ISO 7800:1984
(Main)Metallic materials — Wire — Simple torsion test
Metallic materials — Wire — Simple torsion test
Specifies the method for determining the ability of wire of diameter or thickness 0,3 to 10 mm inclusive to undergo plastic deformation during simple torsion. The test consists of twisting a test piece of wire around its own axis in one direction.
Matériaux métalliques — Fils — Essai de torsion simple
Kovinski materiali - Žica - Enostavni vzvojni preskus
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATlON.MEWYHAPO~HAR OPrAHl43A~MR IlO CTAH~APTt43ALWl.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALlSATlON
Metallic materials - Wire - Simple torsion test
Mathriaux mktalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
First edition - 1984-03-15
UDC 669-426 : 620.175
Ref. No. IS0 7800-1984 (E)
Descriptors : metal products, wire, tests, torsion tests, test equipment, test specimens.
Price based on 2 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing International
Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member body
interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been authorized has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 7800 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 164,
Mechanical testing of metals, and was circulated to the member bodies in January
1983.
It has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries:
Australia
Germany, F. R. Poland ’
Austria
Hungary Romania
Bulgaria Italy South Africa, Rep. of
Canada
Japan Spain
China
Korea, Dem. P. Rep. of Switzerland
Czechoslovakia USA
Mexico
Denmark Netherlands USSR
France
Norway
The member body of the following country expressed disapprova I of the document on
technical grounds :
United Kingdom
This International Standard cancels and replaces International Standards IS0 1364972
and IS0 2627-1973, and IS0 Recommendation R 957-1969, of which it constitutes a
technical revision.
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1984
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
IS0 78004984 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Metallic materials - Wire - Simple torsion test
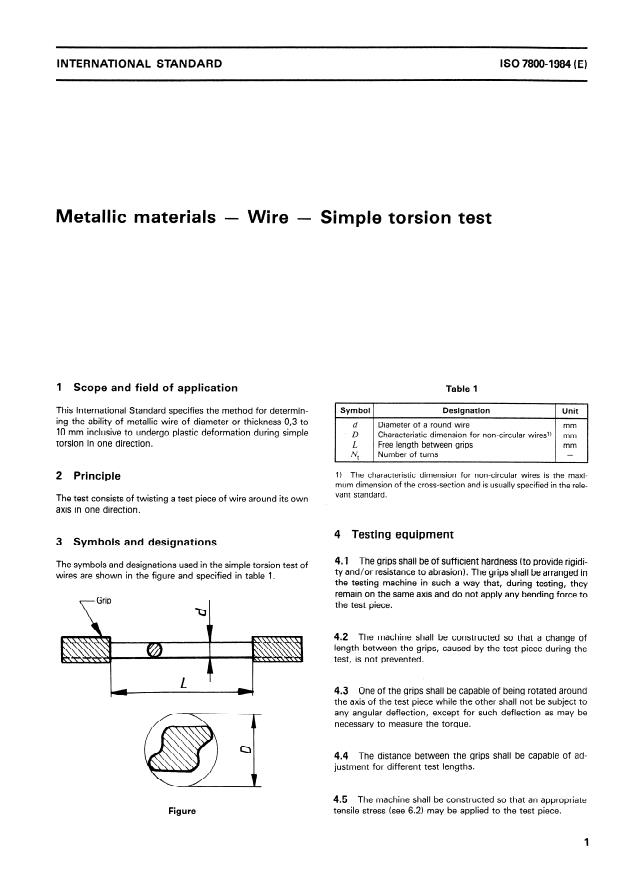
Scope and field of application Table 1
1
Symbol 1 Designation 1 Unit 1
This International Standard specifies the method for determin-
ing the ability of metallic wire of diameter or thickness 0,3 to
Diameter of a round wire mm
10 mm inclusive to undergo plastic deformation during simple Characteristic dimension for non-circular wiresl) mm
torsion in one direction. Free length between grips mm
-
Number of turns
1) The characteristic dimension for non-circular wires is the maxi-
2 Principle
mum dimension of the cross-section and is usually specified in the rele-
vant standard.
The test consists of twisting a test piece of wire around its own
axis in one direction.
4 Testing equipment
3 Symbols and designations
4. ‘I The grips shall be of sufficient hardness (to provide rigidi-
The symbols and designations used in the simple torsion test of
ty and/or resistance to abrasion). The grips shall be arranged in
wires are shown in the figure and specified in table 1.
the testing machine in such a way that, during testing, they
remain on the same axis and do not apply any bending force to
Grip
the test piece.
T
4.2 The machine shall be constructed so that a change of
length between the grips, caused by the test piece during the
test, is not prevented.
4.3 One of the grips shall be capable of being rotated around
the axis of the test piece while the ot
...
SLOVENSKI STANDARD
SIST ISO 7800:1996
01-januar-1996
Kovinski materiali - Žica - Enostavni vzvojni preskus
Metallic materials -- Wire -- Simple torsion test
Matériaux métalliques -- Fils -- Essai de torsion simple
Ta slovenski standard je istoveten z: ISO 7800:1984
ICS:
77.040.10 Mehansko preskušanje kovin Mechanical testing of metals
SIST ISO 7800:1996 en
2003-01.Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
SIST ISO 7800:1996
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
SIST ISO 7800:1996
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATlON.MEWYHAPO~HAR OPrAHl43A~MR IlO CTAH~APTt43ALWl.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALlSATlON
Metallic materials - Wire - Simple torsion test
Mathriaux mktalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
First edition - 1984-03-15
UDC 669-426 : 620.175
Ref. No. IS0 7800-1984 (E)
Descriptors : metal products, wire, tests, torsion tests, test equipment, test specimens.
Price based on 2 pages
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
SIST ISO 7800:1996
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing International
Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member body
interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been authorized has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 7800 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 164,
Mechanical testing of metals, and was circulated to the member bodies in January
1983.
It has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries:
Australia
Germany, F. R. Poland ’
Austria
Hungary Romania
Bulgaria Italy South Africa, Rep. of
Canada
Japan Spain
China
Korea, Dem. P. Rep. of Switzerland
Czechoslovakia USA
Mexico
Denmark Netherlands USSR
France
Norway
The member body of the following country expressed disapprova I of the document on
technical grounds :
United Kingdom
This International Standard cancels and replaces International Standards IS0 1364972
and IS0 2627-1973, and IS0 Recommendation R 957-1969, of which it constitutes a
technical revision.
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1984
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 4 ----------------------
SIST ISO 7800:1996
IS0 78004984 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Metallic materials - Wire - Simple torsion test
Scope and field of application Table 1
1
Symbol 1 Designation 1 Unit 1
This International Standard specifies the method for determin-
ing the ability of metallic wire of diameter or thickness 0,3 to
Diameter of a round wire mm
10 mm inclusive to undergo plastic deformation during simple Characteristic dimension for non-circular wiresl) mm
torsion in one direction. Free length between grips mm
-
Number of turns
1) The characteristic dimension for non-circular wires is the maxi-
2 Principle
mum dimension of the cross-section and is usually specified in the rele-
vant standard.
The test consists of twisting a test piece of wire around its own
axis in one direction.
4 Testing equipment
3 Symbols and designations
4. ‘I The grips shall be of sufficient hardness (to provide rigidi-
The symbols and designations used in the simple torsion test of
ty and/or resistance to abrasion). The grips shall be arranged in
wires are shown in the figure and specified in table 1.
the testing machine in such a way that, during testing, they
remain on the s
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEXJlYHAPOAHAR OPf-AHM3AlJ4R ll0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM.ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Matériaux métalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
Me tallic ma teriak - Wire - Simple torsion test
Première édition - 1984-03-15
CDU 669-426: 620.175 Réf. no : ISO 7800-1984 (FI
iî
-
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 7800 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 164,
Essais mécaniques des métaux, et a été soumise aux comités membres en janvier 1983.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’ Danemark Pays- Bas
Allemagne, R. F.
Espagne Pologne
Australie Roumanie ’
France
Autriche
Hongrie Suisse
Bulgarie Italie Tchécoslovaquie
Canada Japon URSS
Chine Mexique USA
Corée, Rép. dem. p. de Norvège
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’a désapprouvée pour des raisons techniques:
Royaume-Uni
Cette Norme internationale annule et remplace les Normes internationales ISO 136-
1972 et ISO 26274973, ainsi que la Recommandation ISO/R 957-1969, dont elle cons-
titue une révision technique.
0
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
NORME INTERNATIONALE
ISO 7800-1984 (F)
Matériaux métalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
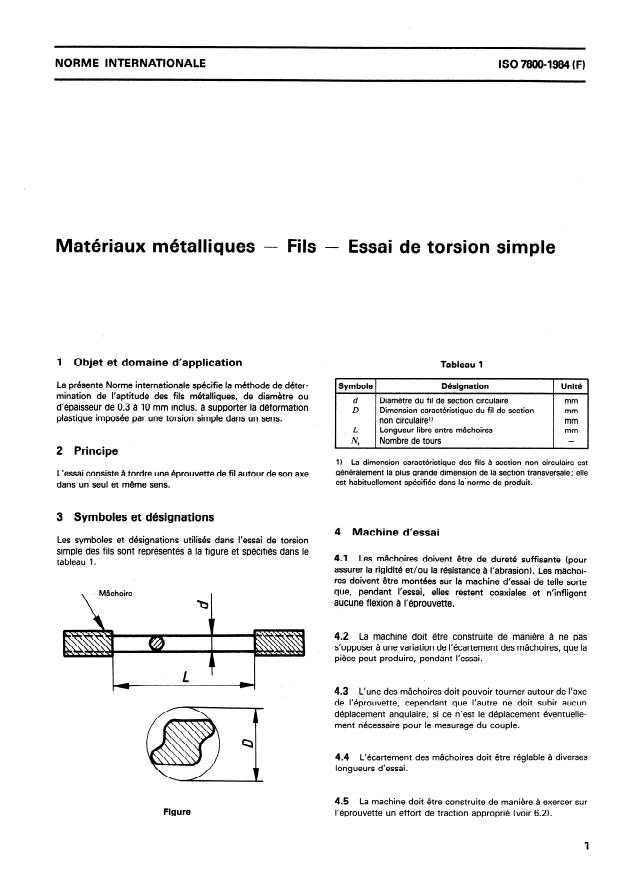
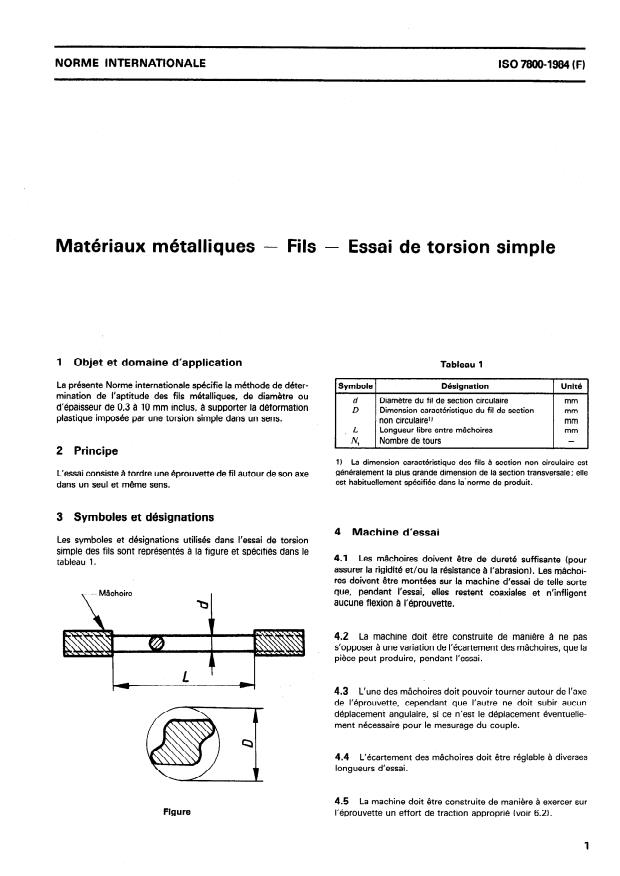
1 Objet et domaine d’application
Tableau 1
La présente Norme internationale spécifie la méthode de déter-
Symbole 1 Ddsignation 1 Unité 1
I
mination de l’aptitude des fils métalliques, de diamétre ou
Diamétre du fil de section circulaire
n mm
d’épaisseur de 0,3 à 10 mm inclus, à supporter la déformation
D Dimension caractéristique du fil de section mm
plastique imposée par une torsion simple dans un sens.
non circulairel)
mm
Longueur libre entre mâchoires mm
. L
-
Nombre de tours
4
2 Principe
1) La dimension caractéristique des fils à section non circulaire est
généralement la plus grande dimension de la section transversale; elle
L’essai consiste à tordre une éprouvette de fil autour de son axe
est habituellement spécifiée dans la’ norme de produit.
dans un seul et même sens.
3 Symboles et désignations
4 Machine d’essai
Les symboles et désignations utilises dans l’essai de torsion
simple des fils sont représentés à la figure et spécifiés dans le
4.1 Les mâchoires doivent être de dureté suffisante (pour
tableau 1.
assurer la rigidité et/ou la résistance à I’abrasion). Les mâchoi-
res doivent être montées sur la machine d’essai de telle sorte
que, pendant l’essai, elles restent coaxiales et n’infligent
aucune flexion à l’éprouvette.
4.2 La machine doit être construite de manière à ne pas
s’opposer à une variation de l’écartement des mâchoires, que la
piéce peut produire, pendant l’essai.
4.3 L’une des mâchoires doit pouvoir tourner autour de l’axe
de l’éprouvette, cependant que l’autre ne doit subir aucun
déplacement angulaire, si ce n’est le déplacement éventuelle-
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEXJlYHAPOAHAR OPf-AHM3AlJ4R ll0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM.ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Matériaux métalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
Me tallic ma teriak - Wire - Simple torsion test
Première édition - 1984-03-15
CDU 669-426: 620.175 Réf. no : ISO 7800-1984 (FI
iî
-
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 7800 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 164,
Essais mécaniques des métaux, et a été soumise aux comités membres en janvier 1983.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’ Danemark Pays- Bas
Allemagne, R. F.
Espagne Pologne
Australie Roumanie ’
France
Autriche
Hongrie Suisse
Bulgarie Italie Tchécoslovaquie
Canada Japon URSS
Chine Mexique USA
Corée, Rép. dem. p. de Norvège
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’a désapprouvée pour des raisons techniques:
Royaume-Uni
Cette Norme internationale annule et remplace les Normes internationales ISO 136-
1972 et ISO 26274973, ainsi que la Recommandation ISO/R 957-1969, dont elle cons-
titue une révision technique.
0
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
NORME INTERNATIONALE
ISO 7800-1984 (F)
Matériaux métalliques - Fils - Essai de torsion simple
1 Objet et domaine d’application
Tableau 1
La présente Norme internationale spécifie la méthode de déter-
Symbole 1 Ddsignation 1 Unité 1
I
mination de l’aptitude des fils métalliques, de diamétre ou
Diamétre du fil de section circulaire
n mm
d’épaisseur de 0,3 à 10 mm inclus, à supporter la déformation
D Dimension caractéristique du fil de section mm
plastique imposée par une torsion simple dans un sens.
non circulairel)
mm
Longueur libre entre mâchoires mm
. L
-
Nombre de tours
4
2 Principe
1) La dimension caractéristique des fils à section non circulaire est
généralement la plus grande dimension de la section transversale; elle
L’essai consiste à tordre une éprouvette de fil autour de son axe
est habituellement spécifiée dans la’ norme de produit.
dans un seul et même sens.
3 Symboles et désignations
4 Machine d’essai
Les symboles et désignations utilises dans l’essai de torsion
simple des fils sont représentés à la figure et spécifiés dans le
4.1 Les mâchoires doivent être de dureté suffisante (pour
tableau 1.
assurer la rigidité et/ou la résistance à I’abrasion). Les mâchoi-
res doivent être montées sur la machine d’essai de telle sorte
que, pendant l’essai, elles restent coaxiales et n’infligent
aucune flexion à l’éprouvette.
4.2 La machine doit être construite de manière à ne pas
s’opposer à une variation de l’écartement des mâchoires, que la
piéce peut produire, pendant l’essai.
4.3 L’une des mâchoires doit pouvoir tourner autour de l’axe
de l’éprouvette, cependant que l’autre ne doit subir aucun
déplacement angulaire, si ce n’est le déplacement éventuelle-
...





Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.