ASTM C1892/C1892M-19e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Strength of Anchors in Masonry
Standard Test Methods for Strength of Anchors in Masonry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These test methods are intended to provide reproducible data from which acceptance criteria, design data, and specifications can be developed for anchors intended to be installed in masonry assemblies.
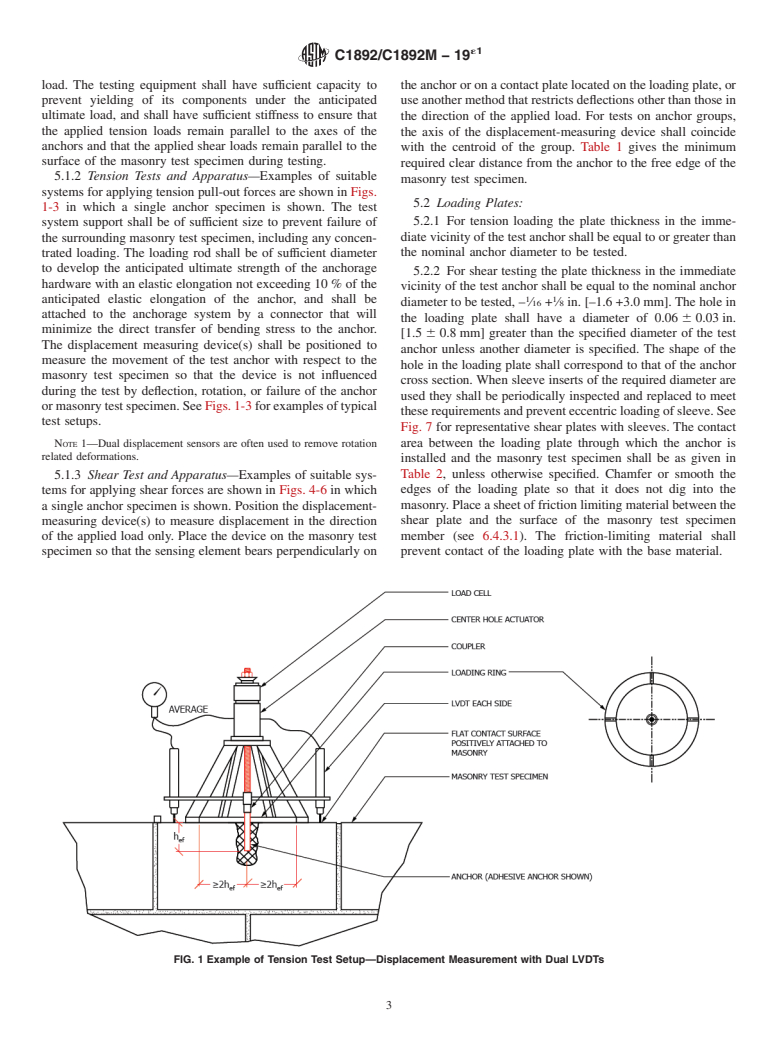
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods address the tensile and shear strengths of post-installed and placed-during-construction anchors in masonry test specimens made of masonry assemblies. Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing, moisture, decreased and elevated temperatures and corrosion. These test methods provide basic testing procedures for use with product-specific evaluation and acceptance standards and are intended to be performed in a testing laboratory. Product-specific evaluation and acceptance standards may add specific details and appropriate parameters as needed to accomplish the testing. Only those tests required by the specifying authority need to be performed.
1.2 Loadings include quasi-static, dynamic, fatigue and shock. Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing, moisture, decreased and elevated temperatures and corrosion.
1.3 These test methods are intended for use with post-installed and placed-during-construction anchors designed for installation projecting from the surface of a masonry test specimen.
1.4 This standard prescribes separate procedures for static, dynamic, fatigue and shock testing. Nothing in this standard, however, shall preclude combined tests incorporating two or more of these types of loading (such as dynamic, fatigue and shock tests in series).
1.5 Both inch-pound and SI units are provided in this standard. The testing may be performed in either system and reported in that system and the results converted to the other. However, anchor diameters, threads, and related testing equipment shall be in accordance with either inch-pound or SI provisions.
1.6 Units—The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: C1892/C1892M − 19
Standard Test Methods for
1
Strength of Anchors in Masonry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1892/C1892M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially corrected throughout in February 2020.
1. Scope 1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 These test methods address the tensile and shear
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
strengths of post-installed and placed-during-construction an-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
chors in masonry test specimens made of masonry assemblies.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing,
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
moisture, decreased and elevated temperatures and corrosion.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
These test methods provide basic testing procedures for use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
with product-specific evaluation and acceptance standards and
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
are intended to be performed in a testing laboratory. Product-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
specific evaluation and acceptance standards may add specific
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
detailsandappropriateparametersasneededtoaccomplishthe
testing. Only those tests required by the specifying authority
2. Referenced Documents
need to be performed.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2 Loadings include quasi-static, dynamic, fatigue and
C1180Terminology of Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry
shock. Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing,
C1232Terminology for Masonry
moisture, decreased and elevated temperatures and corrosion.
E4Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
1.3 These test methods are intended for use with post-
E468Practice for Presentation of Constant Amplitude Fa-
installed and placed-during-construction anchors designed for
tigue Test Results for Metallic Materials
installation projecting from the surface of a masonry test
E575Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
specimen.
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
1.4 This standard prescribes separate procedures for static, semblies
E631Terminology of Building Constructions
dynamic, fatigue and shock testing. Nothing in this standard,
however, shall preclude combined tests incorporating two or
2.2 Other Standards:
more of these types of loading (such as dynamic, fatigue and
ANSI B212.15 American National Standard for Cutting
shock tests in series).
Tools—Carbide-Tipped Masonry Drills and Blanks for
Carbide-Tipped Masonry Drills
1.5 Both inch-pound and SI units are provided in this
standard. The testing may be performed in either system and
3. Terminology
reported in that system and the results converted to the other.
However, anchor diameters, threads, and related testing equip-
3.1 For definitions of general terms related to building
ment shall be in accordance with either inch-pound or SI
construction used in this standard, refer to Terminology E631.
provisions.
For definitions of terms related to masonry refer to Terminol-
ogy C1180 or C1232.
1.6 Units—The values stated in each system are not neces-
sarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
the standard, each system shall be used independently of the
3.2.1 adhesive anchor, n—an anchor that derives its holding
other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
strength from the chemical compound between the wall of the
hole and the anchor rod.
1
3.2.1.1 Discussion—The compounds used include epoxy,
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on
Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
cementitious material, polyester resin, and other similar types.
C15.04 on Research.
3.2.2 anchor spacing, n—the distance between anchors
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published January 2020. DOI: 10.1520/
C1892_C1892M-19E01 measured centerline to centerline.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
C1892/C1892M − 19
3.2.3 displacement, n—movement of an anchor relative to diameter than the portion of the hole between the enlarged
the masonry assembly. s
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: C1892/C1892M − 19 C1892/C1892M − 19
Standard Test Methods for
1
Strength of Anchors in Masonry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1892/C1892M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially corrected throughout in February 2020.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods address the tensile and shear strengths of post-installed and placed-during-construction anchors in
masonry test specimens made of masonry assemblies. Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing, moisture, decreased
and elevated temperatures and corrosion. These test methods provide basic testing procedures for use with product-specific
evaluation and acceptance standards and are intended to be performed in a testing laboratory. Product-specific evaluation and
acceptance standards may add specific details and appropriate parameters as needed to accomplish the testing. Only those tests
required by the specifying authority need to be performed.
1.2 Loadings include quasi-static, dynamic, fatigue and shock. Environmental exposures include freezing and thawing,
moisture, decreased and elevated temperatures and corrosion.
1.3 These test methods are intended for use with post-installed and placed-during-construction anchors designed for installation
projecting from the surface of a masonry test specimen.
1.4 This standard prescribes separate procedures for static, dynamic, fatigue and shock testing. Nothing in this standard,
however, shall preclude combined tests incorporating two or more of these types of loading (such as dynamic, fatigue and shock
tests in series).
1.5 Both inch-pound and SI units are provided in this standard. The testing may be performed in either system and reported in
that system and the results converted to the other. However, anchor diameters, threads, and related testing equipment shall be in
accordance with either inch-pound or SI provisions.
1.6 Units—The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the
standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C1180 Terminology of Mortar and Grout for Unit Masonry
C1232 Terminology for Masonry
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E468 Practice for Presentation of Constant Amplitude Fatigue Test Results for Metallic Materials
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and Assemblies
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
2.2 Other Standards:
ANSI B212.15 American National Standard for Cutting Tools—Carbide-Tipped Masonry Drills and Blanks for Carbide-Tipped
Masonry Drills
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C15.04 on Research.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published January 2020. DOI: 10.1520/C1892_C1892M-1910.1520/C1892_C1892M-19E01
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
C1892/C1892M − 19
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of general terms related to building construction used in this standard, refer to Terminology E631. For
definitions of terms related to masonry refer to Terminology C1180 or C1232.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 adhesive anchor, n—an anchor that derives its holding strength from the chemical compound between the wall of the hole
and the anchor rod.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—
The compounds u
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.