ASTM C1508-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Bromine and Chlorine in UF6 and Uranyl Nitrate by X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectroscopy
Standard Test Method for Determination of Bromine and Chlorine in UF<inf>6</inf> and Uranyl Nitrate by X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectroscopy
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The method is designed to show whether or not the tested materials meet the specifications as given in Specifications C787 and C788.
SCOPE
1.1 This method covers the determination of bromine (Br) and chlorine (Cl) in uranium hexafluoride (UF6) and uranyl nitrate solution. The method as written covers the determination of bromine in UF6 over the concentration range of 0.2 to 8 µg/g, uranium basis. The chlorine in UF6 can be determined over the range of 4 to 160 µg/g, uranium basis. Higher concentrations may be covered by appropriate dilutions. The detection limit for Br is 0.2 µg/g uranium basis and for Cl is 4 µg/g uranium basis.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1508 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Bromine and Chlorine in UF and Uranyl
6
1
Nitrate by X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectroscopy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1508; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C788Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solu-
tion or Crystals
1.1 This method covers the determination of bromine (Br)
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
and chlorine (Cl) in uranium hexafluoride (UF ) and uranyl
6
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
nitrate solution. The method as written covers the determina-
tion of bromine in UF over the concentration range of 0.2 to
6
3. Terminology
8 µg/g, uranium basis. The chlorine in UF can be determined
6
over the range of 4 to 160 µg/g, uranium basis. Higher
3.1 Definitions:
concentrations may be covered by appropriate dilutions. The
3.1.1 For definitions of terms relating to the nuclear fuel
detection limit for Br is 0.2 µg/g uranium basis and for Cl is 4
cycle, refer to Terminology C859.
µg/g uranium basis.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the 4. Summary of Test Method
standard.
4.1 Asample of hydrolyzed UF (uranyl fluoride) or uranyl
6
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
nitratesolutionistreatedwithsodiumnitritetoreduceoxidized
tions and equipment. This standard does not purport to address
formsofbromineandchlorine(bromatesandchlorates)totheir
all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is
respectivehalideions.Additionofsilvernitrateprecipitatesthe
the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
silver halides. Spike recoveries can be improved by the
appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and
addition of potassium iodide causing coprecipitation of the
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
halides. The halides are collected on filter paper and are
use.
analyzed by X-ray fluorescence using two different crystal/
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
detector systems.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
5. Significance and Use
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5.1 The method is designed to show whether or not the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
tested materials meet the specifications as given in Specifica-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
tions C787 and C788.
2. Referenced Documents
2
6. Interferences
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C761Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric,
6.1 Plastic equipment must be used throughout the method
Spectrochemical,Nuclear,andRadiochemicalAnalysisof
for uranyl fluoride as the hydrofluoric acid in the uranyl
Uranium Hexafluoride
fluoride leaches chloride from glassware causing a high bias.
C787Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride for Enrich-
ment 6.2 Low recoveries may occur as the precipitate can be
difficult to transfer quantitatively to the filter paper. A surfac-
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC26onNuclear tant can be added (optional step) to minimize the adhesion of
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
the precipitate to the walls of the beakers and the funnel.
Test.
Current edition approved June 1, 2018. Published June 2018. Originally
7. Apparatus
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C1508–01 (2011).
DOI: 10.1520/C1508-18.
2 7.1 X-Ray Spectrometer, appropriate for the intended use.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
7.2 Plastic Vacuum Filtration Apparatus, for 47 mm diam-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. eter filter paper.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1508 − 18
3
7.3 Filter Paper, 0.45 micron, 47 mm diameter. 8.15 Sodium Chloride, NaCl.
7.4 Beakers, polypropylene, 250 mL. 8.16 Sodium Chloride Solution, 1000 mg Cl/L. Dissolve
1.648 g NaCl (dried at 110° C for 1 hour ) in water and dilute
7.5 Stirring Rods, plastic or Teflon.
to 1 litre in a volumetric flask.
7.6 X-ray Sample Support, Rings. Inner diameter approxi-
8.17 Sp
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1508 − 01 (Reapproved 2011) C1508 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Bromine and Chlorine in UF and Uranyl
6
1
Nitrate by X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectroscopy
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1508; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This method covers the determination of bromine (Br) and chlorine (Cl) in uranium hexafluoride (UF ) and uranyl nitrate
6
solution. The method as written covers the determination of bromine in UF over the concentration range of 0.2 to 8 μg/g, uranium
6
basis. The chlorine in UF can be determined over the range of 4 to 160 μg/g, uranium basis. Higher concentrations may be covered
6
by appropriate dilutions. The detection limit for Br is 0.2 μg/g uranium basis and for Cl is 4 μg/g uranium basis.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C761 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and Radiochemical Analysis of Uranium
Hexafluoride
C787 Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride for Enrichment
C788 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solution or Crystals
C1118C859 Guide for Selecting Components for Wavelength-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) SystemsTerminology
Relating to Nuclear Materials (Withdrawn 2011)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms relating to the nuclear fuel cycle, refer to Terminology C859.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A sample of hydrolyzed UF (uranyl fluoride) or uranyl nitrate solution is treated with sodium nitrite to reduce oxidized
6
forms of bromine and chlorine (bromates and chlorates) to their respective halide ions. Addition of silver nitrate precipitates the
silver halides. Spike recoveries can be improved by the addition of potassium iodide causing coprecipitation of the halides. The
halides are collected on filter paper and are analyzed by X-ray fluorescence using two different crystal/detector systems.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The method is designed to show whether or not the tested materials meet the specifications as given in Specifications C787
and C788.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of Test.
Current edition approved June 1, 2011June 1, 2018. Published June 2011June 2018. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
C1508 – 01 (2011).(2006). DOI: 10.1520/C1508-01R1.10.1520/C1508-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1508 − 18
6. Interferences
6.1 Plastic equipment must be used throughout the method for uranyl fluoride as the hydrofluoric acid in the uranyl fluoride
leaches chloride from glassware causing a high bias.
6.2 Low recoveries may occur as the precipitate can be difficult to transfer quantitatively to the filter paper. A surfactant can be
added (optional step) to minimize the adhesion of the precipitate to the walls of the beakers and the funnel.
7. Apparatus
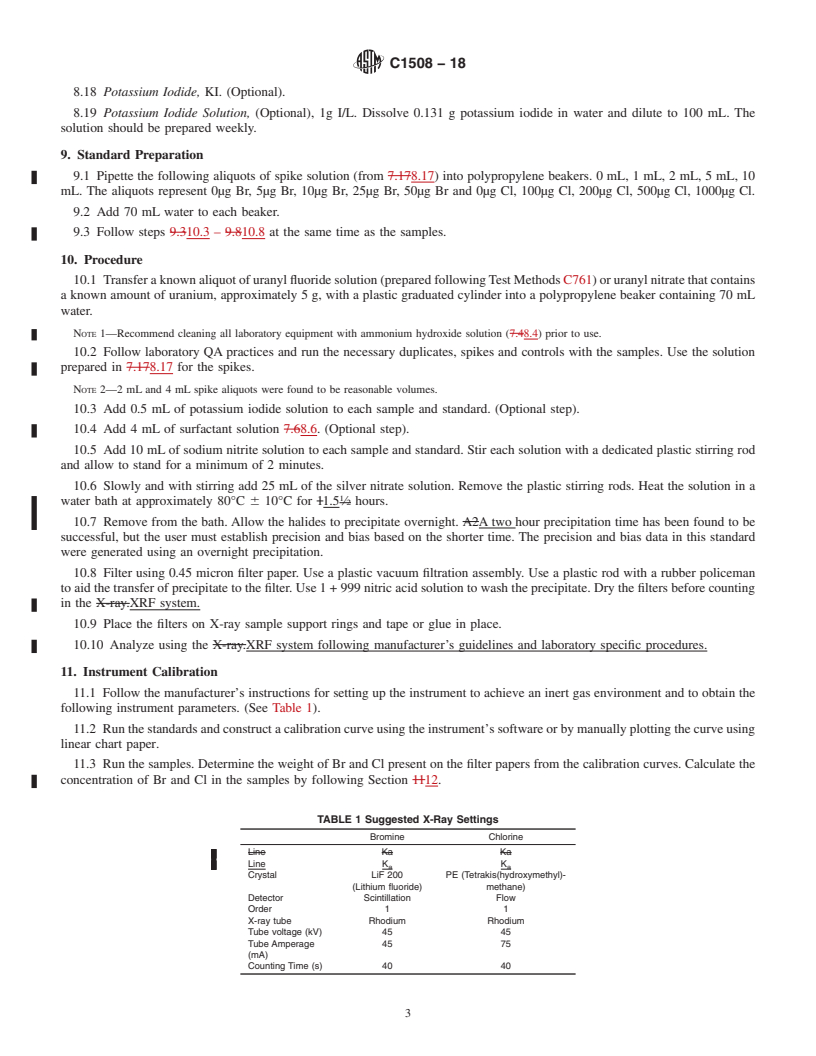
7.1 X-Ray Spectrometer, see Guide appropriate C1118for the selection of the X-ray Spectrometer.intended use.
7.2 Plastic Vacuum Filtrati
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.