ASTM B283-10a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper and Copper-Alloy Die Forgings (Hot-Pressed)
Standard Specification for Copper and Copper-Alloy Die Forgings (Hot-Pressed)
ABSTRACT
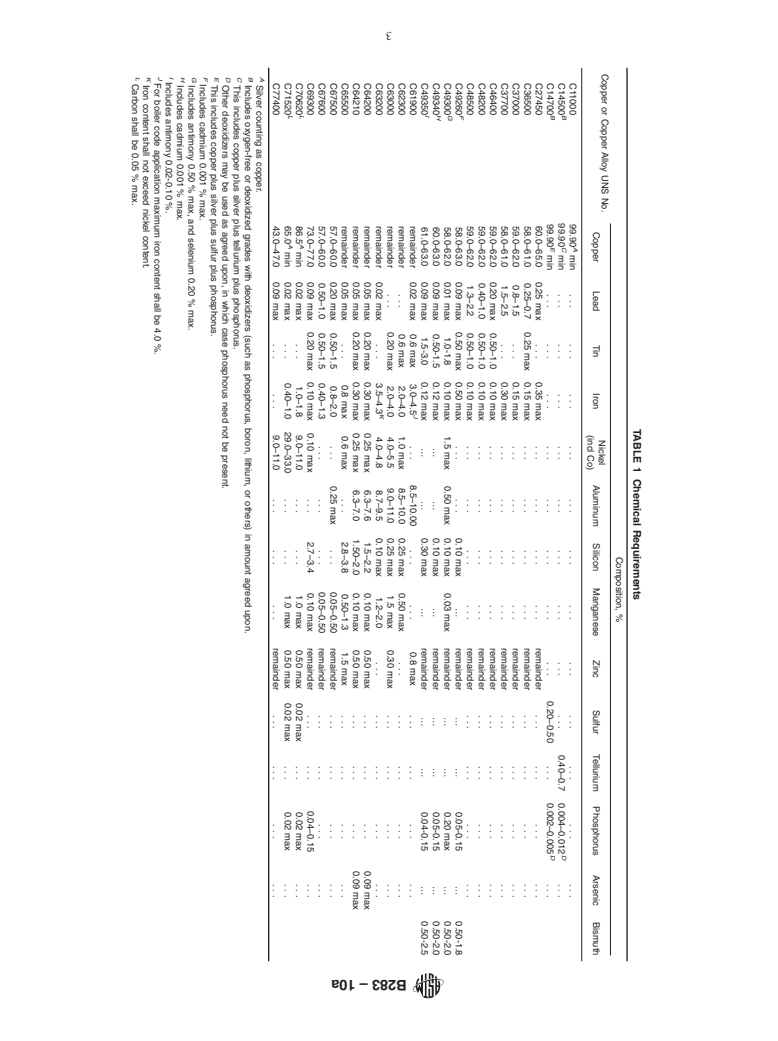
This specification establishes the requirements for copper and copper die forgings produced by hot pressing method. The forgings included here are designated with the following Copper or Copper Alloy UNS Nos.: C11000 (copper), C14500 (copper-tellurium alloy), C14700 (copper-sulfur alloy), C36500 (leaded Muntz metal), C37000 (free-cutting Muntz metal), C37700 (forging brass), C46400 (naval brass), C48200 (medium leaded naval brass), C48500 (leaded naval brass), C61900 (aluminum bronze), C62300 (9% aluminum bronze), C63000 and C63200 (aluminum-nickel bronze), C64200 (aluminum-silicon bronze), C64210 (6.7% aluminum-silicon bronze), C65500 (high-silicon bronze), C67500 (manganese bronze), C67600, C69300 (copper-zinc-silicon alloy), C70620 (90% copper-10% nickel alloy), C71520 (70% copper-30% nickel alloy), and C77400 (45% nickel-10% silver alloy). The materials for manufacture shall be rods, billets, or blanks of such purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing by hot pressing. Products shall be tested to examine their conformance to mechanical (tensile and yield strengths, and elongation), dimensional, and chemical composition requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper and copper alloy die forgings produced by the hot pressing method. The following copper and copper alloys are included:
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B283 – 10a
Standard Specification for
1
Copper and Copper-Alloy Die Forgings (Hot-Pressed)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B283; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
NOTE 2—Wrought product intended for hot forging is described in
1. Scope*
Specification B124/B124M.
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for cop-
1.3 The following safety caveat pertains only to Section 10
per and copper alloy die forgings produced by the hot pressing
of this specification. This standard does not purport to address
method. The following copper and copper alloys are included:
all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is
Copper or Copper Alloy
UNS No. Name the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
C11000 copper
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
C14500 copper-tellurium
C14700 copper-sulfur
C27450 plumbing brass 2. Referenced Documents
C36500 leaded Muntz metal
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C37000 free-cutting Muntz metal
C37700 forging brass B124/B124M Specification for Copper and Copper Alloy
C46400 naval brass
Forging Rod, Bar, and Shapes
C48200 medium leaded naval brass
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for
C48500 leaded naval brass
C49260 copper-zinc-bismuth alloy Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and
C49300 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
Forgings
C49340 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
C49350 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
C61900 aluminum bronze
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
C62300 aluminum bronze, 9 %
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
C63000 aluminum-nickel bronze
3
Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
C63200 aluminum-nickel bronze
C64200 aluminum-silicon bronze E75 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Copper-Nickel
C64210 aluminum-silicon bronze, 6.7 % 3
and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys
C65500 high-silicon bronze (A)
E478 TestMethodsforChemicalAnalysisofCopperAlloys
C67500 manganese bronze (A)
C67600 . . . 2.2 Other Standards:
C69300 copper-zinc-silicon
ISO 7602 Determination of Tellurium Content (High
C70620 copper-nickel 90-10
Content)—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric
C71520 copper-nickel 70-30
4
C77400 nickel silver, 45-10
Method
JIS H 1068:2005 Method for Determination of Bismuth in
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
5
Copper and Copper Alloys (Japanese Industrial Stan-
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
dards)
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
2.3 Military Standards:
information only and are not considered standard.
MIL-STD-792 Identification Marking Requirements for
NOTE 1—Nominal composition and relative forgeability ratings are
given in Appendix X1. Copper-nickel alloys C70620 and C71520 are
2
intended for welded applications with seawater exposure.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper the ASTM website.
3
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
Bar, Wire, Shapes and Forgings. on www.astm.org.
4
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010. Published November 2010. Originally Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as B283 – 10. DOI: 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
10.1520/B0283-10A. Available from Japanese Industrial Standards, http://www.JIS.or.jp/
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B283 – 10a
6
Special Purpose Components 5.2.1 Certification (as specified herein and Supplementary
NAVSEA T9074-AS-GIB-010/271 Requirements for Non- Requirements),
6
destructive Testing Method 5.2.2 Mill test report (as specified in B249/B249M), and
5.2.3 Ultrasonic inspection report (Supplementary Require-
3. General Requirements ments).
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M
6. Material and Manufacture
cons
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B283–10 Designation: B283 – 10a
Standard Specification for
1
Copper and Copper-Alloy Die Forgings (Hot-Pressed)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B283; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper and copper alloy die forgings produced by the hot pressing
method. The following copper and copper alloys are included:
Copper or Copper Alloy
UNS No. Name
C11000 copper
C14500 copper-tellurium
C14700 copper-sulfur
C27450 plumbing brass
C36500 leaded Muntz metal
C37000 free-cutting Muntz metal
C37700 forging brass
C46400 naval brass
C48200 medium leaded naval brass
C48500 leaded naval brass
C49260 copper-zinc-bismuth alloy
C49300 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
C49340 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
C49350 copper-zinc-tin-bismuth alloy
C61900 aluminum bronze
C62300 aluminum bronze, 9 %
C63000 aluminum-nickel bronze
C63200 aluminum-nickel bronze
C64200 aluminum-silicon bronze
C64210 aluminum-silicon bronze, 6.7 %
C65500 high-silicon bronze (A)
C67500 manganese bronze (A)
C67600 . . .
C69300 copper-zinc-silicon
C70620 copper-nickel 90-10
C71520 copper-nickel 70-30
C77400 nickel silver, 45-10
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
NOTE 1—Nominal composition and relative forgeability ratings are given inAppendix X1. Copper-nickel alloys C70620 and C71520 are intended for
welded applications with seawater exposure.
NOTE 2—Wrought product intended for hot forging is described in Specification B124/B124M.
1.3 The following safety caveat pertains only to Section 10 of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B124/B124M Specification for Copper and Copper Alloy Forging Rod, Bar, and Shapes
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, Bar,
Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
Current edition approved AprilOct. 1, 2010. Published MayNovember 2010. Originally approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 20092010 as
B283–09a.B283 – 10. DOI: 10.1520/B0283-10A.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B283 – 10a
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and Forgings
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys
E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
2.2 Other Standards:
3
ISO 7602 Determination of Tellurium Content (High Content)—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method
4
JIS H 1068:2005 Method for Determination of Bismuth in Copper and Copper Alloys (Japanese Industrial Standards)
2.3 Military Standards:
5
MIL-STD-792 Identification Marking Requirements for Special Purpose Components
5
NAVSEA T9074-AS-GIB-010/271 Requirements for Nondestructive Testing Method
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Terminology,
3.1.2 Materials and Manufacture,
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish and Appearance,
3.1.4 Sampling,
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests,
3.1.6 Specimen Pre
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.