ASTM D4782-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Palladium in Molecular Sieve Catalyst by Wet Chemistry
Standard Test Method for Palladium in Molecular Sieve Catalyst by Wet Chemistry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a means of determining the palladium content in fresh catalysts containing molecular sieves.
This test method is not intended to cover samples containing metals other than palladium.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of palladium in molecular sieve-containing fresh catalysts with about 0.5 weight % of palladium.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D4782–04
Standard Test Method for
1
Palladium in Molecular Sieve Catalyst by Wet Chemistry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4782; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This test method covers the determination of palladium 4.1 This test method provides a means of determining the
in molecular sieve-containing fresh catalysts with about 0.5 palladium content in fresh catalysts containing molecular
weight % of palladium. sieves.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.2 This test method is not intended to cover samples
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the containing metals other than palladium.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 pH Meter with Millivolt Scale or automatic recording
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
titrator.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 Silver-Sulfide Electrode.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: 5.3 Silver-Silver Chloride Double Junction reference elec-
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water trode with 10 % KNO in the outer chamber.
3
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in 5.4 Fisher Burner.
ASTM Test Methods 5.5 Low-Temperature Muffle Furnace, 450°C.
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics 5.6 High-Temperature Muffle Furnace, 1000°C.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to 5.7 Hot-Plate, with sand bath as a preferred option.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method 5.8 Magnetic Stirrer and TFE-Fluorocarbon-Coated Stir-
ring Bars.
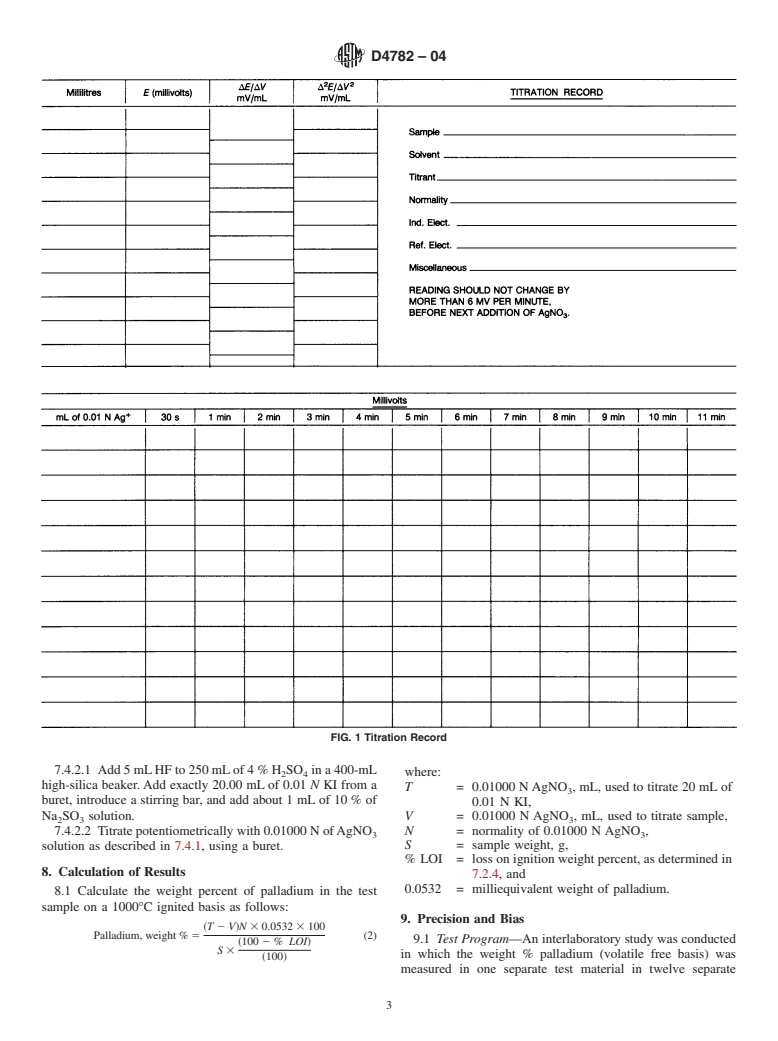
3. Summary of Test Method
5.9 Burets, 25-mL, with 0.1-mL graduations or an equiva-
3.1 The test sample is treated with hydrofluoric acid and lent.
evaporated to dryness to remove silica; the residue is fused 5.10 Volumetric Flasks, 1000-mL.
with potassium pyrosulfate, and the cooled melt is dissolved in
5.11 High-Silica Beakers, 400-mL, with disposable boro-
4% H SO . A measured excess of 0.01 N potassium iodide silicate beakers as an option. Alternatively, a petri dish can be
2 4
(KI) is added to precipitate palladium as palladium iodide
used for the fusion step, with polypropylene beakers being
(PdI ). The precipitate is filtered and washed, and a small used thereafter.
2
amount of sodium sulfite is added to the filtrate to reduce any
5.12 Watch Glasses, preferably ribbed, 87 mm.
free iodine to iodide. The excess iodide is titrated with 0.01 N 5.13 Analytical Balance, capable of weighing to nearest 0.1
AgNO potentiometrically, using a silver electrode versus a
mg.
3
calomel electrode. A second sample taken at the same time is 5.14 Weighing Papers.
3
used to determine loss on ignition.
5.15 Porcelain Crucibles, 10-mL.
5.16 Graduated Cylinders, 5-mL, 10-mL, 25-mL, 100-mL.
5.17 Filter Paper, Whatman No. 40, 11 cm.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
5.18 Funnel, filter.
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.03 on Chemical
Composition. 5.19 Desiccator.
Current edition approved April 1, 2004. Published April 2004. Originally
5.20 Crucible Cover, porcelain.
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D4782–91(1997).
DOI: 10.1520/D4782-04.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
3
the ASTM website. Alundum or other suitable materials may be used.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4782–04
6. Reagents and Materials 7.2.3 Remove the crucible from the furnace, place in des-
iccator to cool, and weigh to nearest 0.1 mg.
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
7.2.4 Calculate weight percent loss on ignition at 1000°C as
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
follows:
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
~I 2 F!
4 Weight % LOI 5 3 100 (1)
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
~I!
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
where:
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
I = initial sample weight, and
accuracy of the determination.
F = final sample weight.
6.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
7.3 Prep
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.