ISO 6507-3:1989
(Main)Metallic materials — Hardness test — Vickers test — Part 3: Less than HV 0,2
Metallic materials — Hardness test — Vickers test — Part 3: Less than HV 0,2
Matériaux métalliques — Essai de dureté — Essai Vickers — Partie 3: Inférieure à HV 0,2
Kovinska gradiva - Preskus trdote - Preskus trdote po Vickersu - 3. del: Manj kot HV 0,2
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
INTER NATIONAL IS0 IS0
STANDARD 6507-3 6507-3
First First edition edition
1989-1 1989-1 1-01 1-01
O
Metallic Metallic materials materials - - Hardness Hardness test test - -
Vickers Vickers test test - -
Part Part 3 3 : :
Less Less than than HV HV 0,2 0,2
Matériaux Matériaux métalliques métalliques - - Essai Essai de de dureté dureté - - Essai Essai Vickers Vickers - -
Partie Partie 3 3 : : Inférieure Inférieure à à HV HV 0,2 0,2
e
Reference Reference number number
IS0 IS0 6507-3 6507-3 : : 1989 1989 (E) (E)
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
IS0 6607-3 : 1989 (E)
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization] is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the .right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. IS0
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all
matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council. They are approved in accordance with IS0 procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard IS0 6507-3 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 164,
Mechanical testing of metals.
IS0 6507 consists of the following parts, under the general title Metallic materials -
Hardness test - Vickers test:
- Part I: HV 5 to HV 100
- Part2: HV 0,2 to less than HV 5
- Part3: Less than HV 0,2
Annex A forms an integral part of this part of IS0 6507. Annex B is for information
only.
O IS0 1989
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in
writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 0 CH-121 1 Genève 20 0 Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (E)
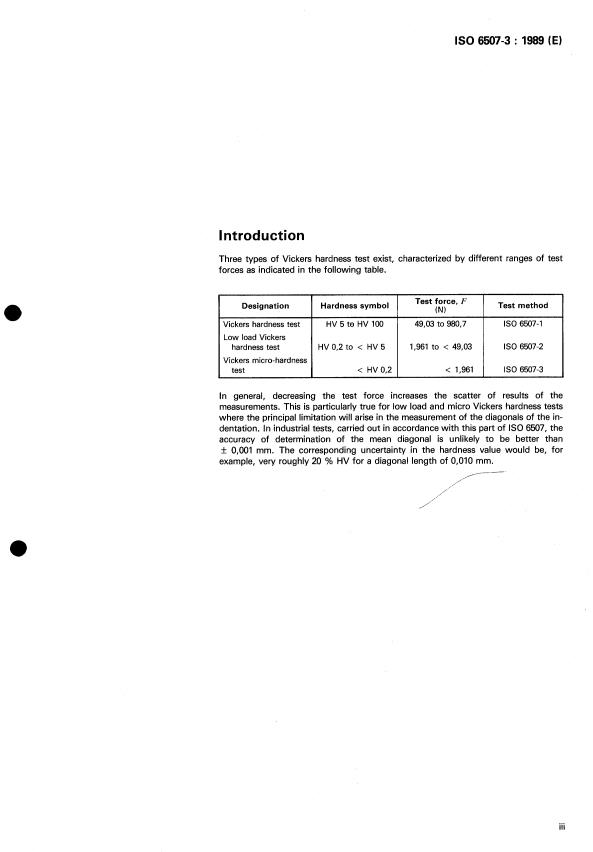
Introduction
Three types of Vickers hardness test exist, characterized by different ranges of test
forces as indicated in the following table.
Test
Designation Hardness symbol Test method
(N)
Vickers hardness test HV 5 te HV 100 49,03 to 980,7 IS0 6507-1
Low load Vickers
hardness test HV 0,2 to < HV 5 1,961 to < 49,03 IS0 6507-2
Vickers micro-hardness
test < HV 0,2 < 1,961 IS0 6507-3
In general, decreasing the test force increases the scatter of results of the
measurements. This is particularly true for low load and micro Vickers hardness tests
where the principal limitation will arise in the measurement of the diagonals of the in-
dentation. In industrial tests, carried out in accordance with this part of IS0 6507, the
accuracy of determination of the mean diagonal is unlikely to be better than
f 0,001 mm. The corresponding uncertainty in the hardness value would be, for
example, very roughly 20 % HV for a diagonal length of 0,010 mm.
..,’
...
111
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Metallic materials - Hardness test - Vickers test -
Part 3:
Less than HV 0,2
1 Scope
3.2 The Vickers hardness is denoted by the symbol HV
preceded by the hardness value and followed by:
This part of IS0 6507 specifies a method of determining a
Vickers hardness of less than HV 0,2 (test force less than a) a number representing the test force (see table 2);
1,961 N) for metallic materials.
b) the duration of loading, in seconds, if different from the
time specified in 7.4.
2 Normative references Examples:
640 HV 0,l = Vickers hardness of 640 determined with a test
The following standards contain provisions which, through
force of 0,980 7 N applied for 10 s to 15 s
reference in this text, constitute provisions of this part of
IS0 6507. At the time of publication, the editions indicated
640 HV 0,1120 = Vickers hardness of 640 determined with a
were valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to
test force of 0,980 7 N applied for 20 s
agreements based on this part of IS0 6507 are encouraged to
investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions
of the standards listed below. Members of IEC and IS0 main-
tain registers of currently valid International Standards.
4 Principle
IS0 6507-1 : 1982, Metallic materials - Hardness test -
Forcing a diamond indenter in the form of a right pyramid with
Vickers test - Part I: HV 5 to HV 100.
a square base and with a specified angle between opposite
faces at the vertex into the surface of a test piece and measur-
IS0 6507-2 : 1983, Metallic materials - Hardness test -
ing the diagonals of the indentation left in the surface after
Vickers test - Part 2: HV 0,2 to less than HV 5.
removal of the test force, F (see figure 1).
The Vickers hardness is porportional to the number obtained by
dividing the test force by the area of the sloping faces of the in-
3 Symbols and their meanings
dentation, which is assumed to be a right pyramid with a
square base and having at the vertex the same angle as the
3.1 See table 1 and figures 1 and 2.
indenter.
Table 1
5 Apparatus
Symbol Meaning
a Angle between the opposite faces at the vertex of
Testing machine, capable of applying a predetermined
5.1
the pyramidal indenter (136")
force or forces less than 1,961 N.
F Test force, in newtons
d Arithmetic mean, in mil
...
SLOVENSKI STANDARD
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
01-november-1995
Kovinska gradiva - Preskus trdote - Preskus trdote po Vickersu - 3. del: Manj kot
HV 0,2
Metallic materials -- Hardness test -- Vickers test -- Part 3: Less than HV 0,2
Matériaux métalliques -- Essai de dureté -- Essai Vickers -- Partie 3: Inférieure à HV 0,2
Ta slovenski standard je istoveten z: ISO 6507-3:1989
ICS:
77.040.10 Mehansko preskušanje kovin Mechanical testing of metals
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995 en
2003-01.Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
INTER NATIONAL IS0 IS0
STANDARD 6507-3 6507-3
First First edition edition
1989-1 1989-1 1-01 1-01
O
Metallic Metallic materials materials - - Hardness Hardness test test - -
Vickers Vickers test test - -
Part Part 3 3 : :
Less Less than than HV HV 0,2 0,2
Matériaux Matériaux métalliques métalliques - - Essai Essai de de dureté dureté - - Essai Essai Vickers Vickers - -
Partie Partie 3 3 : : Inférieure Inférieure à à HV HV 0,2 0,2
e
Reference Reference number number
IS0 IS0 6507-3 6507-3 : : 1989 1989 (E) (E)
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
IS0 6607-3 : 1989 (E)
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization] is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the .right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. IS0
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all
matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council. They are approved in accordance with IS0 procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard IS0 6507-3 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 164,
Mechanical testing of metals.
IS0 6507 consists of the following parts, under the general title Metallic materials -
Hardness test - Vickers test:
- Part I: HV 5 to HV 100
- Part2: HV 0,2 to less than HV 5
- Part3: Less than HV 0,2
Annex A forms an integral part of this part of IS0 6507. Annex B is for information
only.
O IS0 1989
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in
writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 0 CH-121 1 Genève 20 0 Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
---------------------- Page: 4 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (E)
Introduction
Three types of Vickers hardness test exist, characterized by different ranges of test
forces as indicated in the following table.
Test
Designation Hardness symbol Test method
(N)
Vickers hardness test HV 5 te HV 100 49,03 to 980,7 IS0 6507-1
Low load Vickers
hardness test HV 0,2 to < HV 5 1,961 to < 49,03 IS0 6507-2
Vickers micro-hardness
test < HV 0,2 < 1,961 IS0 6507-3
In general, decreasing the test force increases the scatter of results of the
measurements. This is particularly true for low load and micro Vickers hardness tests
where the principal limitation will arise in the measurement of the diagonals of the in-
dentation. In industrial tests, carried out in accordance with this part of IS0 6507, the
accuracy of determination of the mean diagonal is unlikely to be better than
f 0,001 mm. The corresponding uncertainty in the hardness value would be, for
example, very roughly 20 % HV for a diagonal length of 0,010 mm.
..,’
...
111
---------------------- Page: 5 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
---------------------- Page: 6 ----------------------
SIST ISO 6507-3:1995
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Metallic materials - Hardness test - Vickers test -
Part 3:
Less than HV 0,2
1 Scope
3.2 The Vickers hardness is denoted by the symbol HV
preceded by the hardness value and followed by:
This part of IS0 6507 specifies a method of determining a
Vickers hardness of less than HV 0,2 (test force less than a) a number representing the test force (see table 2);
1,961 N) for metallic materials.
b) the duration of loading, in seconds, if different from the
time specified in 7.4.
2 Normative references Examples:
640 HV 0,l = Vickers hardness of 640 determined with a test
The following standards contain provisions which, through
force of 0,980 7 N applied for 10 s to 15 s
reference in this text, constitute provisions of this part of
IS0 6507. At the time of publication, the editions indicated
640 HV 0,1120 = Vickers hardness of 640 determined with a
were valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to
test force of 0,980 7 N applied for 20 s
agreements based on this part of IS0 6507 are encouraged to
investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions
of the standards listed below. Members of IEC and IS0 main-
tain registers of currently valid International Standards.
4 Principle
IS0 6507-1 : 1982, Metallic materials - Hardness test -
Forcing a diamond indenter in the form of a right pyramid with
Vickers test - Part I: HV 5 to HV 100.
a square base and with a specified angle between opposite
faces at the vertex into the surface of a test piece and measur-
IS0 6507-2 : 1983, Metallic materials - Hardness test -
ing the diagonals of the indentation left in the surface after
Vickers test - Part 2: HV 0,2 to less than HV 5.
removal of the test force, F (see figure 1).
The Vickers hardness is porportional to the number obtained by
dividing the test force
...
IS0
NORME
6507-3
I NTER NATIONALE
Première édition
1989-1 1-01
Matériaux métalliques - Essai de dureté -
Essai Vickers -
Partie 3 :
Inférieure à HV 0,2
Metallic materials - Hardness test - Vickers test -
Part 3 : Less than HV 0,2
Numéro de référence
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (FI
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I‘ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale IS0 6507-3 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 164,
Essais mécaniques des métaux.
L’ISO 6507 comprend les parties suivantes présentées sous le titre général Matériaux
métalliques - Essai de dureté - Essai Vickers :
- Partie 1: HV 5 à HV 100
- Partie 2: HV 0,2 à HV 5 exclu
- Partie 3: Inférieure à HV 0,2
L’annexe A fait partie intégrante de la présente partie de I’ISO 6507. L’annexe B est
donnée uniquement à titre d’information.
O IS0 1989
Droits de reproduction réservés. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite ni
utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l‘éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 O CH-I211 Genève 20 O Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
IS0 6507-3 : 1989
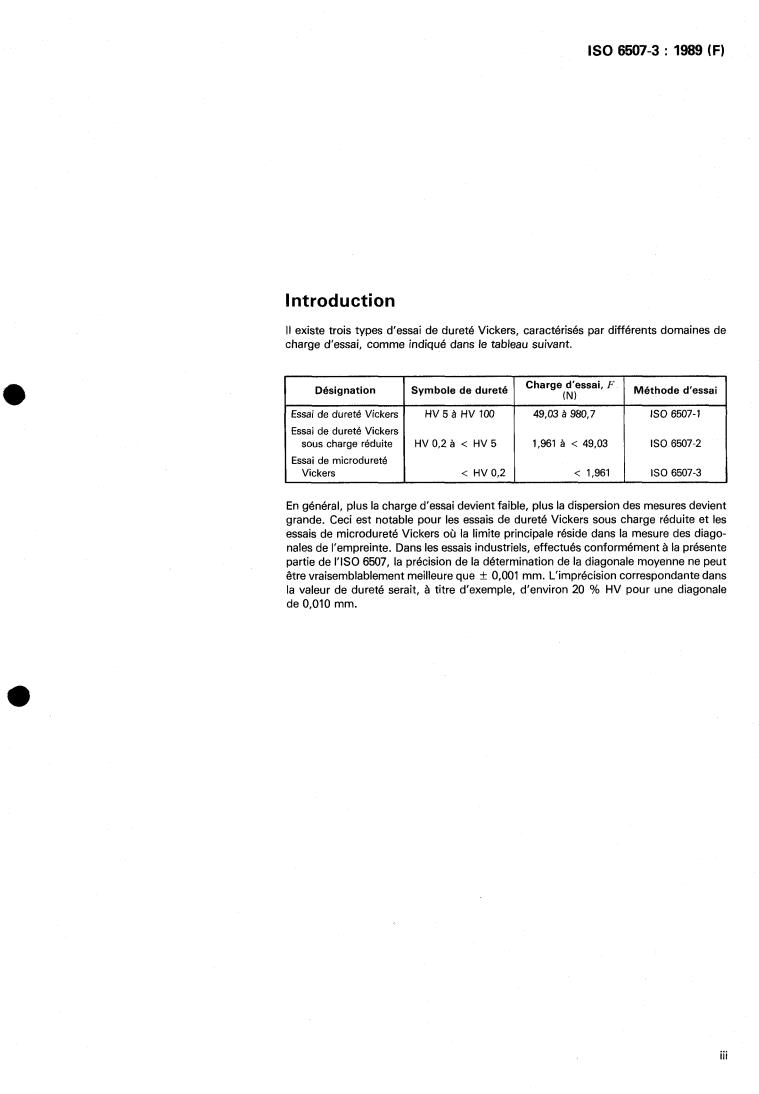
Introduction
Il existe trois types d‘essai de dureté Vickers, caractérisés par différents domaines de
charge d’essai, comme indiqué dans le tableau suivant.
I Désignation I Symbole de dureté I Charge d’essai, I Méthode d‘essai
(N) I
Essai de dureté Vickers HV 5 à HV 100 49,03 à 980.7 IS0 6507-1
Essai de dureté Vickers
SOUS charge réduite HV 0,2 à < HV 5 1,961 à < 49,03 IS0 6507-2
Essai de microdureté
Vickers < HV 0.2 < 1,961 IS0 6507-3
En général, plus la charge d’essai devient faible, plus la dispersion des mesures devient
grande. Ceci est notable pour les essais de dureté Vickers sous charge réduite et les
essais de microdureté Vickers où la limite principale réside dans la mesure des diago-
nales de l‘empreinte. Dans les essais industriels, effectués conformément à la présente
partie de I’ISO 6507, la précision de la détermination de la diagonale moyenne ne peut
f 0,001 mm. L‘imprécision correspondante dans
être vraisemblablement meilleure que
la valeur de dureté serait, à titre d’exemple, d’environ 20 % HV pour une diagonale
de 0,010 mm.
iii
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
NORM E I NTE R NAT1 ON ALE IS0 6507-3 : 1989 (F)
Partie 3:
Inférieure à HV 0,2
1 Domaine d'application 3.2 La dureté Vickers est désignée par le symbole HV pré-
cédé par la valeur de dureté et complété par
La présente partie de I'ISO 6507 prescrit une méthode pour
l'essai de dureté Vickers inférieure à HV 0.2 (charge d'essai ai un nombre représentant la charge d'essai (voir
inférieure à 1,961 NI pour les matériaux métalliques.
tableau 2);
b) la durée d'application de la charge, en secondes, si elle
diffère du temps prescrit en 7.4.
0
2 Références normatives
EXEMPLES
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions qui, par
640 HV 0,l = Dureté Vickers de 640, déterminée sous une
suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des disposi-
charge d'essai de 0,980 7 N appliquée
tions valables pour la présente partie de I'ISO 6507. Au moment
durant 10 s à 15 s
de la publication, les éditions indiquées étaient en vigueur.
Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties prenantes des
640 HV 0,1120 = Dureté Vickers de 640, déterminée sous une
accords fondés sur la présente partie de I'ISO 6507 sont invitées
charge d'essai de 0,980 7 N appliquée
à rechercher la possibilité d'appliquer les éditions les plus récen-
durant 20 s
tes des normes indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CE1 et de
I'ISO possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en
vigueur à un moment donné.
4 Principe
IS0 6507-1 : 1982, Matériauxmétalliques - Essaide dureté -
Essai Vickers - Partie I: HV 5 à HV 100.
Impression, à la surface d'une éprouvette, d'un pénétrateur en
forme de pyramide droite à base carrée, d'angle au sommet
IS0 6507-2 : 1983, Matériaux métalliques - Essai de dureté -
prescrit, et mesurage des diagonales de l'empreinte laissée sur
Essai Vickers - Partie 2: HV 0.2 à HV 5 exclu.
la surface après enlèvement de la charge d'essai F (voir
1).
figure
La dureté Vickers est proportionnelle au quotient de la charge
0 3 Symboles et désignations
d'essai par l'aire de l'empreinte qui est considérée comme une
pyramide droite à base carrée et ayant au sommet le même
Voir tableau 1 et figures 1 et 2.
3.1 angle que le pénétrateur.
Tableau 1
5 Appareillage
Symbole Désignation
5.1 Machine d'essai, permettant l'application d'une charge
pénétrateur pyramidal (136O)
d'essai prédéterminée ou d'autres charges inférieures à
F Charge d'essai, en newtons
1,961 N.
d Moyenne arithmétique, en millimètres, des deux
diagonales d, et d2
Pénétrateur: diamant de la forme d'une pyramide droite
5.2
HV Dureté Vickers
à base carrée.
Charge d'essai
= Constante x -
Aire de l'empreinte
136O
2 F.sin -
6 Éprouvette
2 F
= 0,102 x -- = 0,189 1 x -
d2 d*
6.1 L'essai doit être effectué sur une surface lisse et plane,
I l
NOTE -
...




Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.