ASTM D5273-92(2012)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Analysis of Propylene Concentrates
Standard Guide for Analysis of Propylene Concentrates
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is intended to provide information on the likely composition of propylene concentrates and on probable ways to test them. Since there are currently no ASTM test methods for determining all components of interest, this guide provides information on other potentially available test methods.
4.2 Although this guide is not to be used for specifications, it can provide a starting point for parties to develop mutually agreed upon specifications which meet their respective requirements. It can also be used as a starting point in finding suitable test methods for determining various components of propylene.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers a list of the major grades of propylene concentrates produced in North America. It includes possible components and test methods, both ASTM and other, either actually used, or believed to be in use, to test for these properties. This guide is not intended to be used or construed as a set of specifications for any grade of propylene concentrate.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5273 − 92 (Reapproved 2012)
Standard Guide for
Analysis of Propylene Concentrates
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5273; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope (Potentiometric Method)
D3246 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Gas by Oxida-
1.1 This guide covers a list of the major grades of propylene
tive Microcoulometry
concentrates produced in North America. It includes possible
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
components and test methods, both ASTM and other, either
ing Piston Cylinder
actually used, or believed to be in use, to test for these
D4178 Practice for Calibrating Moisture Analyzers
properties. This guide is not intended to be used or construed
D4468 Test Method for Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by
as a set of specifications for any grade of propylene concen-
Hydrogenolysis and Rateometric Colorimetry
trate.
D4629 Test Method for Trace Nitrogen in Liquid Petroleum
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
HydrocarbonsbySyringe/InletOxidativeCombustionand
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Chemiluminescence Detection
standard.
D4864 Test Method for Determination of Traces of Metha-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
nol in Propylene Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3. Terminology
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1 Definitions:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.1 outaging, n—practice of removing a portion of liquid
contents from a conventional sampling cylinder after filling to
2. Referenced Documents
provide expansion room.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.2 propylene concentrate, n—hydrocarbon product con-
D2163 Test Method for Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum
taining more than 50 % propylene.
(LP) Gases and Propene Concentrates by Gas Chromatog-
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Gradesofpropyleneconcentrateslisted
raphy
inthisguideare:polymer,99.0 %minimumpropylenecontent;
D2384 Test Methods for Traces of Volatile Chlorides in
chemical, 92.0 %; and refinery, 60 %.
Butane-Butene Mixtures
3.2 Abbreviations:
D2504 Test Method for Noncondensable Gases in C and
3.2.1 AgDDC, n—silver diethyldithiocarbamate.
Lighter Hydrocarbon Products by Gas Chromatography
D2505 Test Method for Ethylene, Other Hydrocarbons, and 3.2.2 GC, n—gas chromatograph.
Carbon Dioxide in High-Purity Ethylene by Gas Chroma-
3.2.3 GC-AED, n—gas chromatography atomic emission
tography
detector.
D2712 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Traces in Propylene
3.2.4 GC-ECD, n—gas chromatography electron capture
Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
detector.
D3227 Test Method for (Thiol Mercaptan) Sulfur in
3.2.5 GC-FPD, n—gas chromatography flame photometric
Gasoline, Kerosine,Aviation Turbine, and Distillate Fuels
detector.
3.2.6 GC-PID, n—gas chromatography photoionization de-
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum tector.
ProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD02.D0.03
3.2.7 GC-SCD, n—gas chromatography sulfur chemilumi-
on Propylene.
nescent detector.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2012. Published December 2012. Originally
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D5273–92(2007).
3.2.8 IC, n—ion chromatography.
DOI: 10.1520/D5273-92R12.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.2.9 ICP-MS, n—inductively coupled plasma-mass spec-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
trometry.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 3.2.10 LPG or LP gases, n—liquefied petroleum gas.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5273 − 92 (2012)
4. Significance and Use recapture these light ends in the liquid phases of the sample,
such as repressurization of the cylinder contents with an inert
4.1 This guide is intended to provide information on the
gas, will not completely effect their recovery, especially the
likely composition of propylene concentrates and on probable
permanent gases. However, the loss is not significant to some
ways to test them. Since there are currently no ASTM test
users.
methods for determining all components of interest, this guide
provides information on other potentially available test meth- 5.4 Vaporization Methods—Vaporization of the sample, ei-
ods. ther at the source or in the lab prior to analysis, can cause loss
of heavier components, if present, and concentration of lighter
4.2 Although this guide is not to be used for specifications,
ones. Test Method D2712 describes a low pressure vaporiza-
it can provide a starting point for parties to develop mutually
tion sampling technique that is suitable to determine trace
agreed upon specifications which meet their respective require-
compounds through butadiene.
ments. It can also be used as a starting point in finding suitable
testmethodsfordeterminingvariouscomponentsofpropylene. 5.5 Reactive and Polar Components:
5.5.1 Determination of reactive components, such as certain
5. Sampling
sulfur compounds and arsine, is generally believed to require
5.1 General—Sample propylene concentrates are to be ana-
special sample containers, such as TFE-fluorocarbon lined
lyzed for trace components by a technique that minimizes or
cylinders, or containers that have been specially passivated.
eliminates losses of light components and concentration of
5.5.2 Itisverydifficulttoobtainavalidsampletodetermine
heavy ones. The sections below list some different sampling
traces of polar compounds, such as water and ammonia, in the
methods and principles. However, it is not the intent of this
lab. Online analyzers, if available, or sorption of the analyte at
guide to list procedures that are applicable to all sampling
the sample source for subsequent lab analysis, are believed to
situations.Itisstronglyrecommendedthatsamplesbeobtained
yield the most accurate results.
under the supervision of a person with wide knowledge and
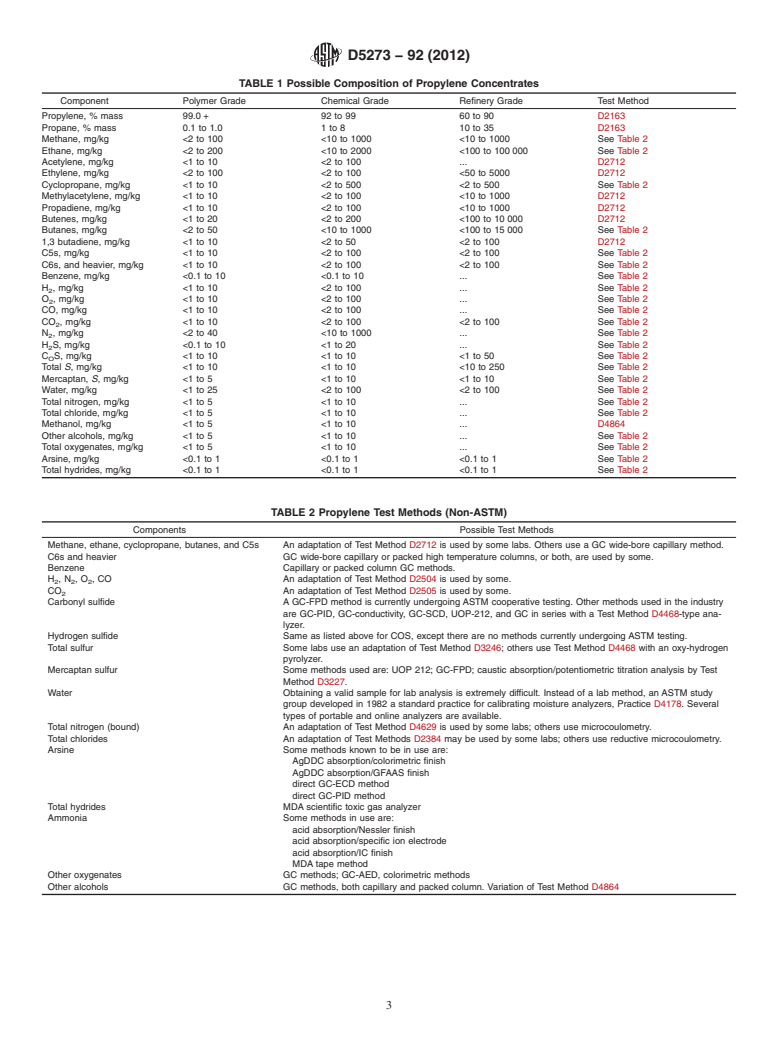
6. Composition and Test Methods
experience in sampling olefinic liquefied petroleum gases.
Also, even though this guide does not address the loc
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.