ASTM F450-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Vacuum Cleaner Hose—Durability and Reliability (Plastic Wire Reinforced)
Standard Test Methods for Vacuum Cleaner Hose—Durability and Reliability (Plastic Wire Reinforced)
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the effect of anticipated stresses and strains that vacuum cleaner hoses will receive in normal use.
1.2 These test methods apply to plastic, wire-reinforced, nonelectric vacuum cleaner hoses for household use.
1.3 The following tests are included:
SectionTorsional flex6Hot and cold flex with aging7Abrasion, external surfaces8 Flex9Pull test on hose fittings with aging10Crush11
1.4 These test methods are individual tests as agreed upon between the hose and vacuum manufacturer.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathmatical conversions to SI units, which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 450 – 96
Standard Test Methods for
Vacuum Cleaner Hose—Durability and Reliability (Plastic
1
Wire Reinforced)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 450; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope TEST METHODS
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the effect
5. Torsional Flex Test
of anticipated stresses and strains that vacuum cleaner hoses
5.1 Scope—This test method covers the determination of
will receive in normal use.
the adhesion of the reinforcing wire coating to the hose jacket,
1.2 These test methods apply to plastic, wire-reinforced,
the jacket strength, and the strength of the reinforcing wire for
nonelectric, vaccum cleaner hoses for household use. Other
plastic hose with inside diameter from 1 to 2 in. (25 to 51 mm).
constructions and applications will be included at a later date.
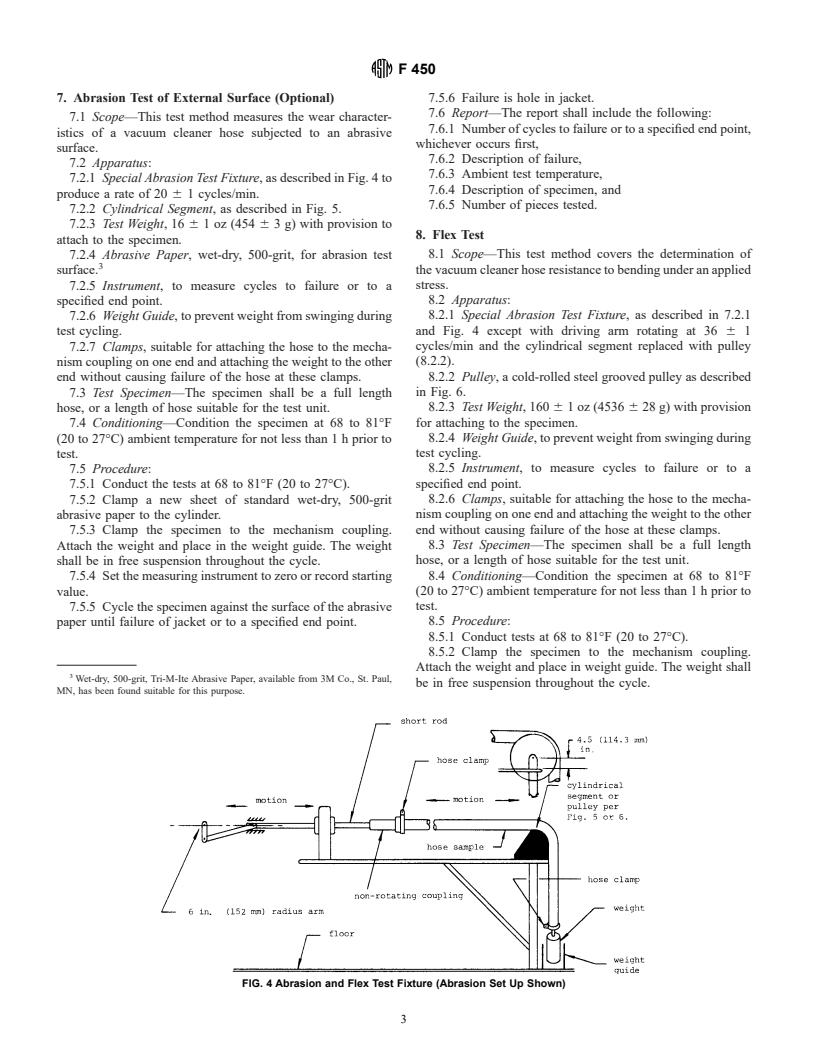
5.2 Apparatus—The apparatus shown in Fig. 1 is suitable
1.3 The following tests are included:
for this test method with the following provisions:
Section
5.2.1 Means to rotate test mandrel in a horizontal plane at 20
Torsional flex 5
Hot and cold flex with aging 6
6 1 rpm, both clockwise and counter-clockwise.
Abrasion, external surfaces 7
5.2.2 Test weight of 48 6 1 oz. (1360 6 28 g) with
Flex 8
provision to attach to sample hose.
Pull test on hose fittings with aging 9
Crush 10
5.2.3 Suitable clamp to attach sample hose to mandrel that
retains the hose without causing failure at the clamp during the
1.4 These test methods are individual tests as agreed upon
test.
between the hose and vacuum manufacturer.
5.2.4 Test mandrel with diameter same as inside diameter of
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
hose with 0.078 in. (2.0 mm) radius at the ends of the mandrel
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
(see Fig. 1).
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.2.5 Guide for weight to prevent hose sample from swing-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ing during test cycle.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.2.6 Instrument to measure cycles to failure or to a speci-
2. Referenced Documents
fied end point.
5.3 Test Specimen—The specimen shall be a length of hose
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
24 6 1 in. (610 6 25 mm) without fittings.
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
5.4 Conditioning—Condition the specimens at an ambient
D 695 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
2
temperature of 68 to 81°F (20 to 27°C) for not less than 1 h
Plastics
prior to test.
3. Significance and Use
5.5 Procedure:
5.5.1 Conduct the tests at 68 to 81°F (20 to 27°C).
3.1 These test methods can be used by buyers of vacuum
5.5.2 Clamp the specimen to the test hose mandrel as shown
cleaner hose to specify the test criteria the hose must meet to
in Fig. 1 and attach a weight to other end of hose sample.
be acceptable for his purposes.
5.5.3 Set measuring instrument at zero or record the initial
4. Sampling
reading.
5.5.4 Test half of the specimens by rotating clockwise and
4.1 The sample size shall be one that is mutually agreed
the other half by rotating counter-clockwise at 20 6 1 rpm until
upon between the hose manufacturer and the vacuum cleaner
failure or to a specified end point.
manufacturer.
5.5.5 Failure may be evidenced by a broken reinforcing
wire, tear, or hole that penetrates the hose jacket, or a collapsed
1
These methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-11 on Vacuum
coil or ply for a lined-type hose, or any combination thereof.
Cleaners and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F11.30 on Durability-
5.6 Report—The report shall include the following:
Reliability.
5.6.1 Number of cycles to failure or to a specified end point,
Current edition approved March 10, 1996. Published May 1996. Originally
published as F 450 – 79. Last previous edition F 450 – 85 (1990). whichever occurs first,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 450
FIG. 1 Schematic for Torsional Flex Test
5.6.2 Type of failure, temperature in accordance with 6.4.
5.6.3 Ambient temperature,
6.5.4 Next place the specimen in the cold box, which has
5.6.4 Description of specimen, and
been brought to a steady temperature of 20 6 1°F (−6.7 6
5.6.5 Number of specimens tested.
0.5°C) for 2 h.
6.5.5 Remove the specimen from the cold box, untie and
6. Hot and Cold Flex Test with Aging
immediately flex it 360°, three times, 1 s per flex
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.