected to the hydro-
static test specified in Section 16.
15. Qualification of Welding Procedure
Metric Equivalents
15.1 Welding procedures shall be qualified in accordance
1 1
in. ⁄16 1 ⁄2 6
with the requirements of AWS B2.1; ASME Boiler and
mm 1.6 38 150
Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX; or other qualification pro-
cedures as noted in the American Welding Society Welding NOTE 1—Weld reinforcement may or may not be removed flush with
the surface of the specimen.
Handbook. Tests and test values shall be as specified in 15.2
NOTE 2—Shown in Fig. 2
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A139/A139M − 04 (Reapproved 2010) A139/A139M − 04 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Specification for
Electric-Fusion (Arc)-Welded Steel Pipe (NPS 4 and Over)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A139/A139M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers five grades of electric-fusion (arc)-welded straight-seam or helical-seam steel pipe. Pipe of NPS
4 (Note 1) and larger with nominal (average) wall thickness of 1.0 in. [25.4 mm] and less are covered. Listing of standardized
dimensions are for reference (Note 2). The grades of steel are pipe mill grades having mechanical properties which differ from
standard plate grades. The pipe is intended for conveying liquid, gas, or vapor.
NOTE 1—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as “nominal diameter,”“
size,” and “nominal size.”
NOTE 2—A comprehensive listing of standardized pipe dimensions is contained in ASME B36.10M.
NOTE 3—The suitability of pipe for various purposes is somewhat dependent on its dimensions, properties, and conditions of service. For example,
for high-temperature service see applicable codes and Specification A691.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or in SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI
units are shown in brackets. The values in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system is to be used independently
of the other.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A691 Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Pipe, Electric-Fusion-Welded for High-Pressure Service at High Temperatures
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
2.2 American Welding Society Standard:
AWS B2.1 Standard for Welding Procedure and Performance Qualifications Welding Handbook, Vol 1, 8th ed
2.3 ASME Standards:
ASME B36.10M Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
ASME B36.19M Stainless Steel Pipe
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX Welding Qualifications
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should include the following, as required, to describe the desired material
adequately:
3.1.1 Quantity (feet, metres, or number of lengths),
3.1.2 Name of material (electric-fusion-(arc) welded steel pipe),
3.1.3 Grade (Table 1),
3.1.4 Size (NPS, or outside diameter, and nominal wall thickness, or schedule number),
3.1.5 Lengths (specific or random, Section 17),
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.09
on Carbon Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010Sept. 1, 2015. Published August 2010September 2015. Originally approved in 1932. Last previous edition approved in 20042010
as A139/A139M–04. –04 (2010). DOI: 10.1520/A0139_A0139M-04R10.10.1520/A0139_A0139M-04R15.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, ThreeTwo Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990,
http://www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A139/A139M − 04 (2015)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Element Composition, max, %
Grade A Grade B Grade C Grade D Grade E
Carbon 0.25 0.26 0.28 0.30 0.30
Manganese 1.00 1.00 1.20 1.30 1.40
Phosphorus 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035
Sulfur 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035 0.035
3.1.6 End finish (Section 18),
3.1.7 Hydrostatic test pressure (Section 16, Note 8, and Note 9),
3.1.8 ASTM specification designation, and
3.1.9 End use of material.
4. Process
4.1 The steel shall be made by one or more of the following processes: open-hearth, basic-oxygen, or electric-furnace.
4.2 Steel may be cast in ingots or may be strand cast. When steels of different grades are sequentially strand cast, identification
of the resultant transition material is required. The producer shall remove the transition material by any established procedure that
positively separates the grades.
NOTE 4—The term “basic-oxygen steelmaking” is used generically to describe processes in which molten iron is refined to steel under a basic slag in
a cylindrical furnace lined with basic refractories, by directing a jet of high-purity gaseous oxygen onto the surface of the hot metal bath.
5. Manufacture
5.1 The longitudinal edges of the steel shall be shaped to give the most satisfactory results by the particular welding process
employed. The weld shall be made by automatic (Note 5) means (except tack welds if used) and shall be of reasonably uniform
width and height for the entire length of the pipe.
NOTE 5—Upon agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer, manual welding by qualified procedure and welders may be used as an equal
alternative under these specifications.
5.2 All weld seams made in manufacturing pipe shall be made using complete joint penetration groove welds.
6. Chemical Composition
6.1 The steel shall conform to the chemical requirements prescribed in Table 1 and the chemical analysis shall be in accordance
with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A751.
7. Tensile Requirements for the Steel
7.1 Longitudinal tension test specimens taken from the steel shall conform to the requirements as to tensile properties prescribed
in Table 2. At the manufacturer’s option, the tension test specimen for sizes 8 ⁄8 in. [219.1 mm] in outside diameter and larger may
be taken transversely as described in 19.4.
7.2 The yield point shall be determined by the drop of the beam, by the halt in the gage of the testing machine, by the use of
dividers, or by other approved methods. The yield strength corresponding to a permanent offset of 0.2 % of the gage length of the
specimen, or to a total extension of 0.5 % of the gage length under load shall be determined.
8. Tensile Requirements of Production Welds
8.1 Reduced-section tension test specimens taken perpendicularly across the weld in the pipe, with the weld reinforcement
removed, shall show a tensile strength not less than 95 % of the minimum specified in Section 7. At the manufacturer’s option,
the test may be made without removing the weld reinforcement, in which case the tensile strength shall be not less than that
specified in Section 7.
9. Heat Analysis
9.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the manufacturer to determine the percentages of the elements specified
in Section 6. This analysis shall be made from a test ingot taken during the pouring of the heat. When requested by the purchaser,
the chemical composition thus determined shall be reported to the purchaser or his representative, and shall conform to the
requirements specified in Section 6.
10. Product Analysis
10.1 An analysis may be made by the purchaser on samples of pipe selected at random and shall conform to the requirements
specified in Section 6. Samples for chemical analysis, except for spectrochemical analysis, shall be taken in accordance with
Method E59. The number of samples shall be determined as follows:
A139/A139M − 04 (2015)
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements
Grade A Grade B Grade C Grade D Grade E
Tensile strength, min, ksi [MPa] 48 [330] 60 [415] 60 [415] 60 [415] 66 [455]
Yield strength, min, ksi [MPa] 30 [205] 35 [240] 42 [290] 46 [315] 52 [360]
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, min, %:
Basic minimum elongation for walls ⁄16 in. [7.9 mm] and over in 35 30 25 23 22
thickness, longitudinal strip tests
A A
For longitudinal strips tests, a deduction for each ⁄32-in. [0.8-mm] 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.50 2.0
decrease in wall thickness below ⁄16 in. [7.9 mm] from the
A
basic minimum elongation of the following percentage
B,C
Elongation in 8 in. or 200 mm, min, % Inch Pound Units, 1500/specified minimum tensile strength (ksi)
SI Units, 10 300/specified minimum tensile strength [MPa]
A
The table below gives the computed minimum values.
B
For wall thicknesses ⁄2 in. [12.7 mm] and greater, the elongation may be taken in 8 in. or 200 mm.
C
The elongation in 8 in. or 200 mm need not exceed 30 %.
Wall Thickness Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, min, %
in. mm Grade A Grade B
⁄16 (0.312) 7.9 35.00 30.00
⁄32 (0.281) 7.1 33.25 28.50
⁄4 (0.250) 6.4 31.50 27.00
⁄32 (0.219) 5.6 29.75 25.50
⁄16 (0.188) 4.8 28.00 24.00
⁄32 (0.156) 4.0 26.25 22.50
⁄8 (0.125) 3.7 24.50 21.00
⁄32 (0.094) 2.4 22.75 19.50
⁄16 (0.062) 1.6 21.00 18.00
Note—The above table gives the computed minimum elongation values for each ⁄32-in. [0.8-mm] decrease in wall thickness. Where the wall thickness lies between two
values shown above, the minimum elongation value shall be determined by the following equation:
Grade Equation Equation
Inch-Pound Units SI Units
A E = 56t + 17.50 E = 2.20t + 17.50
B E = 48t + 15.00 E = 1.89t + 15.00
C E = 40t + 12.50 E = 1.57t + 12.50
D E = 48t + 8 E = 1.89t + 8
E E = 64t + 2 E = 2.52t + 2
where:
E = elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, %, and
t = actual thickness of specimen, in. [mm]
NPS Number of Samples Selected
Under 14 2 for each lot of 200 pipes or fraction thereof
14 to 36, incl 2 for each lot of 100 pipes or fraction thereof
Over 36 2 for each 3000 ft or fraction thereof
10.2 Retests—If the analysis of either length of pipe or length of skelp does not conform to the requirements specified in Section
6, analyses of two additional lengths from the same lot shall be made, each of which shall conform to the requirements specified.
11. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
11.1 Mass—The specified mass per unit length shall be calculated using the following equation:
M 5 C D 2t t (1)
~ !
where:
C = 10.69 [0.02466],
M = mass per unit length, lb/ft [kg/m],
D = outside diameter, in. [mm], specified or calculated (from inside diameter and wall thickness), and
t = specified wall thickness, in. (to 3 decimal places) [mm] (to 2 decimal places)
NOTE 6—The mass per unit length given in ASME B36.10M and ASME B36.19M and the calculated mass given by the equation of 11.1 are for carbon
steel pipe. The mass per unit length of pipe made of ferritic stainless steels may be about 5 % less, and that made of austenitic stainless steel about 2 %
greater than the values given. The specified mass of an individual pipe length shall be calculated as its specified mass per unit length times its length.
11.1.1 The mass of any length of pipe shall not vary more than 10 % over its specified mass.
11.1.2 The mass of any length of pipe shall not vary more than 5 % under the specified mass if the specified wall thickness is
0.188 in. [4.78 mm] or less or more than 5.5 % under if the specified wall thickness is greater than 0.188 in. [4.78 mm].
A139/A139M − 04 (2015)
11.1.3 The mass of a carload lot shall not vary more than 1.75 % under the specified mass. A carload lot is considered to be
a minimum of 40 000 40 000 lb [18 Mg] shipped on a conveyance.
11.2 Thickness—The minimum wall thickness at any point shall be not more than 12.5 % under the nominal wall thickness
specified.
11.3 Circumference—The pipe shall be substantially round. The outside circumference of the pipe shall not vary more than
61.0 %, but not exceeding 6 ⁄4 in. [19.0 mm], from the nominal outside circumference based upon the diameter specified, except
that the circumference at ends shall be sized, if necessary, to meet the requirements of Section 18.
11.4 Straightness—Finished pipe shall be commercially straight. When specific straightness requirements are desired, the order
should so state, and the tolerance shall be a matter of agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer.
11.5 Ovality (Out-of-Roundness) —(Out-of-Roundness)—The pipe diameter, within 4.0 in. [100 mm] of ends, shall not vary
more than 1 % from the specified diameter as measured across any single plane with a bar gage, caliper, or other instrument capable
of measuring actual diameter.
12. Finish
12.1 Repair by Welding—The manual, or automatic arc, welding of injurious defects in the pipe wall, provided their depth does
not exceed one third the specified wall thickness, will be permitted. Defects in the welds, such as sweats or leaks, shall be repaired
or the piece rejected at the option of the manufacturer. Repairs of this nature shall be made by completely removing the defect,
cleaning the cavity, and then welding.
12.2 All repaired pipe shall be tested hydrostatically in accordance with Section 16.
13. Retests
13.1 If any specimen tested under Sections 8 or 15 fails to meet the requirements, retests of two additional specimens from the
same lot of pipe shall be made, all of which shall meet the specified requirements. If any of the retests fail to conform to the
requirements, test specimens may be taken from each untested pipe length, at the manufacturer’s option, and each specimen shall
meet the requirements specified, or that pipe shall be rejected.
14. Number of Production Test Specimens
14.1 One longitudinal tension test specimen specified in 19.2 shall be made from the steel of each heat, or fraction thereof, used
in the manufacture of the pipe.
14.2 One reduced-section production weld test specimen specified in 19.5 shall be taken from a length of pipe from each lot
of 3000 ft (914 m) of pipe, or fraction thereof, of each size and wall thickness.
14.3 If any test specimen shows defective machining or develops flaws not associated with the quality of the steel or the
welding, it may be discarded and another specimen substituted.
14.4 Each length of pipe shall be subjected to
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.