ASTM F1909-98(2012)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Preformed Open–Cell Sponge Rubber Pail and Drum Gaskets
Standard Specification for Preformed Open–Cell Sponge Rubber Pail and Drum Gaskets
ABSTRACT
This specification covers preformed open-cell sponge rubber gaskets, for use in new or reconditioned pails or drums, of the following classes: Class A and Class B, each divided into Grade 1, Grade 2, and Grade 3. Cellular sponge rubber gaskets shall be made by incorporating a blowing agent into the compound, such as sodium bicarbonate, that gives off a gas which expands the mass during the vulcanization process, and shall be manufactured from natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or rubber-like materials, together with added compounding ingredients. Unless otherwise specified, gasket sponge rubber shall have a natural skin on both the top and bottom surfaces. Cellular rubber shall conform to the prescribed requirements as to physical properties such as (1) compression at deflection, (2) change in volume upon oil immersion, (3) change in compression value after heat aging, (4) compression set, and (5) color (tan or black). The following test methods shall be used: (1) compression deflection test, (2) oil immersion test, (3) heat oven aging test, and (4) compression set test under constant deflection. The formula for calculating the compression set is given. The requirements for sampling, test specimens and slabs, and measurements of test specimen such as width and thickness are detailed as well. The location from which standard test specimens are to be cut when testing standard test slabs or commercial flat sheets and the four-cavity frame for standard test slabs of cellular rubbers are illustrated.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers preformed open–cell sponge rubber gaskets of the following classes for use in new or reconditioned pails or drums.
1.1.1 Class A—Non–Oil Resistant.
1.1.2 Class B—Oil Resistant.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to Section 10, General Test Methods. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 1—ISO Equivalency Statement—This proposed specification was found to be not equivalent.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1909 −98 (Reapproved 2012)
Standard Specification for
Preformed Open–Cell Sponge Rubber Pail and Drum
Gaskets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1909; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers preformed open–cell sponge 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
rubber gaskets of the following classes for use in new or 3.1.1 cellular material—a generic term for materials con-
reconditioned pails or drums. taining many open cells dispersed throughout the mass.
1.1.1 Class A—Non–Oil Resistant.
3.1.2 flexible cellular material—a flexible, cellular material
1.1.2 Class B—Oil Resistant.
that will not rupture within 60 s when a specimen 200 by 25 by
25mm(8by1by1in.)isbentarounda25mm(1in.)diameter
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
mandrelatauniformrateofonelapin5sintheformofahelix
standard.
at a temperature between 18 and 29°C (65 and 85°F).
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to
3.1.3 natural skin—a relatively dense layer at the surface of
Section 10, General Test Methods. This standard does not
a cellular material. Normally, this natural skin is formed by
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated
contact with the mold during manufacture. Parts made by
with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
cutting from open–cell (sponge rubber) sheets usually have
to establish appropriate safety and health practices and
natural skin on two faces and open cells at the cut edges.
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
use.
3.1.4 rubber—a material that is capable of recovering from
large deformations quickly and forcibly.
NOTE 1—ISO Equivalency Statement—This proposed specification was
found to be not equivalent.
3.1.5 sponge rubber—cellularrubberconsistingofpredomi-
nantly open cells made from a solid rubber compound.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards: 4. Classification
D395 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set
4.1 Classes—Cellular rubbers are divided into two classes,
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
which are designated by the letters A and B added to the
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
number prefix.
Oven
4.1.1 Class A—Cellular rubbers made from natural rubber,
D575 Test Methods for Rubber Properties in Compression
reclaimed rubber, synthetic rubber, or rubber-like materials,
D1056 Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials—
alone or in combination, where specific resistance to the action
Sponge or Expanded Rubber
of petroleum–base oils is not required.
D3182 PracticeforRubber—Materials,Equipment,andPro-
4.1.2 Class B—Cellular rubbers made from synthetic rubber
cedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing
or rubber-like materials, alone or in combination, having
Standard Vulcanized Sheets
specific requirements for oil resistance.
D3183 Practice for Rubber—Preparation of Pieces for Test
4.2 Grades—Each class is divided into three different
Purposes from Products
grades. Each grade is based on a specific range of firmness as
expressed by a 25 % compression. Grades are designated by
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF03onGaskets
digit, the softer grades being identified with the lower numbers
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeF03.60onSpecificationsforGasket
andthehardergradesbeingidentifiedwiththehighernumbers.
Materials.
4.2.1 Grade 1—A compression deflection range from 15 to
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2012. Published November 2012. Originally
50 kPa (2 to 7 psi).
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as F1909– 98 (2004).
DOI: 10.1520/F1909-98R12.
4.2.2 Grade 2—A compression deflection range from 50 to
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
85 kPa (7 to 12 psi).
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.2.3 Grade 3—A compression deflection range from 85 to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 120 kPa (12 to 17 psi).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1909−98 (2012)
TABLE 1 Physical Requirements of Open–Cell Sponge Rubber
7. Tolerances on Dimensions
Pail and Drum Gaskets
7.1 Tolerances on dimensions of cellular rubber gaskets
Requirements
shall be as specified in Table 2.
Class/ Compression Oil Heat Aged 7 Compression
Grade at 25 % Immersion Days at Set, 22 h
7.2 Measurements of Test Specimens—Thickness and width
Number Deflection 22hat 70°C at 70°C
shall be measured using a dial–type gage , having a maximum
(Limits), kPa 70°C (158°F), (158°F) 50 %
(psi) (158°F), Change in Deflection,
stemandcircularfootmassof25gandacircularfoot31.8mm
Change in Original Max %
(1.250 in.) in diameter.
Volume in Compression
ASTM Oil Values
IRM 903 (Limits), %
8. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
(Limits), %
Class A, Non-Oil Resistant 8.1 Cellular rubber gaskets under this specification shall be
A1 15–50 (2–7) — ±20 15
manufactured from natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or rubber-
A2 50–85 (7–12) — ±20 15
likematerials,togetherwithaddedcompoundingingredientsof
A3 85–120 (12–17) — ±20 15
Class B, Oil-Resistant, Medium Swell such nature and quality that the finished product complies with
B1 15–50 (2–7) +10 to +60 ±20 50
the specification requirements. In permitting choice in the use
B2 50–85 (7–12) +10 to +60 ±20 50
of materials by the producer, it is not intended to imply that the
B3 85–120 (12–17) +10 to +60 ±20 50
different rubber materials are equivalent in respect to all
physical properties. Any special characteristics that may be
desired for specific applications other than those prescribed in
this specification, shall be stated in the product specifications
5. Materials and Manufacture
as they may influence the choice of the type of rubber material
or other ingredients used.All materials and workmanship shall
5.1 Sponge rubber gaskets are made by incorporating a
be in accordance with good commercial practice, and the
blowing agent into the compound, such as sodium bicarbonate,
resulting cellular rubbers shall be free from defects affecting
that gives off a gas which expands the mass during the
serviceability.
vulcanization process.
5.2 Sponge rubber gaskets are manufactured to specified
9. Sampling
dimensions. Unless otherwise specified, gasket sponge rubber
9.1 When possible, the completed manufactured product
shall have a natural skin on both the top and bottom surfaces.
shall be used for the tests specified. Representative samples of
Fabric surface impressions are not objectionable.
the lot being examined shall be selected at random as required.
6. Physical Properties 9.2 When the finished product does not lend itself to testing
ortothetakingoftestspecimensbecauseofcomplicatedshape
6.1 The various grades of cellular rubber shall conform to
or other reasons, standard test slabs shall be prepared. When
the requirements as to physical properties in Table 1 and Table
differences due to the difficulty in obtaining suitable test
2.
specimens from the finished part arise, manufacturer and
6.2 Color—Unless otherwise specified, the color of cellular
purchaser may agree on acceptable deviations. Agreement on
rubber gaskets shall be tan or black.
acceptable deviations can be achieved by comparing results of
standard test specimens with those obtained on actual parts.
10. General Test Methods
TABLE 2 Tolerances on Dimensions for Open–Cell Sponge
10.1 Except as otherwise specified in these test methods for
Rubber Pail or Drum Gaskets
open-cell rubber, the following test methods shall be complied
Thickness
mm (in.) Tolerance ± mm (in.) with as required and are hereby made a part of this specifica-
4.8 (0.188) 1.5 (0.062)
tion.
6.4 (0.250) 1.5 (0.062)
10.1.1 General Physical Test Requirements—Practices
7.9 (0.313) 1.5 (0.062)
9.5 (0.375) 1.5 (0.062) D3182 and D3183.
11.1 (0.438) 1.5 (0.062)
10.1.2 Compression Deflection Test—Specification D1056
12.7 (0.500) 1.5 (0.062)
and Section 12 of this specification.
Width
mm (in.) Tolerance ± mm (in.)
10.1.3 Oil Immersion—TestMethodD471andSection13of
4.8 (0.188) 1.5 (0.062)
this specification.
6.4 (0.250) 1.5 (0.062)
10.1.4 Heat Aging Test—Test Method D573, with modifica-
7.9 (0.313) 1.5 (0.062)
9.5 (0.375) 1.5 (0.062) tions as described in Section 14 of this specification.
11.1 (0.438) 1.5 (0.062)
10.1.5 Compression Set—Test Methods D395 as described
12.7 (0.500) 1.5 (0.062)
in Section 15 of this specification.
Length
Dimension mm (in.)
As Required—Circular open–cell sponge rubber pail and drum gaskets are
manufactured to fit specified pail or drum flanges by cutting to the specified
length and sealing the cut ends together. Agage similar to Federal Products Co. No. 57 B-1Y7692 is satisfactory for this
purpose.
F1909−98 (2012)
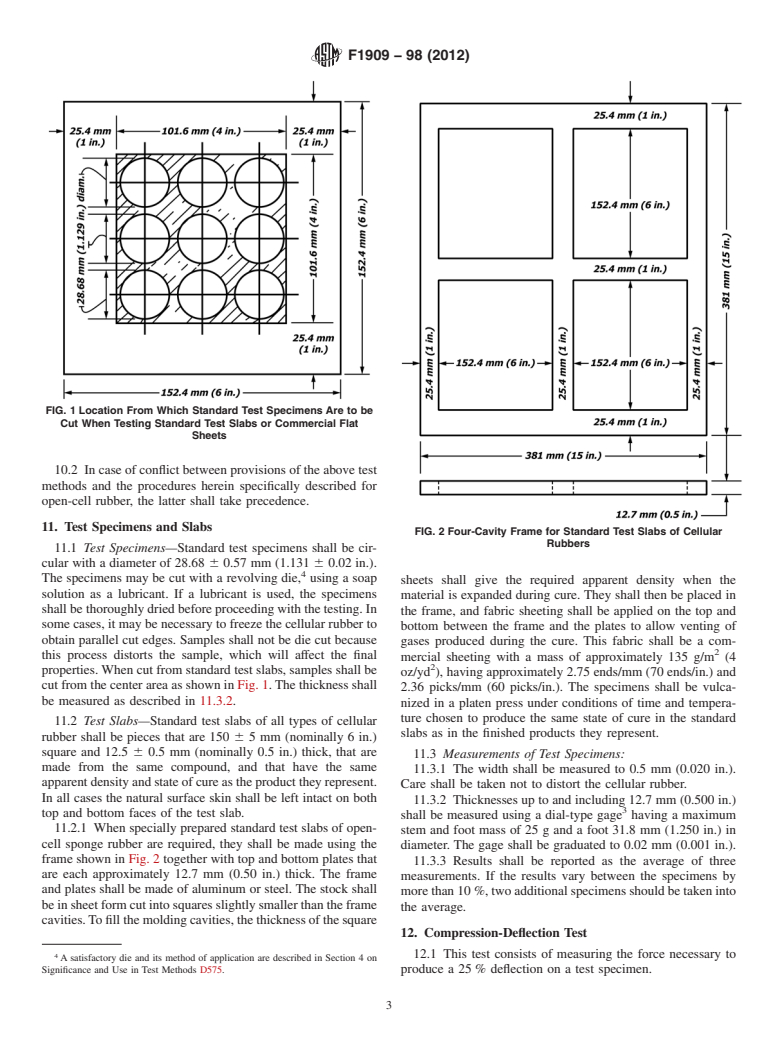
FIG. 1Location From Which Standard Test Specimens Are to be
Cut When Testing Standard Test Slabs or Commercial Flat
Sheets
10.2 In case of conflict between provisions of the above test
methods and the procedures herein specifically described for
open-cell rubber, the latter shall take precedence.
11. Test Specimens and Slabs
FIG. 2Four-Cavity Frame for Standard Test Slabs of Cellular
Rubbers
11.1 Test Specimens—Standard test specimens
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.