ASTM F438-99
(Specification)Standard Specification for Socket-Type Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Plastic Pipe Fittings, Schedule 40
Standard Specification for Socket-Type Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Plastic Pipe Fittings, Schedule 40
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride) (CPVC) Schedule 40 socket-type pipe fittings. Included are requirements for materials, workmanship, dimensions, and burst pressure.
Note 1--The CPVC fittings covered by this standard were covered previously in Specification D2466.
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only, which are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Due to inherent hazards associated with testing components and systems with compressed air or other compressed gases some manufacturers do not allow pneumatic testing of their products. Consult with specific product/component manufacturers for their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.
Note 2--Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases contain large amounts of stored energy which present serious saftey hazards should a system fail for any reason.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are given for information only.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 438 – 99 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Socket-Type Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Plastic
Pipe Fittings, Schedule 40
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 438; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope sure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
1.1 This specification covers chlorinated poly(vinyl chlo-
Plastics
ride) (CPVC) Schedule 40 socket-type pipe fittings. Included
D 1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
are requirements for materials, workmanship, dimensions, and
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
burst pressure.
(CPVC) Compounds
NOTE 1—The CPVC fittings covered by this standard were covered
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
previously in Specification D 2466.
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended
D 2749 Symbols for Dimensions of Plastic Pipe Fittings
for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only, which
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Due to
F 1498 Specification for Taper Pipe Threads 60° for Ther-
inherent hazards associated with testing components and sys-
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
tems with compressed air or other compressed gases some
2.2 Federal Standard:
manufacturers do not allow pneumatic testing of their products.
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
Consult with specific product/component manufacturers for
2.3 Military Standard:
their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
2.4 NSF Standard:
NOTE 2—Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related
contain large amounts of stored energy which present serious saftey
hazards should a system fail for any reason. Materials
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
3. Terminology
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
3.1 Definitions:
notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall
3.1.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D 1600,
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
unless otherwise indicated. The abbreviation for chlorinated
as the standard. The values in parentheses are given for
poly(vinyl chloride) is CPVC.
information only.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
4. Classification
test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
4.1 General—This specification covers Schedule 40 CPVC
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
pipe fittings, socket-type, intended for use with Iron Pipe Size
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
(IPS) outside-diameter plastic pipe.
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
4.1.1 Fittings covered by this specification are normally
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
molded. In-line fittings, such as couplings, unions, bushings,
tions prior to use.
caps, nipples, etc., shall be molded or machined from extruded
stock.
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.2 Fittings fabricated by backwelding are not included in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
this specification.
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 1599 Test Method for Short-Time Hydraulic Failure Pres-
1 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.10 on Fittings. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Current edition approved May 10, 1999. Published July 1999. Originally Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
published as part of D 2466 – 74. Last previous edition F 438 – 97. Available from the National Sanitation Foundation, P.O. Box 1468, Ann Arbor,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. MI 48106.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 438
5. Materials and Manufacture minimum burst pressure shown in Table 4.
6.3.2 Pressures shown are minimum burst pressures and do
5.1 This specification covers CPVC pipe fittings made from
not imply rated working pressures. The burst pressure shall be
compounds meeting the requirements of Class 23447 as
used only as an indication of quality.
defined in Specification D 1784.
NOTE 3—Mechanical strength, heat resistance, flammability, and
7. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
chemical resistance requirements are covered in Specification D 1784.
7.1 The fittings shall be homogeneous throughout and free
5.2 Rework Material—The manufacturers shall use only
of cracks, holes, foreign inclusions, or other defects. The
their own clean rework fitting material and the fittings pro-
fittings shall be as uniform as commercially practicable in
duced shall meet all the requirements of this specification.
color, opacity, density, and other physical properties.
6. Requirements
8. Test Methods
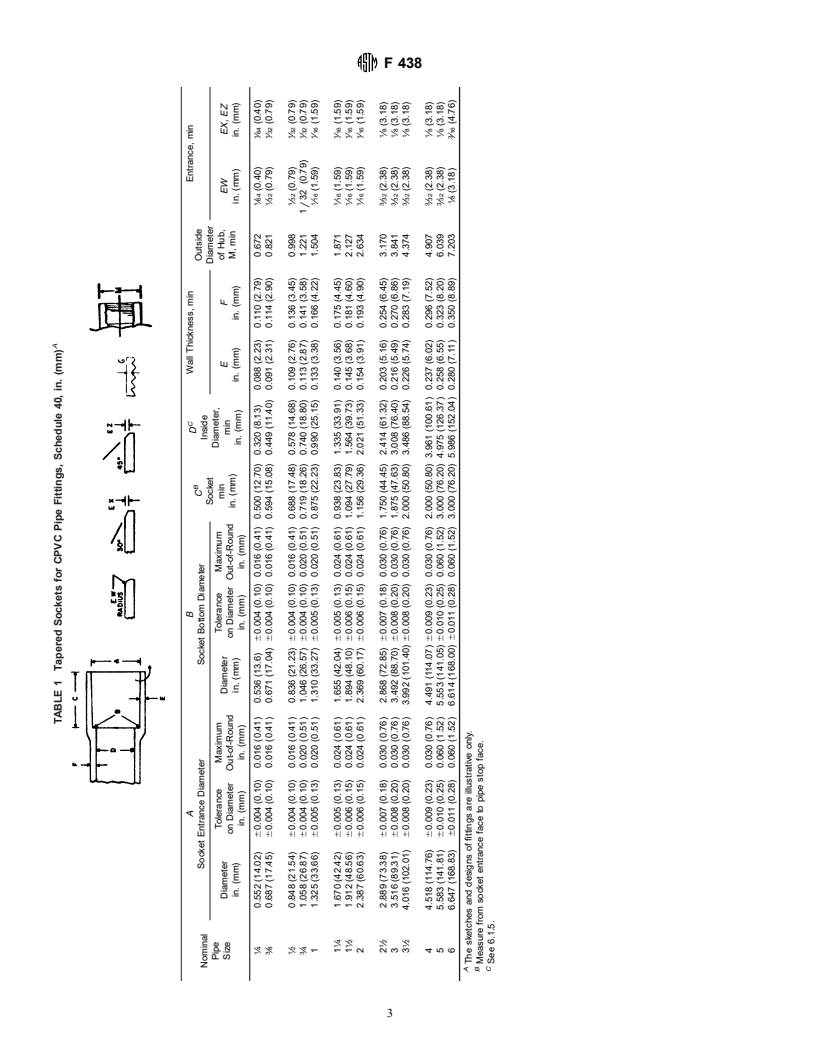
6.1 Dimensions and Tolerances: 8.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 73.4 6
6.1.1 Fitting sockets, inside diameters (waterways), mini-
3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less
mum wall thicknesses, and dimensions shall be as shown in than 40 h prior to test in accordance with Procedure A of
Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 when measured in accordance
Practice D 618, for those tests where conditioning is required.
with Test Method D 2122. 8.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the Standard Labora-
6.1.2 When multistep reducer bushings are cored out, the
tory Atmosphere of 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6 5%
inner socket shall be reinforced from the outer wall by a relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test meth-
minimum of three ribs extending from the top of the inner ods or in this specification.
socket in the deepest extremity of the coring. The transition 8.3 Sampling—A sufficient quantity of fittings as agreed
from D to DJ (Table 3) shall be straight, tapered as shown, or upon between the seller and the purchaser shall be selected at
radiused. A positive taper in the same direction of the taper in
random from each lot or shipment and tested to determine that
the socket on the outside diameter of the bushing is optional. the basic design is in conformance with this specification.
6.1.3 The maximum angular variation of any opening shall
NOTE 4—For individual orders or specifications where supplemental
be not more than ⁄2° off the true centerline axis.
tests are required, only those tests and numbers of tests specifically agreed
6.1.4 The minimum wall thickness of fittings shall be 125 %
upon between the purchaser and the seller need be conducted.
of the minimum wall thickness of the corresponding size of
8.4 Threads—All taper pipe threads shall be gaged in
Schedule 40 pipe for which they are designed to be used,
accordance with Specification F 1498.
except that for the socket, the wall thickness shall be at least
8.5 Burst Pressure—Determine the minimum burst pressure
equal to the minimum wall thickness of the corresponding size
in accordance with Test Method D 1599. The time of testing
of Schedule 40 pipe. For any threaded transition fitting the
each specimen shall be between 60 and 70 s.
minimum wall thickness of the threaded portion shall be at
8.5.1 Apparatus—Fittings shall be tested while held in a test
least equal to the thickness of material under the thread root of
jig constructed in such a manner as to seal the socket by means
threaded Schedule 80 pipe of the same size.
of O-rings, or gaskets but not to reinforce or support the
6.1.5 The minimum inside diameter of the fittings shall be
fittings, except where contact is necessary because of the shape
not less than the minimum specified inside diameter of the
of the fitting to keep the fitting in the test jig. Such contact shall
corresponding size of Schedule 40 pipe. Any fitting having a
be held to the minimum. The socket plug portion of the test
male thread shall have an internal diameter not larger than
fixture must extend one third to two thirds of the socket depth.
Schedule 80 pipe of the same size.
Failure of any part of the test apparatus does not constitute
6.1.6 Minimum dimensions have zero negative tolerance.
failure of the fittings.
Tolerances on other dimensions are shown in Table 1 and Table
3.
9. Retest and Rejection
6.2 Threads—For all fittings having taper pipe threads,
9.1 If the results of any test(s) do not meet the requirements
threads shall conform to Specification F 1498 and be gaged in
of this specification, the tests(s) shall be conducted again only
accordance with 8.4.
by agreement between the purchaser and seller. Under such
6.3 Burst Pressure:
agreement, minimum requirements shall not be lowered,
6.3.1 The minimum burst strength of the fittings shall be not
changed, or modified, nor shall specification limits be changed.
less than that calculated for the size and wall thickness of the
If upon retest, failure occurs, the quantity of product repre-
pipe with which it is to be used, when calculated from the
sented by the test(s) does not meet the requirements of this
following equation:
specification.
S 5 P ~ D 2 t!/2t (1)
O
10. Product Marking
where:
10.1 Quality of Marking—The markings shall be applied to
S 5 hoop stress, psi (or MPa),
the fittings in such a manner that they remain legible under
P 5 internal pressure, psi (or MPa),
normal handling and installation practices.
D
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.