ASTM D5948-05(2012)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Molding Compounds, Thermosetting
Standard Specification for Molding Compounds, Thermosetting
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the basic properties of thermoset molding plastic compounds and the test methods used to establish the properties. The plastic compounds shall be a resin, cellulose-filled or mineral/glass-filled phenolic, melamine, polyester, diallyl iso-phthalate, diallyl ortho-phthalate, silicone, or epoxy. Standard test specimens shall be in the as-received condition or shall be conditioned before testing by humidity, immersion, or temperature conditioning. The specimens shall undergo mechanical or physical qualification tests which shall conform to the following properties: compressive strength; dimensional stability; flexural strength; heat deflection temperature; heat resistance; impact strength; tensile strength; and water absorption. Electrical qualification tests shall be conducted; wherein, the specimens shall comply with the following requirements: arc resistance; dielectric breakdown; dielectric constant; dielectric strength; dissipation factor; surface resistance; comparative track index; volume resistance; and water extract conductance. Tests for combustion qualification shall also be performed to determine the flame resistance ignition time, burning time, flammability, and toxicity requirements. Batch acceptance tests shall be conducted as well to ensure the quality conformance of the specimens.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This specification is a revision of STD MIL-M-14H, Specification for Molding Compound, Thermosetting, retaining the MIL-M-14H material designations and property requirements while conforming to ASTM form and style. It is intended for qualification and batch acceptance for materials used by government and industry, and is intended as a direct replacement for MIL-M-14H.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the basic properties of thermoset molding compounds and the test methods used to establish the properties.
1.2 Classification—Molding thermosetting plastic compounds shall be of the following resins and are covered by the individual specification sheets (see 5.1 and Annex A1-Annex A8).
Resin
Phenolic, cellulose filled
Phenolic, mineral/glass filled
Melamine
Polyester
Diallyl iso-phthalate
Diallyl ortho-phthalate
Silicone
Epoxy
Note 1—There is no equivalent ISO standard.
1.3 Order of Precedence—In the event of a conflict between the text of this specification and the references cited in Section 2 (except for related specification sheets), the text of this specification takes precedence. Nothing in this specification, however, supersedes applicable laws and regulations unless a specific exemption has been obtained.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be considered standard.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5948 −05 (Reapproved 2012)
Standard Specification for
1
Molding Compounds, Thermosetting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5948; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
D229 Test Methods for Rigid Sheet and Plate Materials
1.1 This specification covers the basic properties of thermo-
Used for Electrical Insulation
set molding compounds and the test methods used to establish
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
the properties.
Impact Resistance of Plastics
1.2 Classification—Molding thermosetting plastic com-
D495 Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry Arc
pounds shall be of the following resins and are covered by the
Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
individual specification sheets (see 5.1 and AnnexA1 – Annex
D570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
A8).
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
Resin
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
Phenolic, cellulose filled
Phenolic, mineral/glass filled
D648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
Melamine
Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
Polyester
Diallyl iso-phthalate D695 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
Diallyl ortho-phthalate
Plastics
Silicone
D790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
Epoxy
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
NOTE 1—There is no equivalent ISO standard.
als
1.3 Order of Precedence—In the event of a conflict between
D796 Practice for Compression Molding Test Specimens of
the text of this specification and the references cited in Section
3
Phenolic Molding Compounds (Withdrawn 1992)
2 (except for related specification sheets), the text of this
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
specification takes precedence. Nothing in this specification,
D1896 Practice for Transfer Molding Test Specimens of
however, supersedes applicable laws and regulations unless a
Thermosetting Compounds
specific exemption has been obtained.
D3419 Practice for In-Line Screw-Injection Molding Test
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be considered
Specimens From Thermosetting Compounds
standard.
D3636 Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid
Electrical Insulating Materials
2. Referenced Documents
D3638 Test Method for Comparative Tracking Index of
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Electrical Insulating Materials
D149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
D4350 Test Method for Corrosivity Index of Plastics and
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
Fillers
at Commercial Power Frequencies
D4697 Guide for Maintaining Test Methods in the User’s
D150 Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
3
Laboratory (Withdrawn 2009)
E994 Guide for Calibration and Testing LaboratoryAccredi-
tation Systems General Requirements for Operation and
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
3
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.16 on Thermosetting Recognition (Withdrawn 2003)
Materials.
E1224 GuideforCategorizingFieldsofCapabilityforLabo-
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2012. Published November 2012. Originally
3
ε1 ratory Accreditation Purposes (Withdrawn 2002)
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D5948 - 05 . DOI:
10.1520/D5948-05R12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5948−05 (2012)
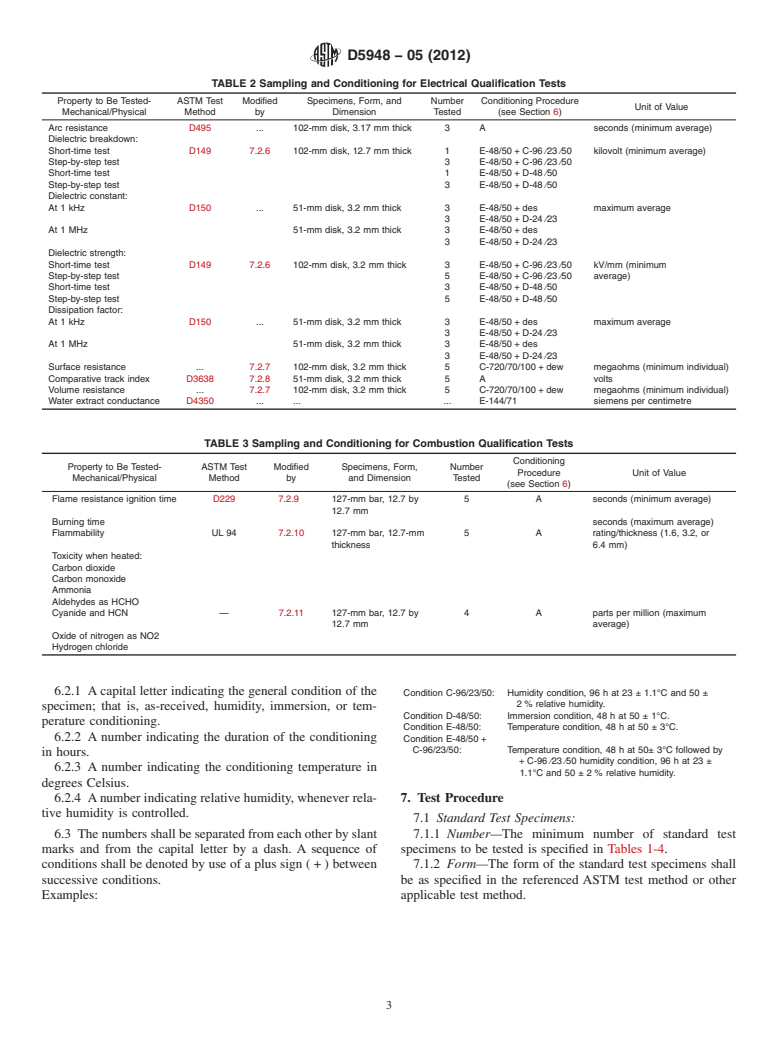
TABLE 1 Sampling and Conditioning for Mechanical/Physical Qualification Tests
NOTE 1—A50 % retention of initial flexural strength is required.
NOTE 2—The side of a test specimen is that area formed by the chase of the mold.
NOTE 3—The face of the test specimen is that area formed by the top or bottom force plug.
NOTE 4—When specified.
Property to Be Tested- ASTM Test Modified Specimens, Form, and Number Conditioning Procedure
Unit of Value
Mechanical/Physical Method by Dimension Tested (see Section 6)
Compressive strength, end- D695 . 25.4 by
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.