ASTM B196/B196M-07(2013)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Rod and Bar
Standard Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Rod and Bar
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for rods and bars in straight lengths of copper-beryllium alloys with Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C17000, C17200, and C17300. The material for manufacture shall be cast and worked to such purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing by hot working, cold working, and annealing to produce a uniform wrought structure and specified temper in the finished product. Products shall be available in the following tempers: solution heat-treated TB00 (A), and cold-drawn hard TD04 (H), which shall be precipitation heat treated after machining or forming. Products that are already precipitation heat treated by the manufacturer shall be available in tempers TF00 (AT) and TH04 (HT). Products shall be sampled and prepared, then tested accordingly to examine their conformance to dimensional (diameter, length, straightness, and edge contour), mechanical (tensile and yield strength, Rockwell hardness, and elongation), and chemical composition requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper-beryllium alloy rod and bar in straight lengths. The following three alloys are included:
Copper Alloy
UNS No.
Previously Used
Designations
Nominal Beryllium
Content, %
C17000
Alloy 165
1.7
C17200
Alloy 25
1.9
C17300
1.9
+0.4 lead
1.2 Unless otherwise required, Copper Alloy UNS No. C17200 shall be the alloy furnished whenever Specification B196/B196Mis specified without any alloy designation.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pounds or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:B196/B196M −07 (Reapproved 2013)
Standard Specification for
Copper-Beryllium Alloy Rod and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B196/B196M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—Corrections were made in Table 3 and 10.2.1 editorially in September 2015.
1. Scope* 2.2 ASTM Standards:
B194 Specification for Copper-BerylliumAlloy Plate, Sheet,
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for
Strip, and Rolled Bar
copper-beryllium alloy rod and bar in straight lengths. The
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for
following three alloys are included:
Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and
Copper Alloy Previously Used Nominal Beryllium
Forgings
UNS No. Designations Content, %
B601 Classification forTemper Designations for Copper and
C17000 Alloy 165 1.7
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
C17200 Alloy 25 1.9
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
C17300 1.9
+0.4 lead E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods forTensionTesting of Metallic Materials
1.2 Unless otherwise required, Copper Alloy UNS No.
[Metric] (Withdrawn 2008)
C17200 shall be the alloy furnished whenever Specification
B196/B196Mis specified without any alloy designation.
3. General Requirements
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pounds or SI units are to
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M
be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI
constitute a part of this specification:
units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system
3.1.1 Terminology;
may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be
3.1.2 Dimensions and Permissible Variations;
used independently of the other. Combining values from the
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance;
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
3.1.4 Sampling;
cation.
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests;
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation;
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.7 Test Methods;
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits;
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.9 Inspection;
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing;
3.1.11 Certification;
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.12 Mill Test Report;
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the
3.1.13 Packaging and Package Marking; and
BookofStandardsformapartofthisspecificationtotheextent
3.1.14 Heat Identification
referenced herein:
1 2
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Bar, Wire, Shapes and Forgings. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 1, 2013. Published April 2013. Originally the ASTM website.
approvedin1945toreplaceportionsofB120 – 41 T.Lastpreviouseditionapproved The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
in 2007 as B196/B196M-07. DOI: 10.1520/B0196_B0196M-07R13E01. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
B196/B196M−07 (2013)
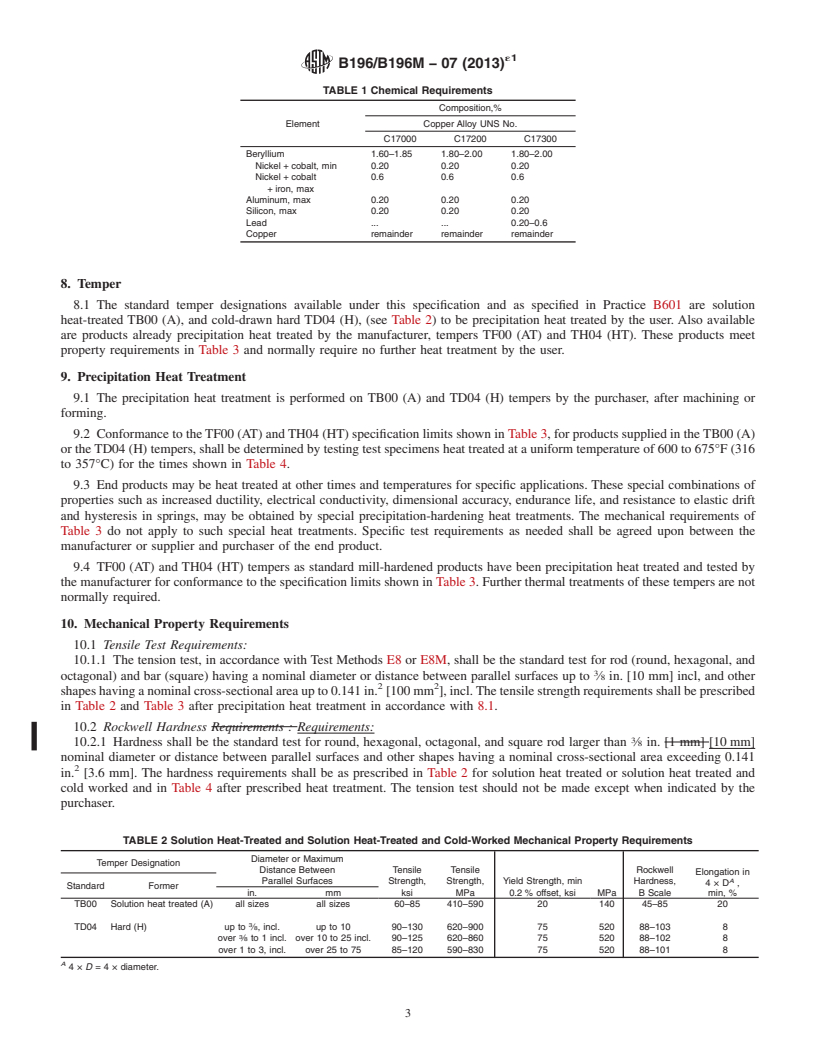
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that
referencedin3.1aboveappearsinthisspecification,itcontains Composition,%
additional requirements which supplement those appearing in Element Copper Alloy UNS No.
Specification B249/B249M. C17000 C17200 C17300
Beryllium 1.60–1.85 1.80–2.00 1.80–2.00
4. Terminology Nickel + cobalt, min 0.20 0.20 0.20
Nickel + cobalt 0.6 0.6 0.6
4.1 For terms related to copper and copper alloys, refer to
+ iron, max
Aluminum, max 0.20 0.20 0.20
Terminology B846.
Silicon, max 0.20 0.20 0.20
4.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Lead . . 0.20–0.6
Copper remainder remainder remainder
4.2.1 Heat—A heat shall be the result of castings poured
simultaneously from the same source of molten metal.
4.2.2 Lot—The lot shall be a heat or fraction thereof.
5. Ordering Information
6.2.1 The product shall be produced with a combination hot
working, cold working, and thermal processing to produce a
5.1 Orders for products should include the following
uniform wrought structure and the specified temper.
information, as applicable:
5.1.1 ASTM specification designation and year of issue,
7. Chemical Composition
5.1.2 Quantity,
5.1.3 Copper Alloy UNS No. designation (Section 1),
7.1 The material shall conform to the chemical composition
5.1.4 Form of material (rod or bar and cross section, such as
requirements prescribed in Table 1 for CopperAlloy UNS No.
round, hexagonal, and so forth),
designation specified in the ordering information.
5.1.5 Temper (Section 8),
7.2 These composition limits do not preclude the presence
5.1.6 Dimensions (diameter or distance between parallel
of other elements. Limits for unnamed elements may be
surfaces, and length),
established and analysis required by agreement between the
5.1.7 How furnished (stock or specific lengths, with or
manufacturer, or supplier, and purchaser.
without ends), and
7.3 Copper is customarily given as remainder, but may be
5.1.8 When material is ordered for agencies of the U.S.
taken as the difference between the sum of all elements
government (See Section 11).
analyzed and 100 %.
5.2 The following options are available and should be
7.4 When all the elements in Table 1 are determined, the
specified in the contract or purchase order when required:
sum of results shall be 99.5 % min.
5.2.1 Type of edge (square corners, rounded corners,
rounded edge, full-rounded edge),
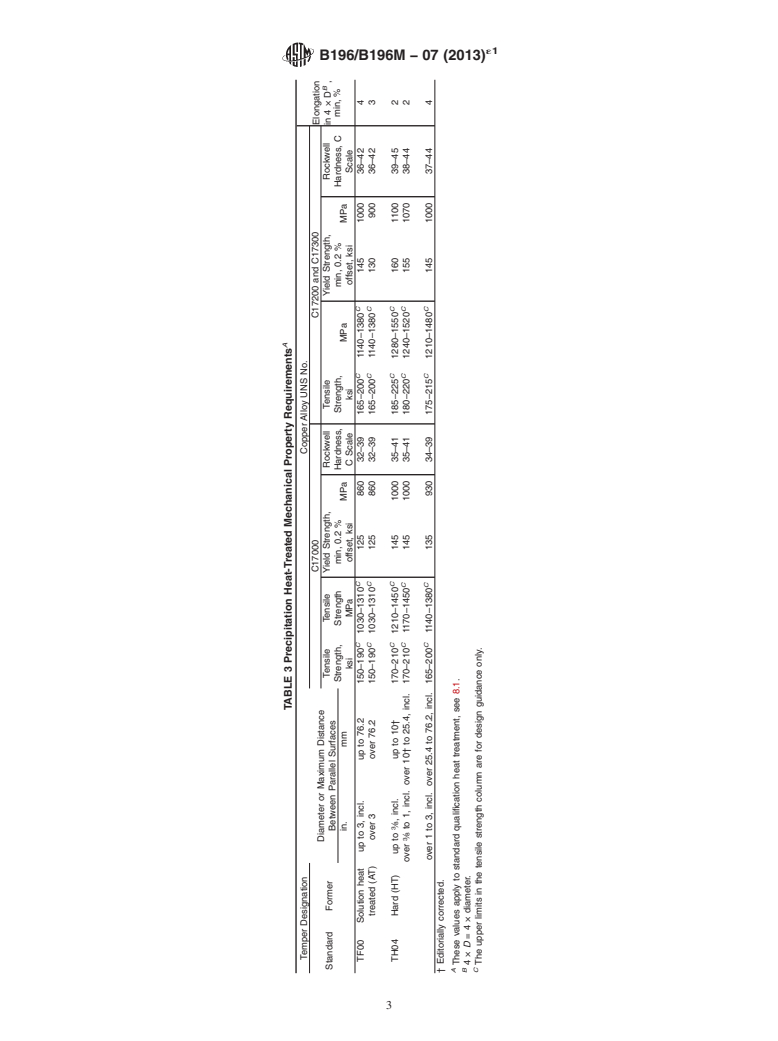
8. Temper
5.2.2 Mechanical properties (tension test and hardness)
(Section 10),
8.1 The standard temper designations available under this
5.2.3 Certification, and
specification and as specified in Practice B601 are solution
5.2.4 Mill Test Report.
heat-treated TB00 (A), and cold-drawn hard TD04 (H), (see
Table 2) to be precipitation heat treated by the user. Also
6. Materials and Manufacture
available are products already precipitation heat treated by the
6.1 Material: manufacturer, tempers TF00 (AT) and TH04 (HT). These
6.1.1 The material of manufacture shall be Copper Alloy
products meet property requirements in Table 3 and normally
UNS No. C17000, C17200, or C17300, cast and worked and of
require no further heat treatment by the user.
such purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing into
the products prescribed herein. 9. Precipitation Heat Treatment
6.1.2 Heat traceability shall be maintained and reported on
9.1 The precipitation heat treatment is performed on TB00
the Mill Test Report or Certification.
(A)andTD04(H)tempersbythepurchaser,aftermachiningor
6.2 Manufacture: forming.
TABLE 2 Solution Heat-Treated and Solution Heat-Treated and Cold-Worked Mechanical Property Requirements
Diameter or Maximum
Temper Designation
Distance Between Tensile Tensile Rockwell
Elongation in
A
Parallel Surfaces Strength, Strength, Yield Strength, min Hardness,
4×D ,
Standard Former
in. mm ksi MPa 0.2 % offset, ksi MPa B Scale min, %
TB00 Solution heat treated (A) all sizes all sizes 60–85 410–590 20 140 45–85 20
TD04 Hard (H) up to ⁄8, incl. up to 10 90–130 620–900 75 520 88–103 8
over ⁄8 to 1 incl. over 10 to 25 incl. 90–125 620–860 75 520 88–102 8
over 1 to 3, incl. over 25 to 75 85–120 590–830 75 520 88–101 8
A
4× D =4×diameter.
´1
B196/B196M−07 (2013)
A
TABLE 3 Precipitation Heat-Treated Mechanical Property Requirements
Temper Designation Copper Alloy UNS No.
C17000 C17200 and C17300
Elongation
Diameter or Maximum Distance
B
Tensile Tensile Yield Strength, Rockwell Tensile Yield Strength, Rockwell
in4×D ,
Standard Former
Between Parallel Surfaces
min, %
Strength, Strength min, 0.2 % Hardness, Strength, min, 0.2 % Hardness, C
in. mm MPa MPa MPa
ksi MPa offset, ksi C Scale ksi offset, ksi Scale
C C C C
TF00 Solution heat up to 3, incl. up to 76.2 150–190 1030–1310 125 860 32–39 165–200 1140–1380 145 1000 36–42 4
C C C C
treated (AT)
over 3 over 76.2 150–190 1030–1310 125 860 32–39 165–200 1140–1380 130 90
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: B196/B196M − 07 (Reapproved 2013) B196/B196M − 07 (Reapproved 2013)
Standard Specification for
Copper-Beryllium Alloy Rod and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B196/B196M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—Corrections were made in Table 3 and 10.2.1 editorially in September 2015.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper-beryllium alloy rod and bar in straight lengths. The following
three alloys are included:
Copper Alloy Previously Used Nominal Beryllium
UNS No. Designations Content, %
C17000 Alloy 165 1.7
C17200 Alloy 25 1.9
C17300 1.9
+0.4 lead
1.2 Unless otherwise required, Copper Alloy UNS No. C17200 shall be the alloy furnished whenever Specification
B196/B196Mis specified without any alloy designation.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pounds or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the Book of Standards form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B194 Specification for Copper-Beryllium Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
B249/B249M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Rod, Bar, Shapes and Forgings
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric] (Withdrawn 2008)
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B249/B249M constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Terminology;
3.1.2 Dimensions and Permissible Variations;
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance;
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.02 on Rod, Bar,
Wire, Shapes and Forgings.
Current edition approved April 1, 2013. Published April 2013. Originally approved in 1945 to replace portions of B120 – 41 T. Last previous edition approved in 2007
as B196/B196M – 07.B196/B196M-07. DOI: 10.1520/B0196_B0196M-07R13.10.1520/B0196_B0196M-07R13E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
B196/B196M − 07 (2013)
3.1.4 Sampling;
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests;
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation;
3.1.7 Test Methods;
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits;
3.1.9 Inspection;
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing;
3.1.11 Certification;
3.1.12 Mill Test Report;
3.1.13 Packaging and Package Marking; and
3.1.14 Heat Identification
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that referenced in 3.1 above appears in this specification, it contains
additional requirements which supplement those appearing in Specification B249/B249M.
4. Terminology
4.1 For terms related to copper and copper alloys, refer to Terminology B846.
4.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
4.2.1 Heat—A heat shall be the result of castings poured simultaneously from the same source of molten metal.
4.2.2 Lot—The lot shall be a heat or fraction thereof.
5. Ordering Information
5.1 Orders for products should include the following information, as applicable:
5.1.1 ASTM specification designation and year of issue,
5.1.2 Quantity,
5.1.3 Copper Alloy UNS No. designation (Section 1),
5.1.4 Form of material (rod or bar and cross section, such as round, hexagonal, and so forth),
5.1.5 Temper (Section 8),
5.1.6 Dimensions (diameter or distance between parallel surfaces, and length),
5.1.7 How furnished (stock or specific lengths, with or without ends), and
5.1.8 When material is ordered for agencies of the U.S. government (See Section 11).
5.2 The following options are available and should be specified in the contract or purchase order when required:
5.2.1 Type of edge (square corners, rounded corners, rounded edge, full-rounded edge),
5.2.2 Mechanical properties (tension test and hardness) (Section 10),
5.2.3 Certification, and
5.2.4 Mill Test Report.
6. Materials and Manufacture
6.1 Material:
6.1.1 The material of manufacture shall be Copper Alloy UNS No. C17000, C17200, or C17300, cast and worked and of such
purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing into the products prescribed herein.
6.1.2 Heat traceability shall be maintained and reported on the Mill Test Report or Certification.
6.2 Manufacture:
6.2.1 The product shall be produced with a combination hot working, cold working, and thermal processing to produce a
uniform wrought structure and the specified temper.
7. Chemical Composition
7.1 The material shall conform to the chemical composition requirements prescribed in Table 1 for Copper Alloy UNS No.
designation specified in the ordering information.
7.2 These composition limits do not preclude the presence of other elements. Limits for unnamed elements may be established
and analysis required by agreement between the manufacturer, or supplier, and purchaser.
7.3 Copper is customarily given as remainder, but may be taken as the difference between the sum of all elements analyzed and
100 %.
7.4 When all the elements in Table 1 are determined, the sum of results shall be 99.5 % min.
´1
B196/B196M − 07 (2013)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition,%
Element Copper Alloy UNS No.
C17000 C17200 C17300
Beryllium 1.60–1.85 1.80–2.00 1.80–2.00
Nickel + cobalt, min 0.20 0.20 0.20
Nickel + cobalt 0.6 0.6 0.6
+ iron, max
Aluminum, max 0.20 0.20 0.20
Silicon, max 0.20 0.20 0.20
Lead . . 0.20–0.6
Copper remainder remainder remainder
8. Temper
8.1 The standard temper designations available under this specification and as specified in Practice B601 are solution
heat-treated TB00 (A), and cold-drawn hard TD04 (H), (see Table 2) to be precipitation heat treated by the user. Also available
are products already precipitation heat treated by the manufacturer, tempers TF00 (AT) and TH04 (HT). These products meet
property requirements in Table 3 and normally require no further heat treatment by the user.
9. Precipitation Heat Treatment
9.1 The precipitation heat treatment is performed on TB00 (A) and TD04 (H) tempers by the purchaser, after machining or
forming.
9.2 Conformance to the TF00 (AT) and TH04 (HT) specification limits shown in Table 3, for products supplied in the TB00 (A)
or the TD04 (H) tempers, shall be determined by testing test specimens heat treated at a uniform temperature of 600 to 675°F (316
to 357°C) for the times shown in Table 4.
9.3 End products may be heat treated at other times and temperatures for specific applications. These special combinations of
properties such as increased ductility, electrical conductivity, dimensional accuracy, endurance life, and resistance to elastic drift
and hysteresis in springs, may be obtained by special precipitation-hardening heat treatments. The mechanical requirements of
Table 3 do not apply to such special heat treatments. Specific test requirements as needed shall be agreed upon between the
manufacturer or supplier and purchaser of the end product.
9.4 TF00 (AT) and TH04 (HT) tempers as standard mill-hardened products have been precipitation heat treated and tested by
the manufacturer for conformance to the specification limits shown in Table 3. Further thermal treatments of these tempers are not
normally required.
10. Mechanical Property Requirements
10.1 Tensile Test Requirements:
10.1.1 The tension test, in accordance with Test Methods E8 or E8M, shall be the standard test for rod (round, hexagonal, and
octagonal) and bar (square) having a nominal diameter or distance between parallel surfaces up to ⁄8 in. [10 mm] incl, and other
2 2
shapes having a nominal cross-sectional area up to 0.141 in. [100 mm ], incl. The tensile strength requirements shall be prescribed
in Table 2 and Table 3 a
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.