ASTM D5405/D5405M-98(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Conducting Time-to-Failure (Creep-Rupture) Tests of Joints Fabricated from Nonbituminous Organic Roof Membrane Material
Standard Test Method for Conducting Time-to-Failure (Creep-Rupture) Tests of Joints Fabricated from Nonbituminous Organic Roof Membrane Material
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 An important factor affecting the performance of joints of nonbituminous membranes is their ability to remain bonded over the membrane's expected service life. Time-to-failure tests provide a means of characterizing the behavior of joints under constant load over time.
5.2 Creep is a sensitive index of rheological properties that depend on material, load, temperature, and time. Time-to-failure data that are obtained over a relatively short time period can evaluate one factor affecting a joint's ability to withstand static loading over a relatively long time period.
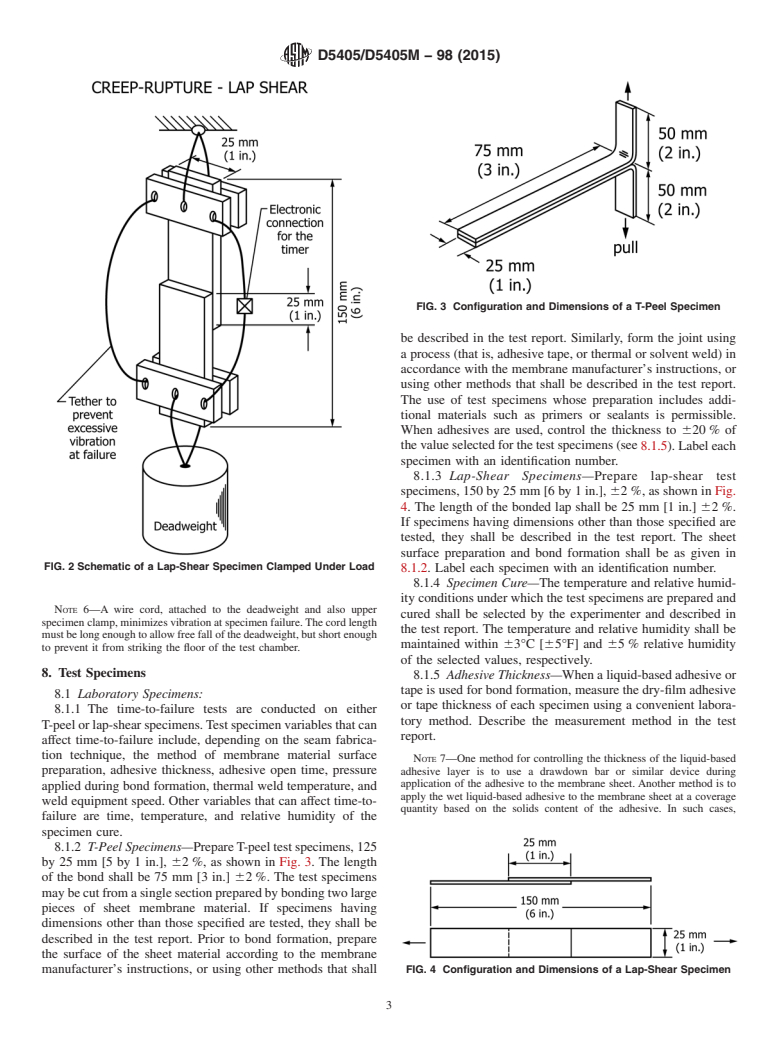
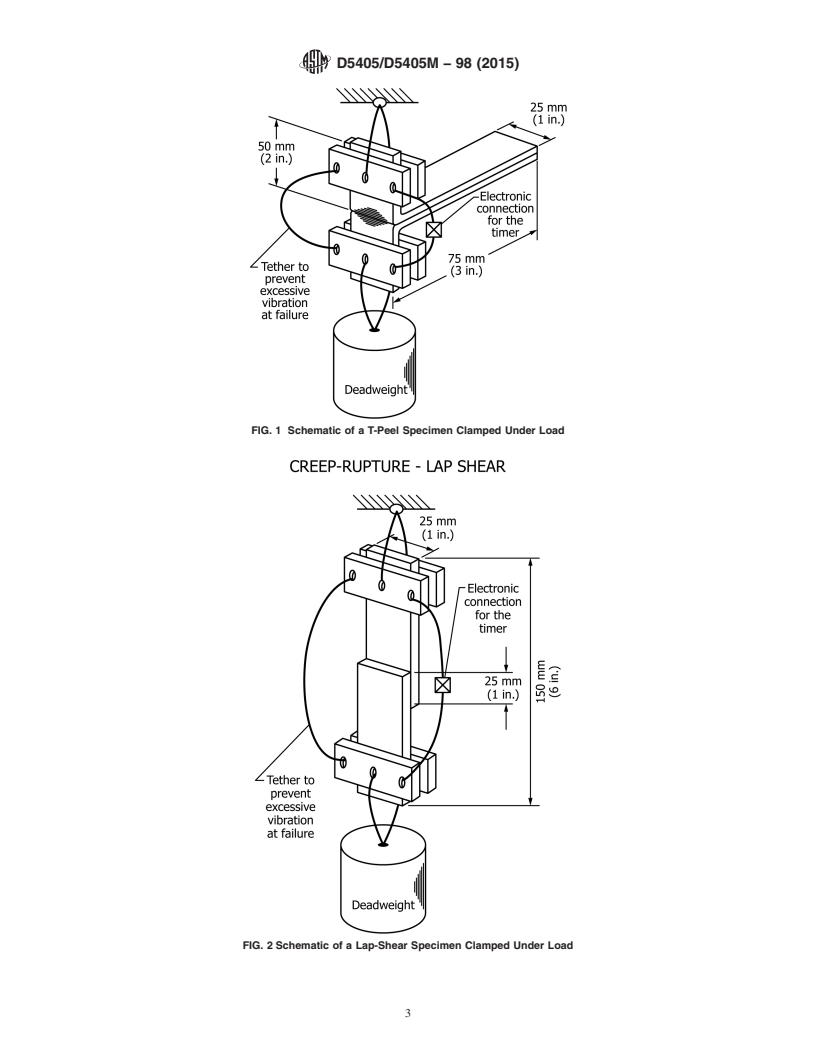
5.3 Time-to-failure data for joints of nonbituminous organic roof membrane specimens can be used for the following: (1) to provide a measure of the load-carrying ability of the joint as a function of time at various levels of load, temperature, and relative humidity; (2) to characterize the joint with regard to factors affecting performance, such as surface preparation of the adherend, solvent-based adhesive thickness and open time, environment during adhesive application and cure, and temperature of thermal welding processes; and (3) to compare the effects of different bonding processes or adhesive bonding materials on joint performance.
5.4 While it is considered that the results obtained by this laboratory test may afford a measure of the performance of seams in service, provided that load, temperature, and humidity conditions are known, no direct correlation has been established.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers laboratory determination of the time-to-failure (creep-rupture) of joints fabricated from nonbituminous organic roof membrane material. The test method covers both T-peel and lap-shear joints subjected to constant tensile load under controlled environmental conditions. The joints, made from either unreinforced or fabric-reinforced membrane material, are prepared in the laboratory or sampled from roofs in service.
1.2 Sheet materials from which the joints are fabricated include vulcanized rubbers, nonvulcanized polymeric sheets, and thermoplastics. The bonding methods for joint formation include the use of liquid-based adhesives, preformed tapes, and thermal and solvent weld processes.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5405/D5405M − 98 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Conducting Time-to-Failure (Creep-Rupture) Tests of Joints
Fabricated from Nonbituminous Organic Roof Membrane
1
Material
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5405/D5405M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1079 Terminology Relating to Roofing and Waterproofing
D1876 Test Method for Peel Resistance of Adhesives (T-
1.1 This test method covers laboratory determination of the
Peel Test)
time-to-failure (creep-rupture) of joints fabricated from nonbi-
tuminous organic roof membrane material. The test method
3. Terminology
covers both T-peel and lap-shear joints subjected to constant
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
tensile load under controlled environmental conditions. The
method, refer to Terminology D907 and D1079.
joints, made from either unreinforced or fabric-reinforced
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
membrane material, are prepared in the laboratory or sampled
3.2.1 creep-rupture test—a test that measures the time-to-
from roofs in service.
failure of a specimen subjected to a constant load; progressive
1.2 Sheet materials from which the joints are fabricated
specimen deformation may also be measured.
include vulcanized rubbers, nonvulcanized polymeric sheets,
3.2.2 failure—rupture of the bond resulting in complete
and thermoplastics. The bonding methods for joint formation
separation of its adherends under the test conditions; or,
includetheuseofliquid-basedadhesives,preformedtapes,and
alternatively, rupture of the membrane material away from the
thermal and solvent weld processes.
bonded section of the test specimen (that is, material rupture).
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.2.3 time-to-failure—the period of time beginning when a
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
joint specimen is placed under load and ending when failure
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
occurs.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
4. Summary of Test Method
with the standard.
4.1 This test method is a creep-rupture test without mea-
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
surement of specimen deformation. The time-to-failure, in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
hours, of joints fabricated from nonbituminous organic roof
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
membrane materials is measured when subject to constant
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
deadweight loads under controlled temperature and humidity
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
conditions.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 An important factor affecting the performance of joints
D816 Test Methods for Rubber Cements
of nonbituminous membranes is their ability to remain bonded
D907 Terminology of Adhesives
over the membrane’s expected service life. Time-to-failure
tests provide a means of characterizing the behavior of joints
under constant load over time.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D08 on Roofing
5.2 Creep is a sensitive index of rheological properties that
and Waterproofing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D08.18 on
Nonbituminous Organic Roof Coverings.
depend on material, load, temperature, and time. Time-to-
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015. Published November 2015. Originally
failure data that are obtained over a relatively short time period
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D5405/D5405M – 98
ɛ1
can evaluate one factor affecting a joint’s ability to withstand
(2011) . DOI: 10.1520/D5405_D5405M-98R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or static loading over a relatively long time period.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.3 Time-to-failure data for joints of nonbituminous organic
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. roof membrane specimens can be used for the following: (1)to
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5405/D5405M − 98 (2015)
provide a measure of the load-carrying ability of the joint as a
function of time at various levels of load, temperatur
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D5405/D5405M − 98 (Reapproved 2011) D5405/D5405M − 98 (Reapproved
2015)
Standard Test Method for
Conducting Time-to-Failure (Creep-Rupture) Tests of Joints
Fabricated from Nonbituminous Organic Roof Membrane
1
Material
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5405/D5405M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Units information was editorially revised in June 2011.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers laboratory determination of the time-to-failure (creep-rupture) of joints fabricated from
nonbituminous organic roof membrane material. The test method covers both T-peel and lap-shear joints subjected to constant
tensile load under controlled environmental conditions. The joints, made from either unreinforced or fabric-reinforced membrane
material, are prepared in the laboratory or sampled from roofs in service.
1.2 Sheet materials from which the joints are fabricated include vulcanized rubbers, nonvulcanized polymeric sheets, and
thermoplastics. The bonding methods for joint formation include the use of liquid-based adhesives, preformed tapes, and thermal
and solvent weld processes.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D816 Test Methods for Rubber Cements
D907 Terminology of Adhesives
D1079 Terminology Relating to Roofing and Waterproofing
D1876 Test Method for Peel Resistance of Adhesives (T-Peel Test)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D907 and D1079.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 creep-rupture test—a test that measures the time-to-failure of a specimen subjected to a constant load; progressive
specimen deformation may also be measured.
3.2.2 failure—rupture of the bond resulting in complete separation of its adherends under the test conditions; or, alternatively,
rupture of the membrane material away from the bonded section of the test specimen (that is, material rupture).
3.2.3 time-to-failure—the period of time beginning when a joint specimen is placed under load and ending when failure occurs.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D08 on Roofing and Waterproofing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D08.18 on
Nonbituminous Organic Roof Coverings.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011Nov. 1, 2015. Published June 2011November 2015. Originally approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 20042011 as
ɛ1
D5405 – 98D5405/D5405M – 98 (2011) (2004). . DOI: 10.1520/D5405_D5405M-98R11E01.10.1520/D5405_D5405M-98R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5405/D5405M − 98 (2015)
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This test method is a creep-rupture test without measurement of specimen deformation. The time-to-failure, in hours, of
joints fabricated from nonbituminous organic roof membrane materials is measured when subject to constant deadweight loads
under controlled temperature and humidity conditions.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 An important factor affecting the performance of joints of nonbituminous membranes is their ability to remain bonded over
the membrane’s expected service life. Time-to-failure tests provide a means of characterizing the behavior of joints under constant
load over time.
5.2 Creep is a sensitive index of rheological properties that depend on material, load, te
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.