ASTM B929-23
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Rod and Bar
Standard Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Rod and Bar
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the requirements for UNS C72900 copper-nickel-tin alloy rods and bars. Products should be manufactured by hot working, cold working, and annealing processes to produce a uniform wrought structure in the finished product. Each product should then be hot or cold worked to the finished size, and if required, should be subsequently annealed to meet the specified temper properties. The tensile strength and Rockwell hardness values from prescribed tests on the products should fall within the required range.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for copper-nickel-tin alloy UNS No. C72900 rod and bar.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B929 − 23
Standard Specification for
1
Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Rod and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B929; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
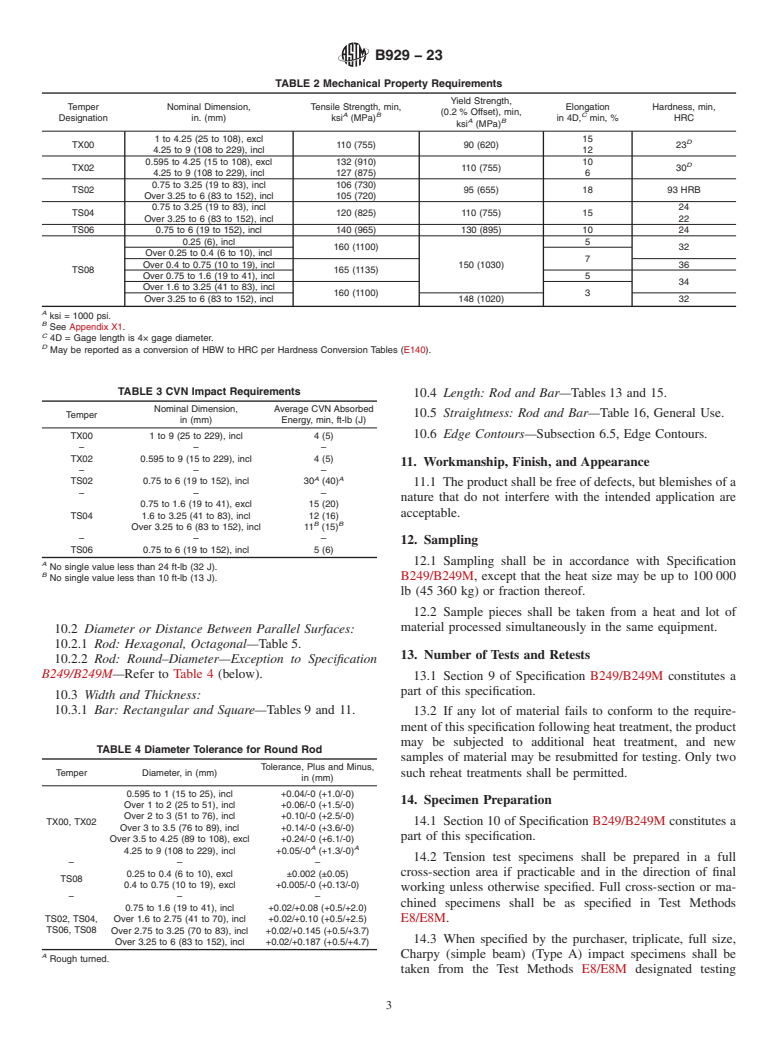
1. Scope* E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for copper-
terials
nickel-tin alloy UNS No. C72900 rod and bar.
E23 Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Me-
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
tallic Materials
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for 3
Copper by Gravimetry (Withdrawn 2022)
information only and are not considered standard.
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel
3
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the
and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
test methods described in this specification: This standard does E140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this Hardness, Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, Sclero-
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environ-
scope Hardness, and Leeb Hardness
mental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
limitations prior to use.
E1823 Terminology Relating to Fatigue and Fracture Testing
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3. General Requirements
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- constitute a part of this specification:
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical 3.1.1 Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. 3.1.2 Number of Tests and Retests
3.1.3 Specimen Preparation
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.4 Significance of Numerical Limits
2
3.1.5 Inspection
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.6 Rejection and Rehearing
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for
3.1.7 Certification
Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and
3.1.8 Test Report
Forgings
3.1.9 Packaging and Package Marking
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and
3.1.10 Supplementary Requirements
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that
B950 Guide for Editorial Procedures and Form of Product
referenced in 3.1 appears in this specification, it contains
Specifications for Copper and Copper Alloys
additional requirements which supplement those appearing in
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Ma-
Specification B249/B249M.
terials
4. Terminology
4.1 For definitions of terms related to copper and copper
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper
alloys, refer to Terminology B846.
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod,
Bar, Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
5. Ordering Information
Current edition approved April 1, 2023. Published April 2023. Originally
5.1 Include the following specified choices when placing
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as B929 – 17. DOI:
10.1520/B0929-23.
orders for products under this specification, as applicable:
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B929 − 23
5.1.1 ASTM designation and year of issue, 7.2 These composition limits do not preclude the presence
5.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS No. C72900, of other elements. By agreeme
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B929 − 17 B929 − 23
Standard Specification for
1
Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Rod and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B929; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishescovers the requirements for copper-nickel-tin alloy UNS No. C72900 rod and bar. The following
alloy is included:
Copper Alloy
Nominal Composition, Weight %
UNS No.
Copper Nickel Tin
C72900 77 15 8
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test method(s) described in this specification.
1.3 The following safety hazard caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification: This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and to safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability
of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and Forgings
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
B950 Guide for Editorial Procedures and Form of Product Specifications for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E23 Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, Bar,
Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
Current edition approved May 15, 2017April 1, 2023. Published June 2017April 2023. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 20112017 as
ɛ1
B929B929 – 17.- 05(2011) . DOI: 10.1520/B0929-17.10.1520/B0929-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B929 − 23
3
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed Copper by Gravimetry (Withdrawn 2022)
3
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
E140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell Hardness,
Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, Scleroscope Hardness, and Leeb Hardness
E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
E1823 Terminology Relating to Fatigue and Fracture Testing
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations;Variations
3.1.2 Number of Tests and Retests;Retests
3.1.3 Specimen Preparation;Preparation
3.1.4 Significance of Numerical Limits;Limits
3.1.5 Inspection;Inspection
3.1.6 Rejection and Rehearing;Rehearing
3.1.7 Certification;Certification
3.1.8 Test Report
3.1.9 Packaging and Package Marking; andMarking
3.1.10 Supplementary Requirements.Requirements
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that referenced in 3.1 above appears in this specification, it contains
additional requirements which supp
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.