ASTM D951-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Water Resistance of Shipping Containers by Spray Method
Standard Test Method for Water Resistance of Shipping Containers by Spray Method
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the water resistance of shipping containers.
1.2 This test method is frequently used in conjunction with other tests made prior to or after the spray test, such as the drop test, vibration test, inclined impact test, or compression test.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 951 – 99
Standard Test Method for
Water Resistance of Shipping Containers by Spray Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 951; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the water
resistance of shipping containers.
1.2 This test method is frequently used in conjunction with
other tests made prior to or after the spray test, such as the drop
test, vibration test, inclined impact test, or compression test.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 685 Practice for Conditioning Paper and Paper Products
for Testing
D 996 Terminology of Packaging and Distribution Environ-
ments
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
method, refer to Terminology D 996.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is used to determine the water resis-
tance of shipping containers. It can be used to determine the
ability of the container to resist deterioration caused by water
or the ability of the container to protect the contents from
water. It is frequently used in conjunction with other tests made
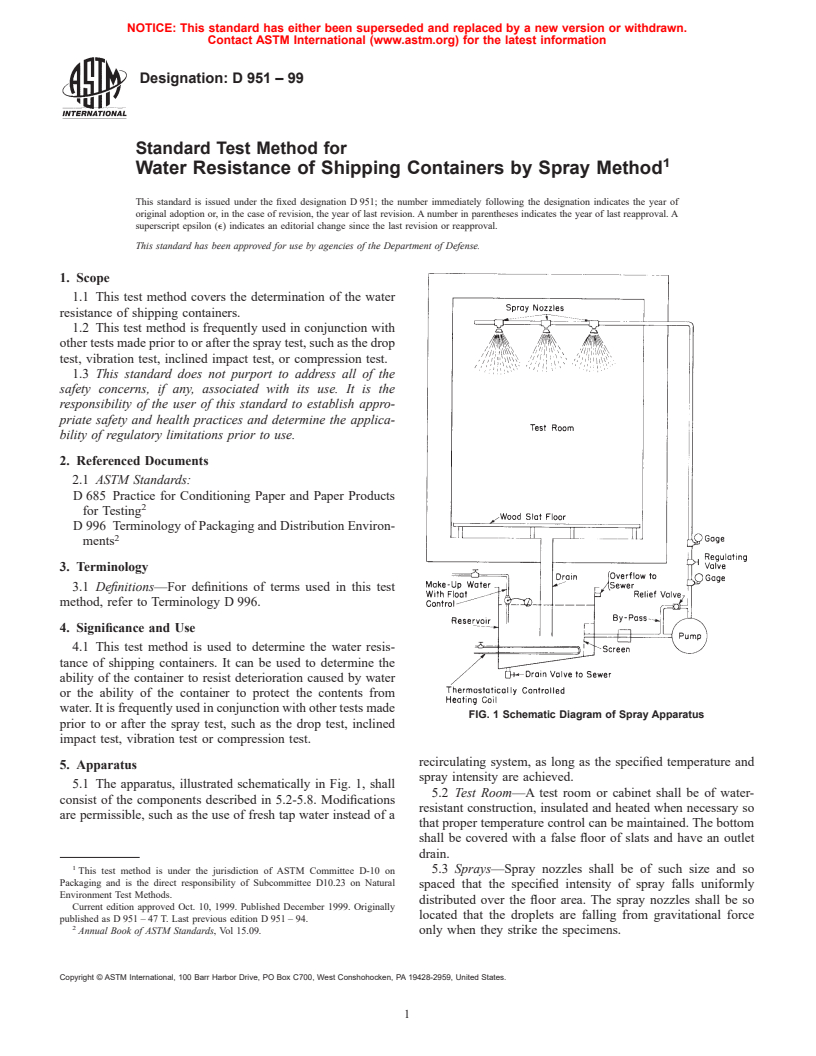
FIG. 1 Schematic Diagram of Spray Apparatus
prior to or after the spray test, such as the drop test, inclined
impact test, vibration test or compression test.
recirculating system, as long as the specified temperature and
5. Apparatus
spray intensity are achieved.
5.1 The apparatus, illustrated schematically in Fig. 1, shall
5.2 Test Room—A test room or cabinet shall be of water-
consist of the components described in 5.2-5.8. Modifications
resistant construction, insulated and heated when necessary so
are permissible, such as the use of fresh tap water instead of a
that proper temperature control can be maintained. The bottom
shall be covered with a false floor of slats and have an outlet
drain.
5.3 Sprays—Spray nozzles shall be of such size and so
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-10 on
Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D10.23 on Natural
spaced that the specified intensity of spray falls uniformly
Environment Test Methods.
distributed over the floor area. The spray nozzles shall be so
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1999. Published December 1999. Originally
located that the droplets are falling from gravitational force
published as D 951 – 47 T. Last previous edition D 951 – 94.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.09. only when they strike the specimens.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D951–99
5.4 Flow Control Valves—Flow control valves, to control specifically called for in the test. Be certain the distance
the intensity of the spray, are required. between adjacent samples is not less than 6 in. (150 mm).
5.5 Circulating System—A circulating system shall, where Operate the water sprays continuously at the specified intensity
used, consist of a fine-mesh strainer, pump, relief by-pass, for the duration of the test. (The duration of the test is to be
gages, and pressure regulating valve, together with the neces- determined by the user.)
sary piping between the flow control valves, spray nozzles, and 8.5 Immediately at the conclusion of the spray test, remove
water reservoir. any liquid water from the exterior surfaces of each sample
5.6 Reservoir—A reservoir for storage and conditioning of using a squeegee or other suitable means, and weigh the
the spray water shall, where used, be equipped with an samples.
overflow to a sewer and with a drain to facilitate changing the 8.6 Immediately following the weighing of the container,
water at the start of each test. Make-up water, regulated by a make any required examination to determine the condition of
float control, shall also discharge into this tank. the containers and their contents. Observe location and extent
5.7 Water Temperature Control—A thermostatically con- of any leakage into the container where the test is being
trolled means of heating for maintaining the supply water at the performed to determine the ability of the container to protect
desired temperature is requ
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.