ASTM F585-16
(Guide)Standard Guide for Insertion of Flexible Polyethylene Pipe Into Existing Sewers
Standard Guide for Insertion of Flexible Polyethylene Pipe Into Existing Sewers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The procedures described in this guide are intended as a design and review aid for use by the design engineer in conjunction with manufacturer's recommendations for installing a polyethylene pipe using the insertion method.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes design and selection considerations and installation procedures for the rehabilitation of sanitary and storm sewers by the insertion of solid wall or profile wall or corrugated polyethylene pipe into an existing pipe and along its existing line and grade. The procedures in this guide are intended to minimize traffic disruption, surface damage, surface restoration and interruption of service.
1.2 The polyethylene piping product manufacturer should be consulted to determine the polyethylene piping product’s suitability for insertion renewal as described in this guide.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.1, 7.1, and 8.1 for additional safety precautions.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F585 − 16
Standard Guide for
1
Insertion of Flexible Polyethylene Pipe Into Existing Sewers
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF585;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope* 2.2 Other Documents:
PPI Material Handling Guide
1.1 Thisguidedescribesdesignandselectionconsiderations
andinstallationproceduresfortherehabilitationofsanitaryand
3. Terminology
storm sewers by the insertion of solid wall or profile wall or
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
corrugatedpolyethylenepipeintoanexistingpipeandalongits
nology F412, unless otherwise specified.
existing line and grade. The procedures in this guide are
intended to minimize traffic disruption, surface damage, sur-
4. Significance and Use
face restoration and interruption of service.
4.1 The procedures described in this guide are intended as a
1.2 The polyethylene piping product manufacturer should
design and review aid for use by the design engineer in
be consulted to determine the polyethylene piping product’s
conjunction with manufacturer’s recommendations for install-
suitability for insertion renewal as described in this guide.
ing a polyethylene pipe using the insertion method.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
5. Design and Selection Considerations
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only 5.1 General Guidelines:
and are not considered standard.
5.1.1 Host Pipe Condition Assessment—Prior to the selec-
tion of polyethylene pipe size and installation procedure,
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
measures should be taken to determine in detail the condition
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of the host (original) sewer piping. A detailed examination
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
should determine if the host sewer piping is structurally
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
sufficient, and that any joint offsets or other host pipe defects
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.1, 7.1, and
will permit polyethylene pipe insertion.
8.1 for additional safety precautions.
5.1.2 The presence of obstructions should be determined
(see 6.3). Protrusions of lateral or service piping into the host
2. Referenced Documents
sewer pipe, root growths, sedimentation, mineral deposits, or
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
any combination of such obstructions, may require remedial
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
work prior to inserting the polyethylene pipe.
F1417 Practice for Installation Acceptance of Plastic Non-
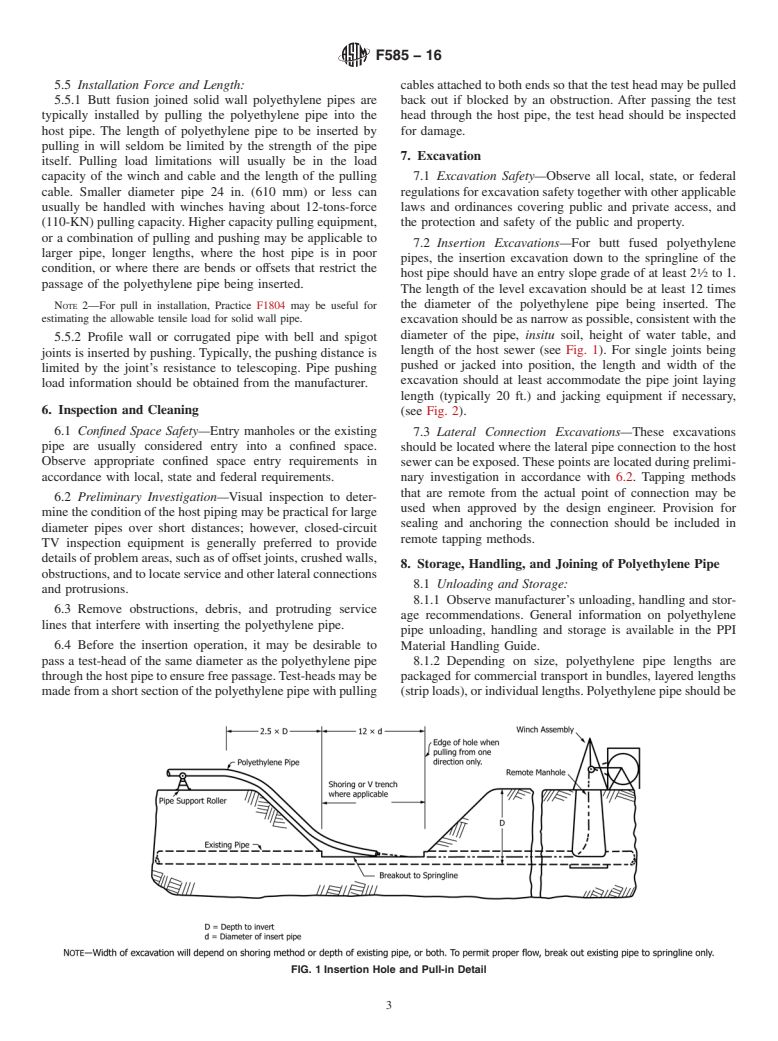
5.1.3 To ensure against interference during insertion, the
pressure Sewer Lines Using Low-Pressure Air
minimumannularclearancebetweenthepolyethylenepipeOD
F1804 Practice for Determining Allowable Tensile Load for
and the host pipe ID should be 10 % of the host pipe ID or 2
Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pipe During Pull-In Installation
in. (50 mm) whichever is less. Greater annular clearance is
F2620 Practice for Heat Fusion Joining of Polyethylene Pipe
acceptable. Outside diameter information should be obtained
and Fittings
from the polyethylene pipe manufacturer.
5.1.4 The number of insertion excavations should be kept to
a minimum and should coincide with areas where problems
have been detected in the existing sewer (see Section 7).
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping
Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer. 5.1.5 Solid wall or profile wall or corrugated polyethylene
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016. Published December 2016. Originally
pipe may be assembled at the time of insertion using heat
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as F585 – 13. DOI:
fusion in accordance with Practice F2620, integral bell and
10.1520/F0585-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Plastics Pipe Institute (PPI), 105 Decker Court, Suite 825,
the ASTM website. Irving, TX 75062, http://www.plasticpipe.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F585 − 13 F585 − 16
Standard Guide for
1
Insertion of Flexible Polyethylene Pipe Into Existing Sewers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F585; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This guide describes design and selection considerations and installation procedures for the rehabilitation of sanitary and
storm sewers by the insertion of solid wall or profile wall or corrugated polyethylene pipe into an existing pipe and along its
existing line and grade. The procedures in this guide are intended to minimize traffic disruption, surface damage, surface restoration
and interruption of service.
1.2 The polyethylene piping product manufacturer should be consulted to determine the polyethylene piping product’s
suitability for insertion renewal as described in this guide.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. See 6.1, 7.1, and 8.1 for additional safety precautions.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F1417 Practice for Installation Acceptance of Plastic Non-pressure Sewer Lines Using Low-Pressure Air
F1804 Practice for Determining Allowable Tensile Load for Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pipe During Pull-In Installation
F2620 Practice for Heat Fusion Joining of Polyethylene Pipe and Fittings
3
2.2 Other Documents:
PPI Material Handling Guide
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412, unless otherwise specified.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The procedures described in this guide are intended as a design and review aid for use by the design engineer in conjunction
with manufacturer’s recommendations for installing a polyethylene pipe using the insertion method.
5. Design and Selection Considerations
5.1 General Guidelines:
5.1.1 Host Pipe Condition Assessment—Prior to the selection of polyethylene pipe size and installation procedure, measures
should be taken to determine in detail the condition of the host (original) sewer piping. A detailed examination should determine
if the host sewer piping is structurally sufficient, and that any joint offsets or other host pipe defects will permit polyethylene pipe
insertion.
1
This practiceguide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.62 on Sewer.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2013Oct. 1, 2016. Published September 2013December 2016. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20072013
as F585 – 94F585 – 13.(2007). DOI: 10.1520/F0585-13.10.1520/F0585-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Plastics Pipe Institute (PPI), 105 Decker Court, Suite 825, Irving, TX 75062, http://www.plasticpipe.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F585 − 16
5.1.2 The presence of obstructions should be determined (see 6.3). Protrusions of lateral or service piping into the host sewer
pipe, root growths, sedimentation, mineral deposits, or any combination of such obstructions, may require remedial work prior to
inserting the polyethylene pipe.
5.1.3 To ensure against interference during insertion, the minimum annular clearance between the polyethylene pipe OD and
the host pipe ID should be 10 % of the host pipe ID or 2 in. (50 mm) whichever is less. Greater annular clearance is acceptable.
Outside dia
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.