ASTM D2729-17
(Specification)Standard Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Sewer Pipe and Fittings
Standard Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Sewer Pipe and Fittings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, chemical resistance, and joint tightness of poly (vinyl chloride) (PVC) sewer and drain pipe and fittings. The pipe shall be made from virgin cell 12164 with a certain minimum tensile strength, 12454 or 12454 poly(vinyl chloride) compounds. The fittings shall be made from virgin poly(vinyl chloride) compounds of cell classification PVC 12454, PVC 12454, or PVC 13343. Compounds that have different cell classification because one or more properties are superior to those of the specified compounds are also acceptable. In order to determine the overall performance of the pipes and fittings, the following tests shall be done: flattening test, joint tightness test, and perforation test. The pipe and fittings shall be homogeneous throughout and free from visible cracks, holes, foreign inclusions, or other injurious defects. The pipe shall be as uniform as commercially practical in color, opacity, density, and other physical properties.
SCOPE
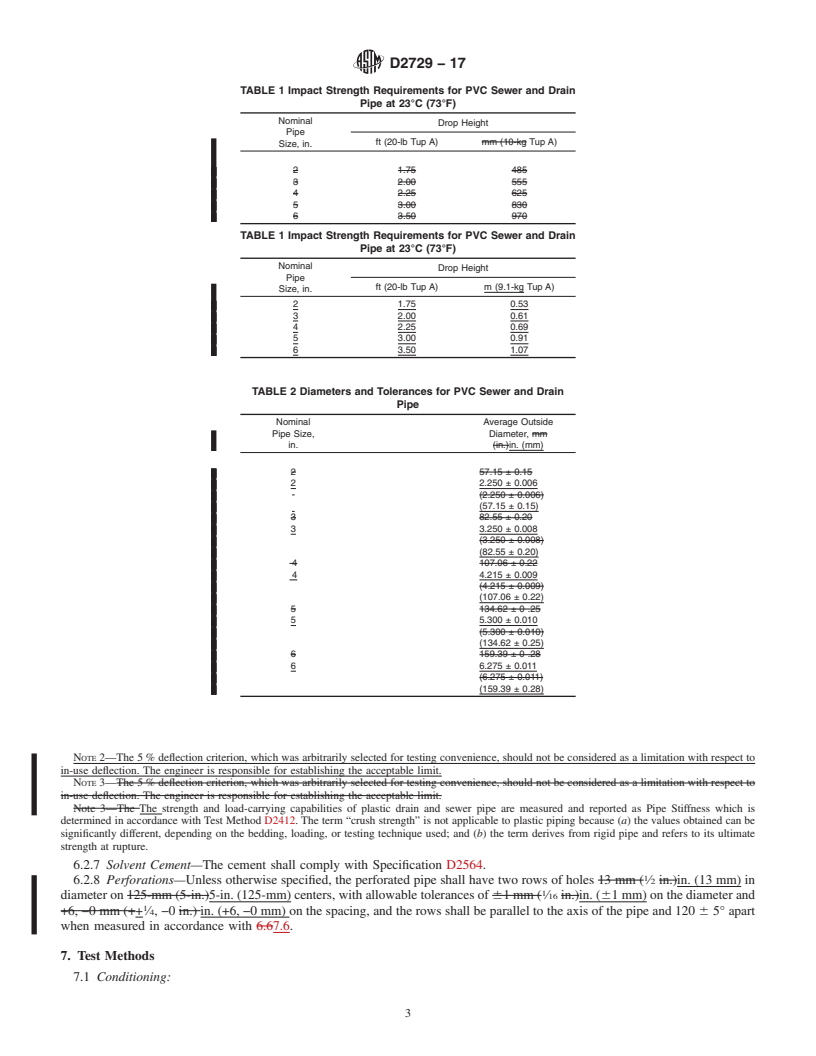
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, chemical resistance, and joint tightness of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) sewer and drain pipe and fittings. Perforated pipe is also covered; the joint tightness test is not applicable for perforated pipe. A form of marking to indicate compliance with this specification is also included.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2729 −17
Standard Specification for
1
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Sewer Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2729; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D1784Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods
(CPVC) Compounds
for materials, dimensions, workmanship, chemical resistance,
D2122Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
and joint tightness of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) sewer and
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
drainpipeandfittings.Perforatedpipeisalsocovered;thejoint
D2152Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded
tightness test is not applicable for perforated pipe. A form of
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
marking to indicate compliance with this specification is also
Acetone Immersion
included.
D2321PracticeforUndergroundInstallationofThermoplas-
1.2 Thetextofthisspecificationreferencesnotes,footnotes,
tic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
D2412Test Method for Determination of External Loading
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
D2444Practice for Determination of the Impact Resistance
of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for (Falling Weight)
D2564Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl
information only.
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
F412Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
2.2 Federal Standard:
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
3
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
2.3 Military Standard:
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
3
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Terminology
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1 Definitions—Definitions used are in accordance with
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Terminology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Terminology D1600, unless otherwise specified.The abbrevia-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
tion for poly(vinyl chloride) is PVC.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.1 perforated pipe—pipe having holes cut through the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
wall along its length.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1 The pipe and fittings in this specification are designed
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
andhavethephysical,chemical,andotherpropertiesforsewer
D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
and drainage applications outside the building. The pipe is not
tics
intended for use as public or municipal collector sewers. The
following lists the typical applications for the sewer and drain
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
pipe:
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer.
4.1.1 Building sewers and underground drains—standard,
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2017. Published November 2017. Originally
4.1.2 Storm drainage—standard and perforated,
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D2729–11. DOI:
10.1520/D2729-17. 4.1.3 House connections to septic tanks—standard,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
the ASTM website. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2729−17
4.1.4 Leaching system piping for
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2729 − 11 D2729 − 17
Standard Specification for
1
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Sewer Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2729; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, chemical resistance, and
joint tightness of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) sewer and drain pipe and fittings. Perforated pipe is also covered; the joint tightness
test is not applicable for perforated pipe. A form of marking to indicate compliance with this specification is also included.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.4 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 67, of this specification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC)
Compounds
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
D2152 Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone
Immersion
D2321 Practice for Underground Installation of Thermoplastic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
D2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resistance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a Tup (Falling
Weight)
D2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
2.2 Federal Standard:
3
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
2.3 Military Standard:
3
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2011Sept. 1, 2017. Published February 2011November 2017. Originally approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 20032011
as D2729 – 03.D2729 – 11. DOI: 10.1520/D2729-11.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094,
Attn: NPODS.http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2729 − 17
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions used are in accordance with Terminology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with
Terminology D1600, unless otherwise specified. The abbreviation for poly(vinyl chloride) is PVC.
3.1.1 perforated pipe—Pipe having perforations is called perforated pipe; without perforations it is called standard pipe. pipe
having
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.