ASTM D5898-96(2005)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Standard Details for Adhered Sheet Waterproofing
Standard Guide for Standard Details for Adhered Sheet Waterproofing
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide illustrates general details for below grade and plaza waterproofing. It serves as a guide that will enable the designer to prepare complete waterproofing details for each specific condition that occurs on a project.
SCOPE
p>1.1 This guide covers details for typical conditions encountered in adhered sheet waterproofing on below grade structures and plazas.
1.2 This guide does not cover liquid applied waterproofing.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5898 – 96 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Guide for
Standard Details for Adhered Sheet Waterproofing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5898; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.4 reinforcement, n—generally, one or more strips of
membrane, felts, or fabrics, installed at corners and over
1.1 This guide covers details for typical conditions encoun-
construction joints.
tered in adhered sheet waterproofing on below grade structures
3.3 Abbreviations:
and plazas.
3.3.1 LAM—liquid applied membrane.
1.2 This guide does not cover liquid applied waterproofing.
3.3.2 SS—stainless steel.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.3.3 EJ—expansion joint.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.3.4 NR—not recommended.
only.
3.3.5 MTL—noncorrosive metal.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1 Thisguideillustratesgeneraldetailsforbelowgradeand
D1079 Terminology Relating to Roofing and Waterproofing
plaza waterproofing. It serves as a guide that will enable the
3. Terminology
designer to prepare complete waterproofing details for each
specific condition that occurs on a project.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this guide,
refer to Terminology D1079.
5. Drawings
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.1 This guide is not all inclusive. The designer should
3.2.1 adhered sheet waterproofing, n—a system consisting
detail all typical and special conditions on the project, paying
of one or more plies of organic or glass fiber felts or fabrics
particular attention to transitions in plane and intersection of
appliedinhotorcoldbitumensormodifiedbitumens,oroneor
different details. The applicator should provide shop drawings
more plies of a manufactured sheet of modified bitumen that
of each condition to confirm field conditions and to verify his
may be reinforced or laminated with scrim or polyethylene, or
understanding of the design intent.
a polymeric or vulcanized elastomeric membrane. The system
5.2 Waterproofing membranes and reinforcement are indi-
is applied directly to concrete or masonry surfaces below
cated on the figures as a single thick line, regardless of the
grade.
number of plies.
3.2.2 elevated slab, n—a framed or suspended concrete slab
5.3 Protection layers have been omitted for clarity. See
over a habitable or useable space.
Section 6.
3.2.3 fillet, n—liquid applied modified bitumen or mastic
used at internal corners before membrane application to form a
6. Protection
transition of less than 90°.
6.1 Protection materials are required over all waterproofing
to prevent damage from backfill, reinforcing chairs, and
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D08 on Roofing and
construction traffic, unless the membrane system incorporates
Waterproofing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D08.22 on
an integral protection layer. Protection also is required where
Waterproofing and Damproofing Systems.
membranes terminate above grade and may be exposed to
Current edition approved July 1, 2005. Published July 2005. Originally approved
in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as D5898 – 96. DOI: 10.1520/ ultraviolet light.
D5898-96R05.
6.2 Materials for protection include: asphalt composition
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
boards, plastic drainage panels, low density expanded polysty-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
rene boards, and extruded polystyrene insulation. Low density
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D5898 – 96 (2005)
expanded polystyrene boards and some types of plastic drain- 9. Expansion Joints
age panels are not suitable for protection on horizontal sur-
9.1 Structural expansion joints should be designed to permit
faces. Protection materials are loose-laid on horizontal mem-
independent movement of structural elements on each side of
branes and attached to vertical membranes with compatible
the joint. Control joints should be located to permit non-
adhesives. They should be installed as soon as possible after
reversible movement and may be dynamic. The size and
the membrane, or each portion of it, is completed or water
location of expansion and control joints should be determined
tested.
by the structural engineer. Expansion joint covers should be
designed to maintain continuity at all changes in plane. They
7. Reinforcement
should be designed to prevent displacement when subjected to
waterpressure.Wheretheyoccurinelevatedslabs,theyshould
7.1 Reinforcement is required for built-up and modified
be raised above the surface. Control joints are not detailed as
bitumenmembranesattransitions,suchasinternalandexternal
expansion joints but should be reinforced in all membrane
corners and at static concrete construction joints and cracks.
systems.
Reinforcement also is required where reinforcing bars, pipes,
and conduits penetrate the membrane. Separate reinforcement
10. Structural Items
generally is not required for polymeric and vulcanized elasto-
10.1 Water stops, keyways, and other structural elements
meric membranes.
that are frequently installed in construction and control joints
7.2 Reinforcement usually is installed before the membrane
are not indicated on the details.
but may be applied over it. Refer to the membrane manufac-
turer for details.
11. Mud Mats
7.3 The minimum reinforcement is one ply. Systems using a
11.1 Mud mats are cast on the subgrade to support water-
multiple ply membrane usually require two or more reinforce-
proofing. Protection boards and tamped sand beds may be
ment plies, whereas single ply modified bitumen systems
acceptable alternates with some manufacturers.
generally require one.
12. Planters, Bench, and Equipment Supports
7.4 When additional plies are used as reinforcement, they
should extend at least 150 mm (6 in.) beyond the corner or
12.1 Waterproofing membranes on horizontal surfaces
penetration and each succeeding ply should extend 75 mm (3
should be carried under planters and supports without inter-
in.) beyond the previous ply.
ruption. Such items should be installed on the concrete
7.5 Where reinforcing bars penetrate waterproofing, such as protection slab. Waterproofing of planters should be indepen-
at rock anchors and wall to slab transitions, they should be dent of the slab waterproofing.
sealedwithreinforcingpliesfingercutaroundthebarsorliquid
13. Explanatory Notes
applied membrane or both.
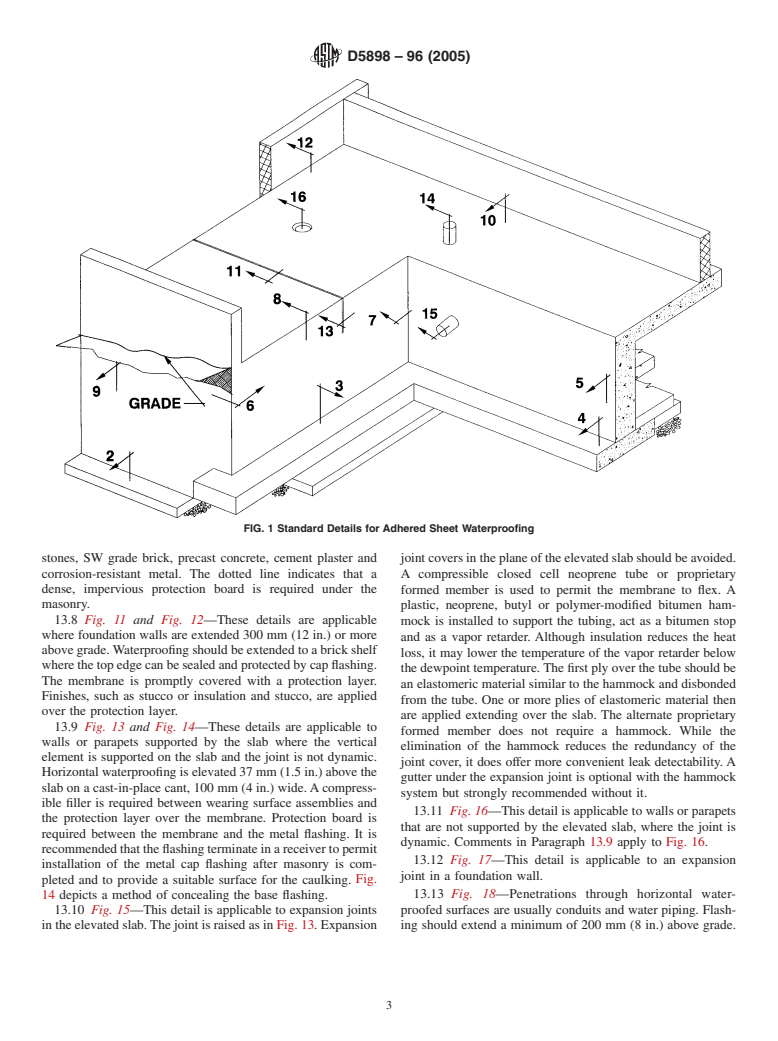
13.1 Fig. 1—Standard details for adhered sheet waterproof-
7.6 Some manufacturers require cementitious cants or a
ing.
liquid applied waterproofing or mastic fillet at reentrant angles,
13.2 Fig. 2—This detail is applicable to tunnels and condi-
chamfered external corners, and other special conditions to be
tions where the width of excavations is limited.Alternately, the
implemented during construction. These should be indicated
mud mat may be omitted and waterproofing applied to the top
on project details.
of a structural slab and turned down to the toe. Then,
7.7 Details should recognize the normal sequencing of
waterproofing is covered with a cementitious wearing course.
construction. Foundation walls may be cast before or after
13.3 Fig. 3—Slab with mud mat.
slabs on grade. Structural slabs are cast after walls. Water-
13.4 Fig. 4—Footing with mud mat.
proofing of individual elements frequently follows this se-
13.5 Fig. 5—This detail is applicable to conditions where
quence, for example, walls are waterproofed before the struc-
there is no hydrostatic head below the slab.
tural slab is cast. The resultant cold joints may be dynamic.
13.6 Fig. 6, Fig. 7, and Fig. 8—Where internal and external
vertical corners meet horizontal surfaces, isometric drawings
8. Penetrations
prepared by the designer or applicator are required to indicate
8.1 Flashing at penetrations should accommodate differen-
the assembly of the overlapping plies.
tial movement between the s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.