ASTM A513-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon and Alloy Steel Mechanical Tubing
Standard Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon and Alloy Steel Mechanical Tubing
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers electric-resistance-welded carbon and alloy steel tubing for use as mechanical tubing.
1.2 This specification covers mechanical tubing made from hot- or cold-rolled steel.
1.3 This specification covers round, square, rectangular, and special shape tubing. Size Range Type (Round Tubing) Electric-Resistance-Welded Tubing outside diameter from 1/2 to 15 in. from Hot-Rolled Steel (19.0 to 381.0 mm) wall from 0.065 to 0.650 in. (1.65 to 16.50 mm) Electric-Resistance-Welded Tubing outside diameter from 3/4 to 8 in. from Cold-Rolled Steel (9.52 to 203.2 mm) wall from 0.022 to 0.134 in. (0.71 to 3.40 mm)
1.4 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 513 – 00
Standard Specification for
Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon and Alloy Steel
Mechanical Tubing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 513; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope netic Steel Tubular Products
2.2 ANSI Standard:
1.1 This specification covers electric-resistance-welded car-
B 46.1 Surface Texture
bon and alloy steel tubing for use as mechanical tubing.
2.3 Military Standards:
1.2 This specification covers mechanical tubing made from
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
hot- or cold-rolled steel.
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products Preparation for Ship-
1.3 This specification covers round, square, rectangular, and
ment and Storage
special shape tubing.
2.4 Federal Standard:
Size Range
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipments (CivilAgencies)
Type (Round Tubing)
Electric-Resistance-Welded Tubing outside diameter from ⁄2
from Hot-Rolled Steel to 15 in. (19.0 to 381.0 mm)
3. Ordering Information
wall from 0.065 to 0.650 in.
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should
(1.65 to 16.50 mm)
Electric-Resistance-Welded Tubing outside diameter from ⁄8 to 12 in.
include the following as required to adequately describe the
from Cold-Rolled Steel (9.92 to 304.8 mm)
desired material:
wall from 0.022 to 0.134 in. (0.71
3.1.1 Quantity (feet or number of lengths),
to 3.40 mm)
3.1.2 Name of material (electric resistance-welded carbon
1.4 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and
or alloy steel mechanical tubing),
when desired, shall be so stated in the order.
3.1.3 Type, description and code letters, (Section 1 and
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
12.1),
as the standard.
3.1.4 Thermal condition, (12.2),
3.1.5 Flash condition, (12.3),
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.6 Grade designation, if required, (Section 5),
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.7 Report chemical analysis and product analysis, if
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for MechanicalTesting
required (Sections 6 and 7),
of Steel Products
3.1.8 Individual supplementary requirements, if required
E 1806 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determi-
(S1 to S10, inclusive),
nation of Chemical Composition
3.1.9 Cross section (round, square, rectangular and special
E 213 Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Metal Pipe
shapes),
and Tubing
3.1.10 Dimensions, round, outside and inside and wall
E 273 Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Longitudinal
thickness (see 8.1 and 8.2) or square and rectangular, outside
Welded Pipe and Tubing
dimension and wall thickness and corner radii, if required (see
E 309 Practice for Eddy-Current Examination of Steel Tu-
9.1 and 9.2),
bular Products Using Magnetic Saturation
3.1.11 Surface finish (see 11.2),
E 570 Practice for Flux Leakage Examination of Ferromag-
3.1.12 Length, round, mill lengths or definite cut length (see
8.3), square and rectangular, specified length (see 9.4),
3.1.13 Squareness of cut, round tubing, if required, (see
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
8.4),
Stainless Steel, and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.09 on Carbon Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved March 10, 2000. Published May 2000. Originally
published as A 513 – 64. Last previous edition A 513 – 98. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
3 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06. AvailablefromStandardizationDocumentsOrderDesk,Bldg.4SectionD,700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.03. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 513–00
3.1.14 Burrs removed, if required (see 11.3), 6. Heat Analysis
3.1.15 Protective coating (see 14.1),
6.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the
3.1.16 Special packaging (see 17.1),
steel manufacturer to determine the percentages of the ele-
3.1.17 Specification designation, ments specified; if secondary melting processes are employed,
the heat analysis shall be obtained from one remelted ingot or
3.1.18 End use,
the product of one remelted ingot of each primary melt. The
3.1.19 Special requirements,
heat analysis shall comform to the requirements specified,
3.1.20 Special marking (Section 16), and
except that where the heat identity has not been maintained or
3.1.21 Straightness Test Method (see 8.5 and 9.6).
where the analysis is not sufficiently complete to permit
conformance to be determined, the chemical composition
4. Materials and Manufacture
determined from a product analysis made by the tubular
4.1 The steel may be made by any process.
manufacturer shall conform to the requirements specified for
4.2 If a specific type of melting is required by the purchaser,
heat analysis. When requested in the order or contract, a report
it shall be as stated on the purchase order.
of such analysis shall be furnished to the purchaser.
4.3 The primary melting may incorporate separate degas-
sing or refining, and may be followed by secondary melting,
7. Product Analysis
such as electroslag or vacuum-arc remelting. If secondary
7.1 When requested on the purchase order, a product analy-
melting is employed, the heat shall be defined as all of the
sis shall be made by the supplier. The number and source of
ingots remelted from a single primary heat.
samples for such product analysis shall be based on the
4.4 Steel may be cast in ingots or may be strand cast. When
individual heat or lot identity of one of the following forms of
steel of different grades is sequentially strand cast, identifica-
material:
tion of the resultant transition material is required. The
7.1.1 Heat Identity Maintained—One product analysis per
producer shall remove the transition material by an established
heat shall be made on either the flat-rolled stock or tube.
procedure that positively separates the grades.
7.1.2 Heat Identity Not Maintained—A product from one
4.5 Tubes shall be made by the electric-resistance-welded
tube per 2000 ft (610 m) or less for sizes over 3 in. (76.2 mm),
process and shall be made from hot- or cold-rolled steel as
and one tube per 5000 ft (150 m) or less for sizes 3 in. and
specified.
under.
7.2 Samplesforproductanalysisexceptforspectrochemical
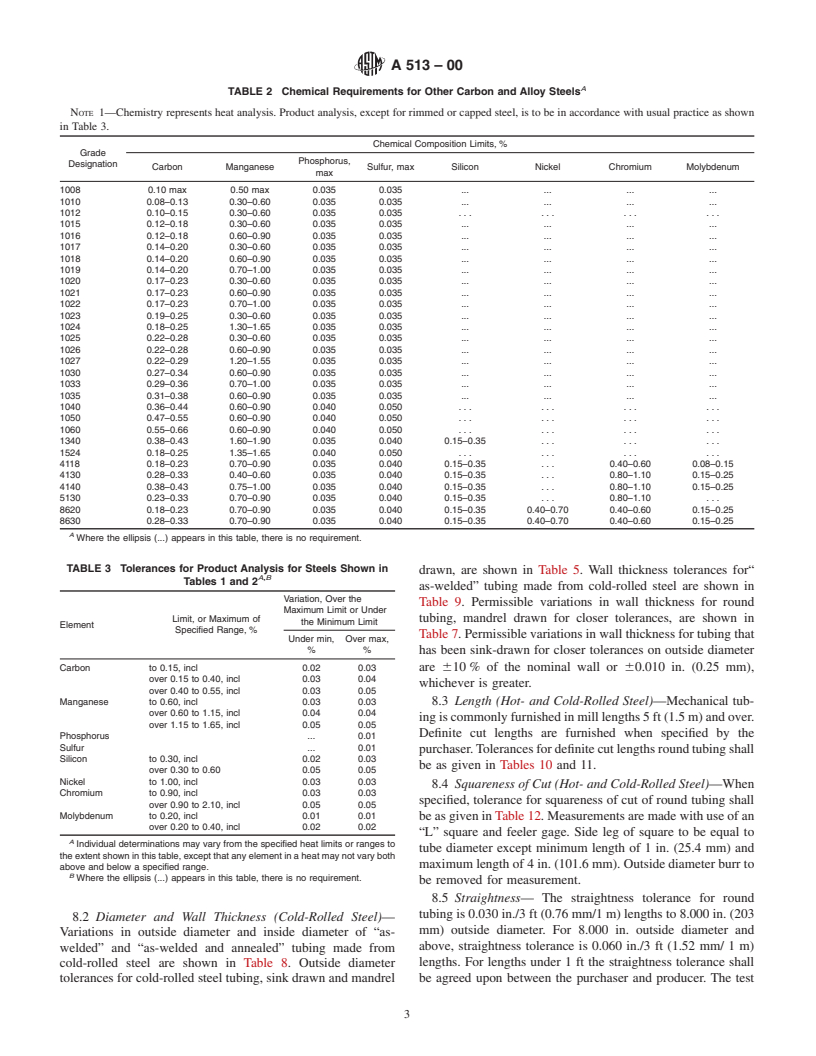
5. Chemical Composition
analysisshallbetakeninaccordancewithPracticeE 1806.The
composition thus determined shall correspond to the require-
5.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements as to
ments of Tables 1-3.
chemical composition prescribed inTables 1 and 2. If no grade
7.3 If the original test for product analysis fails, retests of
is specified, Grades MT 1010 to MT 1020 may be furnished.
two additional lengths of flat-rolled stock or tubes shall be
Analyses of steels other than those listed are available. To
made. Both retests for the elements in question shall meet the
determine their availability, the purchaser should contact the
requirements of the specification; otherwise, all remaining
producer.
material in the heat or lot shall be rejected or, at the option of
5.2 When a carbon steel grade is ordered under this speci-
the producer, each length of flat-rolled stock or tube may be
fication, supplying an alloy grade that specifically requires the
individually tested for acceptance. Lengths of flat-rolled stock
addition of any element other than those listed for the ordered
or tubes which do not meet the requirements of the specifica-
grade in Tables 1 and 2 is not permitted.
tion shall be rejected.
8. Permissible Variations in Dimensions for Round
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements for Standard Low-Carbon
A
Tubing
Steels
8.1 Diameter and Wall Thickness (Hot-Rolled Steel)—
NOTE 1— Chemistry represents heat analysis. Product analysis, except
Variations from specified outside diameter for “as-welded” and
for rimmed or capped steel, is to be in accordance with usual practice as
“as-welded and annealed” tubing made from hot-rolled steel
shown in Table 3.
shallnotexceedtheamountsprescribedinTable4.Permissible
Chemical Composition Limits, %
Grade
variations in outside diameter for tubing that has been sink-
Phosphorus, Sulfur,
Designation
Carbon Manganese
drawn for closer tolerance on outside diameter are shown in
max max
Table 5. Permissible variations in wall thickness for tubing that
B
MT 1010 0.05–0.15 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035
has been sink-drawn for closer tolerances on outside diameters
MT 1015 0.10–0.20 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035
are 610 % of the nominal wall or 60.010 in. (0.25 mm),
MT X 1015 0.10–0.20 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035
whichever is greater. Permissible variations in wall thickness
MT 1020 0.15–0.25 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035
MT X 1020 0.15–0.25 0.70–1.00 0.035 0.035
for tubing made from hot-rolled steel are shown in Table 6.
A
Rimmed or capped steels which may be used for the above grades are Permissible variation in outside and inside diameter for tubing
characterized by a lack of uniformity in their chemical composition, and for this
made from hot-rolled steel that has been mandrel drawn for
reasonproductanalysisisnottechnologicallyappropriateunlessmisapplicationis
closer tolerances are shown in Table 5 with wall tolerances
clearly indicated.
B
The letters MT under grade designation indicate Mechanical Tubing. shown in Table 7.
A 513–00
A
TABLE 2 Chemical Requirements for Other Carbon and Alloy Steels
NOTE 1—Chemistry represents heat analysis. Product analysis, except for rimmed or capped steel, is to be in accordance with usual practice as shown
in Table 3.
Chemical Composition Limits, %
Grade
Phosphorus,
Designation
Carbon Manganese Sulfur, max Silicon Nickel Chromium Molybdenum
max
1008 0.10 max 0.50 max 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1010 0.08–0.13 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1012 0.10–0.15 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . . . . . . . . . .
1015 0.12–0.18 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1016 0.12–0.18 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1017 0.14–0.20 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1018 0.14–0.20 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1019 0.14–0.20 0.70–1.00 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1020 0.17–0.23 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1021 0.17–0.23 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1022 0.17–0.23 0.70–1.00 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1023 0.19–0.25 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1024 0.18–0.25 1.30–1.65 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1025 0.22–0.28 0.30–0.60 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1026 0.22–0.28 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1027 0.22–0.29 1.20–1.55 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1030 0.27–0.34 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1033 0.29–0.36 0.70–1.00 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1035 0.31–0.38 0.60–0.90 0.035 0.035 . . . .
1040 0.36–0.44 0.60–0.90 0.040 0.050 . . . . . . . . . . . .
1050 0.47–0.55 0.60–0.90 0.040 0.050 . . . . . . . . . . . .
1060 0.55–0.66 0.60–0.90 0.040 0.050 . . . . . . . . . . . .
1340 0.38–0.43 1.60–1.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . . . . . . .
1524 0.18–0.25 1.35–1.65 0.040 0.050 . . . . . . . . . . . .
4118 0.18–0.23 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . 0.40–0.60 0.08–0.15
4130 0.28–0.33 0.40–0.60 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . 0.80–1.10 0.15–0.25
4140 0.38–0.43 0.75–1.00 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . 0.80–1.10 0.15–0.25
5130 0.23–0.33 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . 0.80–1.10 . . .
8620 0.18–0.23 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 0.40–0.70 0.40–0.60 0.15–0.25
8630 0.28–0.33 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 0.40–0.70 0.40–0.60 0.15–0.25
A
Where the ellipsis (.) appears in this table, there is no requirement.
TABLE 3 Tolerances for Product Analysis for Steels Shown in
drawn, are shown in Table 5. Wall thickness tolerances for“
A,B
Tables 1 and 2
as-welded” tubing made from cold-rolled steel are shown in
Variation, Over the
Table 9. Permissible variations in wall thickness for round
Maximum Limit or Under
Limit, or Maximum of tubing, mandrel drawn for closer tolerances, are shown in
the Minimum Limit
Element
Specified Range, %
Table 7. Permissible variations in wall thickness for tubing that
Under min, Over max,
% %
has been sink-drawn for closer tolerances on outside diameter
are 610 % of the nominal wall or 60.010 in. (0.25 mm),
Carbon to 0.15, incl 0.02 0.03
over 0.15 to 0.40, incl 0.03 0.04
whichever is greater.
over 0.40 to 0.55, incl 0.03 0.05
Manganese to 0.60, incl 0.03 0.03
8.3 Length (Hot- and Cold-Rolled Steel)—Mechanical tub-
over 0.60 to 1.15, incl 0.04 0.04
ingiscommonlyfurnishedinmilllengths5ft(1.5m)andover.
over 1.15 to 1.65, incl 0.05 0.05
Definite cut lengths are furnished when specified by the
Phosphorus . 0.01
Sulfur . 0.01
purchaser.Tolerancesfordefinitecutlengthsroundtubingshall
Silicon to 0.30, incl 0.02 0.03
be as given in Tables 10 and 11.
over 0.30 to 0.60 0.05 0.05
Nickel to 1.00, incl 0.03 0.03
8.4 Squareness of Cut (Hot- and Cold-Rolled Steel)—When
Chromium to 0.90, incl 0.03 0.03
specified, tolerance for squareness of cut of round tubing shall
over 0.90 to 2.10, incl 0.05 0.05
Molybdenum to 0.20, incl 0.01 0.01 be as given inTable 12. Measurements are made with use of an
over 0.20 to 0.40, incl 0.02 0.02
“L” square and feeler gage. Side leg of square to be equal to
A
Individual determinations may vary from the specified heat limits or ranges to
tube diameter except minimum length of 1 in. (25.4 mm) and
theextentshowninthistable,exceptthatanyelementinaheatmaynotvaryboth
maximum length of 4 in. (101.6 mm). Outside diameter burr to
above and below a specified range.
B
Where the ellipsis (.) appears in this table, there is no requirement.
be removed for measurement.
8.5 Straightness— The straightness tolerance for round
tubing is 0.030 in./3 ft (0.76 mm/1 m) lengths to 8.000 in. (203
8.2 Diameter and Wall Thickness (Cold-Rolled Steel)—
mm) outside diameter. For 8.000 in. outside diameter and
Variations in outside diameter and inside diameter of “as-
above, straightness tolerance is 0.060 in./3 ft (1.52 mm/ 1 m)
welded” and “as-welded and annealed” tubing made from
lengths. For lengths under 1 ft the straightness tolerance shall
cold-rolled steel are shown in Table 8. Outside diameter
tolerances for cold-rolled steel tubing, sink drawn and mandrel be agreed upon between the purchaser and producer. The test
A 513–00
TABLE 4 Diameter Tolerances for Type I (A.W.H.R.) Round Tubing
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.