ASTM F34-13
(Practice)Standard Practice for Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible Barrier Materials
Standard Practice for Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible Barrier Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Knowledge of extractives from flexible barrier materials may serve many useful purposes. A test cell constructed as described in this practice may be used for obtaining such data. Another test cell has been found equivalent to the one described in this practice. See the appendix for the source of the alternate cell.
5.2 United States Federal Regulations 21CFR 176.170 (d)(3), 21CFR 177.1330 (e)(4), 21CFR 177.1360 (b), 21CFR 177.1670 (b), and 21CFR Appendix VI (b) cite this standard practice as the basis for determining the amount of extractables from the surface of a package or multilayer film or modified paper in contact with food. In some cases, it is the only practice defined for this purpose. No alternative detail is given in the regulations for conducting extractions.
5.3 Test Method D4754 is not an equivalent to this test method. It is for two-sided extraction of films having the same material on both of the exposed surfaces of the film.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the construction of test cells which may be used for the extraction of components from flexible barrier materials by suitable extracting liquids, including foods and food simulating solvents.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F34 − 13
Standard Practice for
Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible
1
Barrier Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F34; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
4
1. Scope 2.3 Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21 —The following
regulations cite this standard:
1.1 This practice covers the construction of test cells which
21CFR 176.170 (d)(3)
may be used for the extraction of components from flexible
21CFR 177.1330 (e)(4)
barrier materials by suitable extracting liquids, including foods
21CFR 177.1360 (b)
and food simulating solvents.
21CFR 177.1670 (b)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Appendix VI (b) Cells for Migration Testing, Guidance for
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Industry: Preparation of Premarket Submissions for Food
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Contact Substances: Chemistry Recommendations (2007)
and are not considered standard.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 flexible— for purpose of this practice, a term applying
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
onlytothoseflexiblematerialswhichcanbeinsertedinthetest
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
cell without affecting their barrier properties.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Summary of Preactice
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1 Thistestcelldefinesthesurfaceareaofaflexiblebarrier
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
structure that may contribute extractable/leachable substances
D4754 Test Method for Two-Sided Liquid Extraction of
to a packaged article. Although stainless steel and other
Plastic Materials Using FDA Migration Cell
materials are cited in the body of the practice, the test cell may
2.2 AOAC International Methods of Analysis:
be constructed of any durable material that does not contribute
Official Method 964.15 Extraction from Flexible Barrier
to the extractable content. The test cell should be evaluated for
3
Materials
leaks after manufacture. It should be washed of manufacturing
or milling fluids that may contribute to the extraction result.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F02 on Flexible
4.2 Both pure chemicals as well as food simulants may be
Barrier Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.15 on
used as extracting solvents. FDA regulations usually specify
Chemical/Safety Properties.
the extracting fluid of choice, but other solvents may be chosen
Current edition approved April 1, 2013. Published June 2013. Originally
based on known or expected effects on the exposed surface.
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as F34 – 02 (2007). DOI:
10.1520/F0034-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Federal Regulations may be purchased from the U.S. Government Printing
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Office Bookstore, 710 North Capitol Street, N.W., Washington, D. C. or may be
the ASTM website. downloaded from the internet. The website for the chemistry guidelines document
3
This method is available through the Association of Official Analytical may be found at:
Chemists, International, 481 North Frederick Ave., Suite 500, Gaithersburg, MD http://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidance
20877 or from the AOAC website at www.aoac.org. Documents/FoodIngredientsandPackaging/ucm081818.htm
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F34−13
4.3 The extractable content is usually measured by gravi- 6.3 n-Heptane, ACS reagent grade.
metric analysis after evaporation of the extracting fluid, but
7. Procedure
other types of analysis may be performed if considered to be
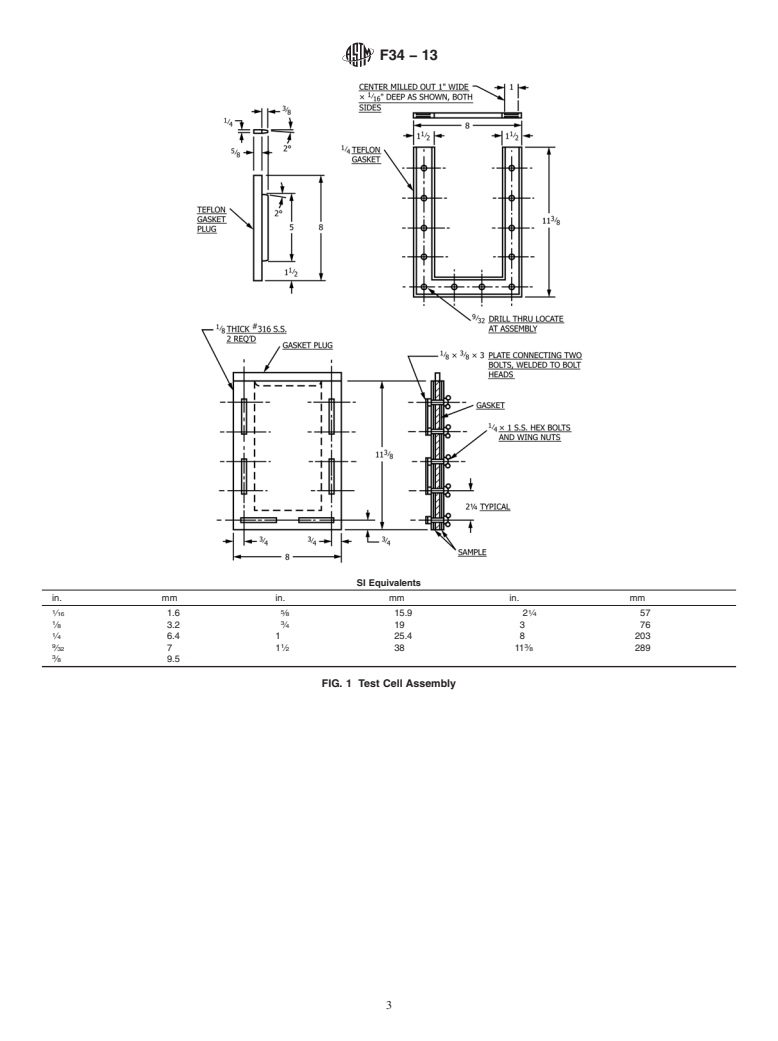
7.1 Construction of Test Cell (Fig. 1, Fig. 2)—Assemble as
appropriate. Some methodologies are cited in the FDA regu-
follows:
lations.
3 1
7.1.1 Two 8 by 11 ⁄8 by ⁄8-in. (203 by 289 by 3.2-mm) No.
4.4 Unlessotherwisespecified,thetestcellisdesignedtobe
316 stainless steel plates, degreased.
used at room temperature and ambient environmental condi-
1 1
7.1.2 One ⁄4 by 1 ⁄2-in. (6.4 by 38-mm) U-shaped virgin
tions.
TF
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F34 − 02 (Reapproved 2007) F34 − 13
Standard Practice for
Construction of Test Cell for Liquid Extraction of Flexible
1
Barrier Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F34; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the construction of test cells which may be used for the extraction of components from flexible barrier
materials by suitable extracting liquids, including foods and food simulating solvents.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D4754 Test Method for Two-Sided Liquid Extraction of Plastic Materials Using FDA Migration Cell
2.2 AOAC International Methods of Analysis:
3
Official Method 964.15 ExtractivesExtraction from Flexible Barrier Materials
4
2.3 Code of Federal Regulations:Regulations, Title 21 —The following regulations cite this standard:
21CFR 176.170 (d)(3)
Title 21,21CFR 177.1330 (e)(4) Sections 176.170
21CFR 177.1360 (b)
21CFR 177.1670 (b)
Appendix VI (b) Cells for Migration Testing, Guidance for Industry: Preparation of Premarket Submissions for Food Contact
Substances: Chemistry Recommendations (2007)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 flexible— for purpose of this practice, a term applying only to those flexible materials which can be inserted in the test
cell without affecting their barrier properties.
4. Summary of Preactice
4.1 This test cell defines the surface area of a flexible barrier structure that may contribute extractable/leachable substances to
a packaged article. Although stainless steel and other materials are cited in the body of the practice, the test cell may be constructed
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F02 on Flexible Barrier Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.15 on Chemical/Safety
Properties.
Current edition approved April 1, 2007April 1, 2013. Published May 2007June 2013. Originally approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 20022007 as
F34 – 02.F34 – 02 (2007). DOI: 10.1520/F0034-02R07.10.1520/F0034-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
This method is available through the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, International, 481 North Frederick Ave., Suite 500, Gaithersburg, MD
20877–2417.20877 or from the AOAC website at www.aoac.org.
4
Available from Federal Regulations may be purchased from the U.S. Government Printing Office Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE,
Washington, DC 20401, http://www.access.gpo.gov. Bookstore, 710 North Capitol Street, N.W., Washington, D. C. or may be downloaded from the internet. The website for
the chemistry guidelines document may be found at:
http://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidance
Documents/FoodIngredientsandPackaging/ucm081818.htm
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
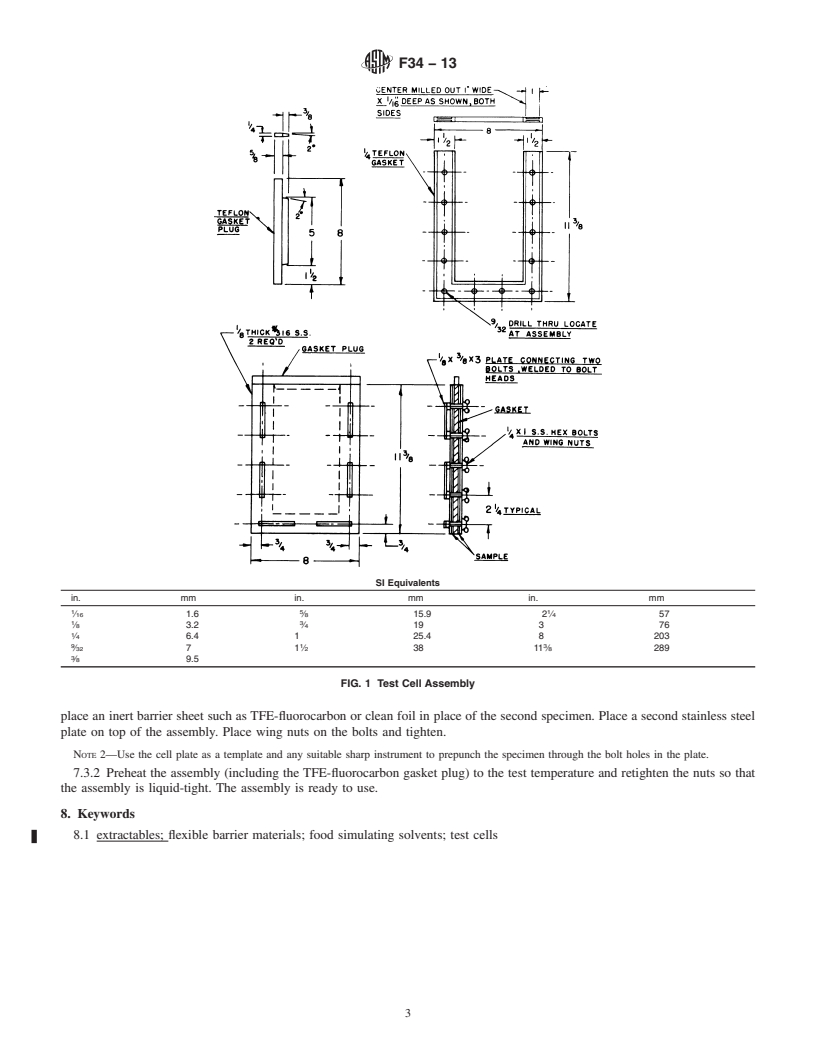
F34 − 13
of any durable material that does not contribute to the extractable content. The test cell should be evaluated for leaks after
manufacture. It should be washed of manufacturing or milling fluids that may contribute to the extraction result.
4.2 Both pure chemicals as well as food simulants may be used as extracting solvents. FDA regulations usually specify the
extracting fluid of choice, but other solvents may be chosen based on known or expected effects on the exposed surface.
4.3 The extractable content is usually measured by gravimetric analysi
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.