ASTM B809-95(2018)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Porosity in Metallic Coatings by Humid Sulfur Vapor (“Flowers-of-Sulfur”)
Standard Test Method for Porosity in Metallic Coatings by Humid Sulfur Vapor (“Flowers-of-Sulfur”)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 A major use of this test procedure is for determining coating quality. Porosity tests are indications of the completeness of protection or coverage offered by the coatings, since the coatings described in 1.2 are intended to be protective when properly applied. The porosity test results are therefore a measure of the deposition process control.
5.2 A particular purpose of the humid sulfur vapor test is for determining the quality of underplates of nickel or nickel alloy in those finish systems that have thin, 1.2 μm or less (50 μin. or less) top layers above the nickel, since porosity in the underplate usually continues into such top layers.
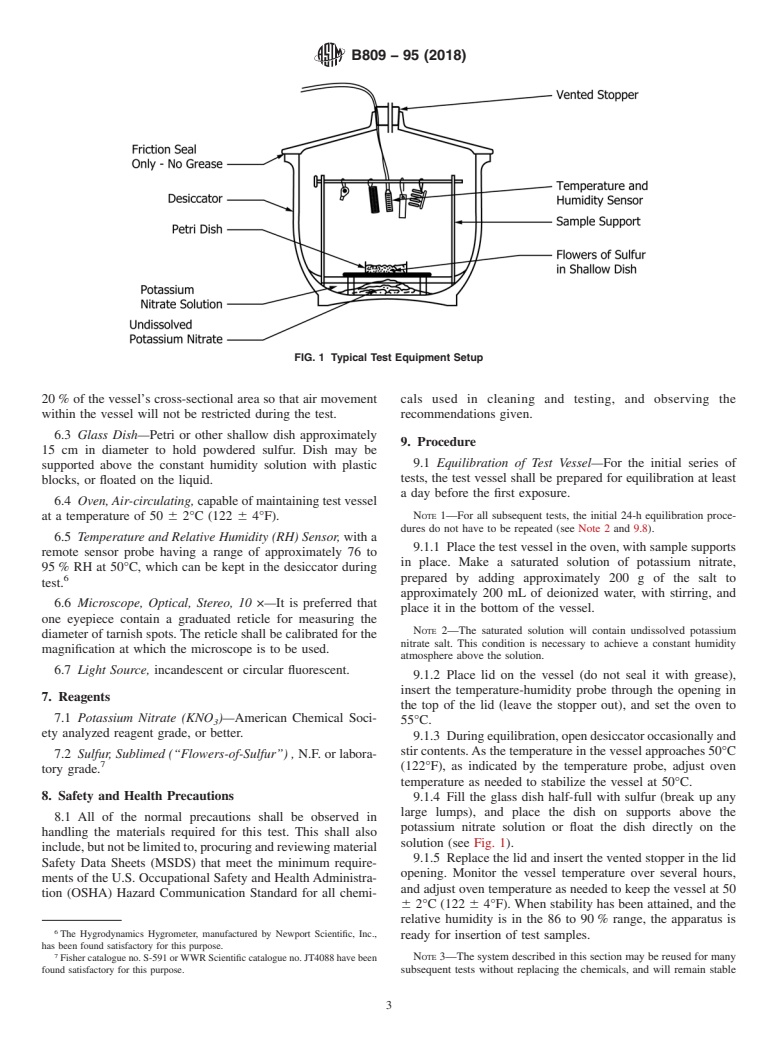
5.3 The humid sulfur vapor test is often used as an environmental test to simulate many indoor humid atmosphere tarnishing and tarnish creepage effects. However, the chemistry and properties of these tarnish films may not resemble those found in other service environments. For such product performance evaluations, the test should only be used in combination with other performance evaluation tests, as specified in the referencing document for that product.
5.4 Porosity tests differ from corrosion and aging tests, since the latter are intended to measure the chemical inertness of the coating. In contrast, in a good porosity test procedure the corrosive agent should not attack the coating. It must instead, clean, depolarize, or activate the substrate metal exposed by the pore, or both, and attack it sufficiently to cause reaction products to fill the pore to the surface of the coating.
5.5 The humid sulfur test is highly sensitive, and is capable of detecting virtually all porosity that penetrates down to copper or copper alloys. Since nickel is not attacked by moist sulfur vapor at 100°C or less, this test will not detect pores or cracks in the top coating if such pores or cracks do not penetrate through the nickel underplate overlaying the copper.
5.6 The level of porosity in the coating that may be tolerable d...
SCOPE
1.1 This standard covers equipment and test methods for determining the porosity of metallic coatings, where the pores penetrate down to a silver, copper, or copper-alloy substrate.
1.2 This test method is suitable for coatings consisting of single or combined layers of any coating that does not significantly tarnish in a reduced sulfur atmosphere, such as gold, nickel, tin, tin-lead, and palladium, or their alloys.
1.3 This test method is designed to determine whether the porosity level is less than or greater than some value which by experience is considered by the user to be acceptable for the intended application.
1.4 Recent reviews of porosity testing and testing methods can be found in the literature.2,3 Guide B765 is suitable to assist in the selection of porosity tests for electrodeposits and related metallic coatings. Other porosity test standards are Test Methods B735, B741, B798, and B799.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazards statements, see Section 8.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B809 − 95 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Test Method for
Porosity in Metallic Coatings by Humid Sulfur Vapor
1
(“Flowers-of-Sulfur”)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B809; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 This standard covers equipment and test methods for
determining the porosity of metallic coatings, where the pores
2. Referenced Documents
penetrate down to a silver, copper, or copper-alloy substrate.
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2 This test method is suitable for coatings consisting of
B374Terminology Relating to Electroplating
single or combined layers of any coating that does not
B542Terminology Relating to Electrical Contacts andTheir
significantly tarnish in a reduced sulfur atmosphere, such as
Use
gold, nickel, tin, tin-lead, and palladium, or their alloys.
B735Test Method for Porosity in Gold Coatings on Metal
1.3 This test method is designed to determine whether the
Substrates by Nitric Acid Vapor
porosity level is less than or greater than some value which by
B741Test Method for Porosity In Gold Coatings On Metal
5
experience is considered by the user to be acceptable for the
Substrates By Paper Electrography (Withdrawn 2005)
intended application.
B765GuideforSelectionofPorosityandGrossDefectTests
for Electrodeposits and Related Metallic Coatings
1.4 Recent reviews of porosity testing and testing methods
2,3
B798Test Method for Porosity in Gold or Palladium Coat-
can be found in the literature. Guide B765 is suitable to
ings on Metal Substrates by Gel-Bulk Electrography
assist in the selection of porosity tests for electrodeposits and
B799Test Method for Porosity in Gold and Palladium
related metallic coatings. Other porosity test standards areTest
Coatings by Sulfurous Acid/Sulfur-Dioxide Vapor
Methods B735, B741, B798, and B799.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3. Terminology
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.1 Definitions—Many terms used in this test method are
only.
defined in Terminologies B374 and B542.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.1 corrosion products—reaction products of the basis
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
metal or underplate, that protrude from, or are otherwise
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
attached to, the coating surface after the test exposure.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
For specific hazards statements, see Section 8. 3.2.2 measurement area—in this test method,thatportionor
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor- portions of the surface that is examined for the presence of
porosity. The measurement area shall be indicated on the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the drawings of the parts, or by the provision of suitably marked
samples.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.2.3 metallic coatings—in this test method, include
platings, claddings, or other metallic coatings applied to the
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB08onMetallic
substrate. The coating can comprise a single metallic layer or
and Inorganic Coatings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B08.10 on
a combination of metallic layers.
Test Methods.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2018. Published August 2018. Originally
approvedin1990.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2013asB809–95(2013).DOI:
4
10.1520/B0809-95R18. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
2
Clarke, M., “Porosity and Porosity Tests,” Properties of Electrodeposits, Sard, contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Leidheiser, and Ogburn, eds., The Electrochemical Society, 1975, p. 122. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
3
Krumbein, S. J., “Porosity Testing of Contact Platings,” Transactions of the the ASTM website.
5
Connectors and Interconnection Technology Symposium, Philadelphia, PA, October The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
1987, p. 47. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM Inter
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.