ASTM A1064/A1064M-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon-Steel Wire and Welded Wire Reinforcement, Plain and Deformed, for Concrete
Standard Specification for Carbon-Steel Wire and Welded Wire Reinforcement, Plain and Deformed, for Concrete
SCOPE
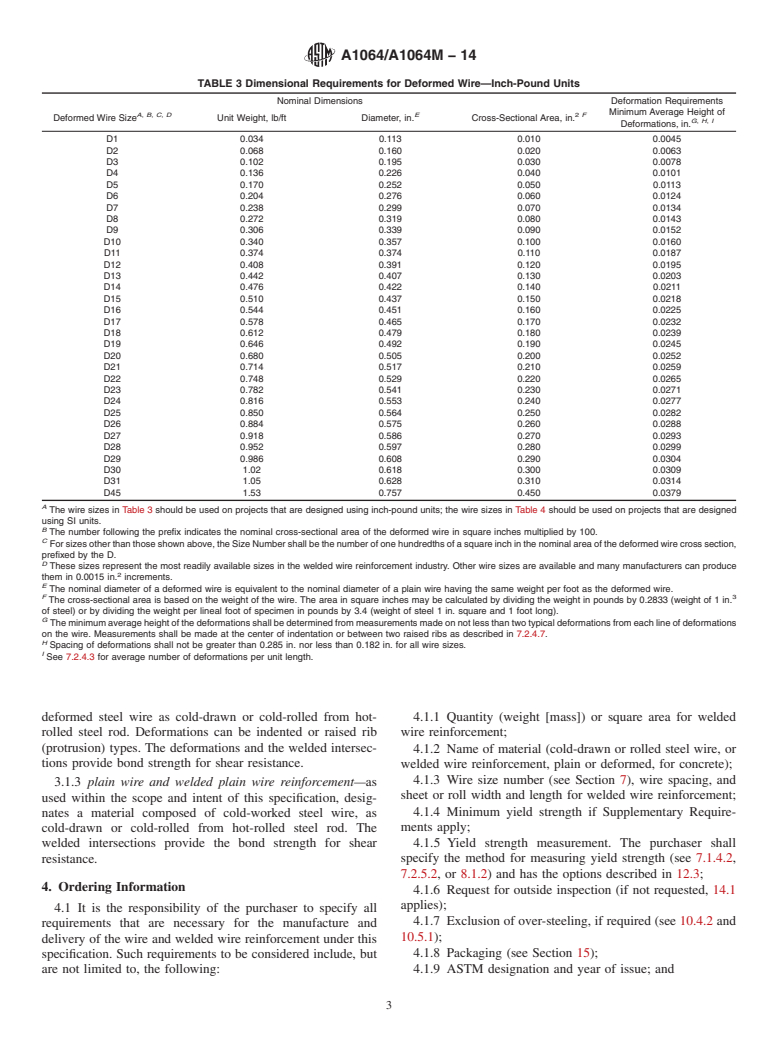
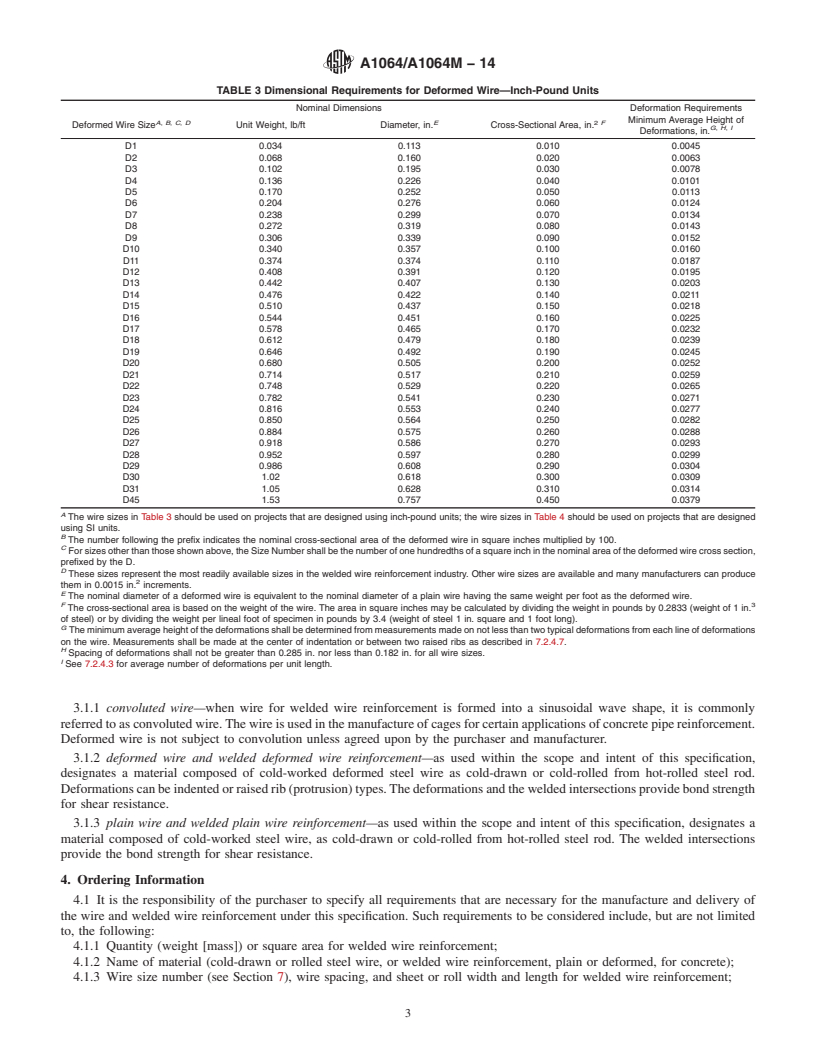
1.1 This specification covers carbon-steel wire and welded wire reinforcement produced from hot-rolled rod to be used for the reinforcement of concrete. The steel wire is cold-worked, drawn or rolled, plain (non-deformed, as-drawn or galvanized), or deformed. Welded wire reinforcement is made from plain or deformed wire, or a combination of plain and deformed wire. Common wire sizes and dimensions are given in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4. Actual wire sizes are not restricted to those shown in the tables. (A) Table 1 should be used on projects that are designed using inch-pound units; Table 2 should be used on projects that are designed using SI units.(B) The number following the prefix indicates the nominal cross-sectional area of the wire in square inches multiplied by 100.(C) For sizes other than those shown above, the Size Number shall be the number of one hundredth of a square inch in the nominal area of the wire cross section, prefixed by the W.(D) These sizes represent the most readily available sizes in the welded wire reinforcement industry. Other wire sizes are available and many manufactures can produce them in 0.0015 in.2 increments.(E) The nominal diameter is based on the nominal area of the wire. (A) The wire sizes in Table 1 should be used on projects that are designed using inch-pound units; the wire sizes in Table 2 should be used on projects that are designed using SI units.(B) The number following the prefix indicates the nominal cross-sectional area of the wire in square milimetres.(C) For sizes other than those shown above, the Size Number shall be the number of square millimetres in the nominal area of the wire cross section, prefixed by the MW.(D) These sizes represent the most readily available sizes in the welded wire reinforcement industry. Other wire sizes are available and many manufactures can produce them in 1 mm2 increments.(E) The nominal diameter is based on the nominal area of the wire. (A) The wire sizes in Table 3 should be used on projects that are designed using inch-pound units; the wire sizes in Table 4 should be used on projects that are designed using SI units.(B) The number following the prefix indicates the nominal cross-sectional area of the deformed wire in square inches multiplied by 100.(C) For sizes other than those shown above, the Size Number shall be the number of one hundredths of a square inch in the nominal area of the deformed wire cross section, prefixed by the D.(D) These sizes represent the most readily available sizes in the welded wire reinforcement industry. Other wire sizes are available and many manufacturers can produce them in 0.0015 in.2 increments.(E) The nominal diameter of a deformed wire is equivalent to the nominal diameter of a plain wire having the same weight per foot as the deformed wire.(F) The cross-sectional area is based on the weight of the wire. The area in square inches may be calculated by dividing the weight in pounds by 0.2833 (weight of 1 in.3 of steel) or by dividing the weight per lineal foot of specimen in pounds by 3.4 (weight of steel 1 in. square and 1 foot long).(G) The minimum average height of the deformations shall be determined from measurements made on not less than two typical deformations from each line of deformations on the wire. Measurements shall be made at the center of indentation or between two raised ribs as described in 7.2.4.7.(H) Spacing of deformations shall not be greater than 0.285 in. nor less than 0.182 in. for all wire sizes.(I) See 7.2.4.3 for average number of deformations per unit length. (A) The wire sizes in Table 3 should be used on projects that are designed using inch-pound units; the wire sizes in Table 4 should be used on projects that are designed using SI units.(B) The number following the prefix indicates the nominal cross-sectional area of the deformed wire in square millimetres.(C) For sizes other than those shown above, the Size Number shall be the number of square ...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A1064/A1064M −14
StandardSpecification for
Carbon-Steel Wire and Welded Wire Reinforcement, Plain
1
and Deformed, for Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1064/A1064M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This specification covers carbon-steel wire and welded
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
wirereinforcementproducedfromhot-rolledrodtobeusedfor
of Steel Products
the reinforcement of concrete. The steel wire is cold-worked,
A641/A641M Specification for Zinc–Coated (Galvanized)
drawnorrolled,plain(non-deformed,as-drawnorgalvanized),
Carbon Steel Wire
or deformed.Welded wire reinforcement is made from plain or
A700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Meth-
deformed wire, or a combination of plain and deformed wire.
3
ods for Steel Products for Shipment (Withdrawn 2014)
CommonwiresizesanddimensionsaregiveninTable1,Table
E83 Practice for Verification and Classification of Exten-
2, Table 3, and Table 4. Actual wire sizes are not restricted to
someter Systems
those shown in the tables.
4
2.2 U.S. Military Standard:
NOTE 1—Welded wire for concrete reinforcement has historically been
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
described by various terms: welded wire fabric, WWF, fabric, and mesh.
4
2.3 U.S. Military Standard:
The wire reinforcement industry has adopted the term welded wire
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipments (Civil Agencies)
reinforcement (WWR) as being more representative of the applications of
5
the products being manufactured. Therefore, the term welded wire fabric 2.4 American Concrete Institute (ACI) Standard:
has been replaced with the term welded wire reinforcement in this
ACI 318 Building Code Requirements for Structural Con-
specification and in related specifications.
crete
2.5 Adjuncts:
1.2 Supplementary Requirements describe high-strength
6
wire, which manufacturers furnish when specifically ordered. Weld Tester Drawing
Manufacturers furnish high-strength wire in place of regular
3. Terminology
wire if mutually agreed to by the purchaser and the manufac-
turer. 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 convoluted wire—when wire for welded wire rein-
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to
forcement is formed into a sinusoidal wave shape, it is
be regarded separately as standard. Within the text the SI units
commonly referred to as convoluted wire. The wire is used in
are shown in brackets (except in Table 2 and Table 4). The
the manufacture of cages for certain applications of concrete
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents;
pipe reinforcement. Deformed wire is not subject to convolu-
therefore,eachsystemmustbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
tion unless agreed upon by the purchaser and manufacturer.
Combining values may result in nonconformance with the
3.1.2 deformed wire and welded deformed wire
specification.
reinforcement—as used within the scope and intent of this
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee www.dodssp.daps.mil.
5
A01.05 on Steel Reinforcement. Available fromAmerican Concrete Institute (ACI), P.O. Box 9094, Farmington
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally Hills, MI 48333-9094, http://www.concrete.org.
6
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as A1064/A1064M – 13. Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
DOI: 10.1520/A1064_A1064M-14. ADJA0185. Original adjunct produced in 1967.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A1064/A1064M − 13 A1064/A1064M − 14
Standard Specification for
Carbon-Steel Wire and Welded Wire Reinforcement, Plain
1
and Deformed, for Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1064/A1064M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers carbon-steel wire and welded wire reinforcement produced from hot-rolled rod to be used for the
reinforcement of concrete. The steel wire is cold-worked, drawn or rolled, plain (non-deformed, as-drawn or galvanized), or
deformed. Welded wire reinforcement is made from plain or deformed wire, or a combination of plain and deformed wire.
Common wire sizes and dimensions are given in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4. Actual wire sizes are not restricted to those
shown in the tables.
NOTE 1—Welded wire for concrete reinforcement has historically been described by various terms: welded wire fabric, WWF, fabric, and mesh. The
wire reinforcement industry has adopted the term welded wire reinforcement (WWR) as being more representative of the applications of the products
being manufactured. Therefore, the term welded wire fabric has been replaced with the term welded wire reinforcement in this specification and in related
specifications.
1.2 Supplementary Requirements describe high-strength wire, which manufacturers furnish when specifically ordered.
Manufacturers furnish high-strength wire in place of regular wire if mutually agreed to by the purchaser and the manufacturer.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text the SI units are
shown in brackets (except in Table 2 and Table 4). The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
system must be used independently of the other. Combining values may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A641/A641M Specification for Zinc–Coated (Galvanized) Carbon Steel Wire
3
A700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods for Steel Products for Shipment (Withdrawn 2014)
E83 Practice for Verification and Classification of Extensometer Systems
4
2.2 U.S. Military Standard:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
4
2.3 U.S. Military Standard:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipments (Civil Agencies)
5
2.4 American Concrete Institute (ACI) Standard:
ACI 318 Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete
2.5 Adjuncts:
6
Weld Tester Drawing
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.05
on Steel Reinforcement.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013Nov. 1, 2014. Published November 2013November 2014. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 20122013
as A1064/A1064M – 12.13. DOI: 10.1520/A1064_A1064M-13. 10.1520/A1064_A1064M-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://www.dodssp.daps.mil.
5
Available from American Concrete Institute (ACI), P.O. Box 9094, Farmington Hills, MI 48333-9094, http://www.concrete.org.
6
Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJA0185. Original adjunct produced in 1967.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A1064/A1064M − 14
A
TABLE 1 Dimensional Requirements for P
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.