ASTM E124-94(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Weighing and Drying Apparatus for Microchemical Analysis
Standard Specification for Weighing and Drying Apparatus for Microchemical Analysis
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the general requirements for the components that comprise the apparatus used for the weighing and drying operations in the laboratory practice of microchemical analysis. The components covered here are the following: combustion boats; weighing bottles, cup, and tubes; spatulas; forceps; tare flasks; metal cooling block; metal crucible container with glass cover; and micro glass desiccator with metal insert.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers apparatus used for weighing and drying operations in microchemical laboratory practice.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The metric equivalents may be approximate.
Note1—This specification was originally developed by the Committee on Microchemical Apparatus, Division of Analytical Chemistry, American Chemical Society.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E124 – 94 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
Weighing and Drying Apparatus for Microchemical Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E124; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
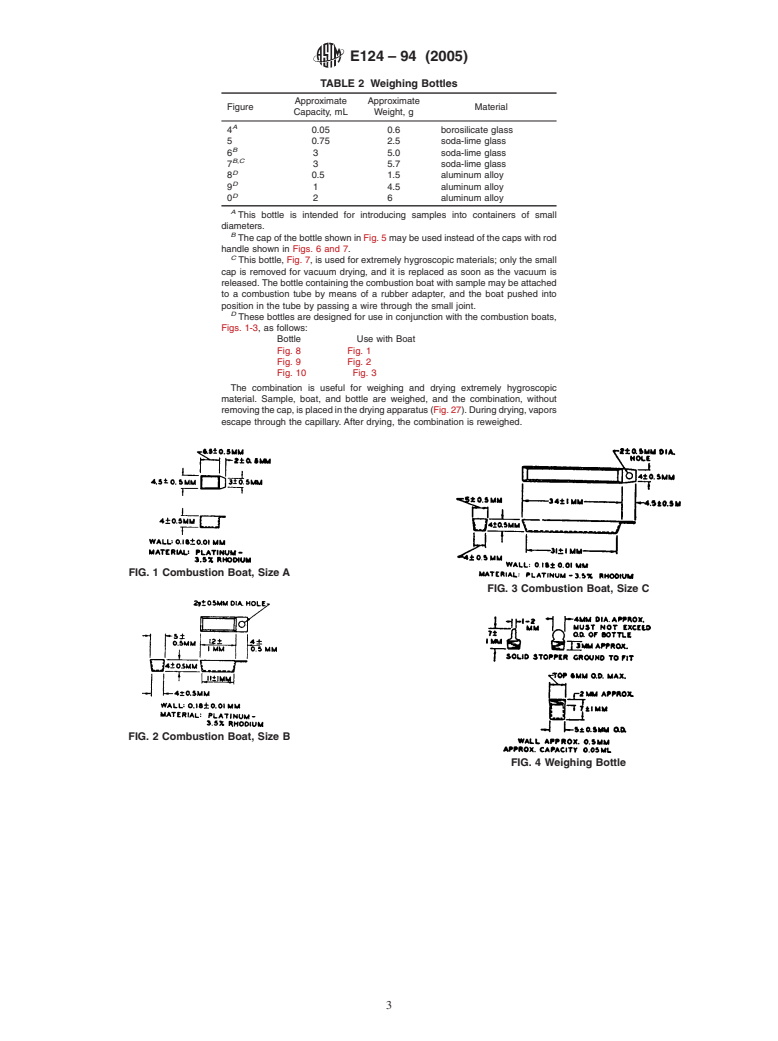
1. Scope 4. Weighing Bottles
1.1 This specification covers apparatus used for weighing 4.1 Weighing bottles of seven capacities shall conform to
and drying operations in microchemical laboratory practice. the requirements in Table 2 and Figs. 4-9, inclusive.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
5. Weighing Cup
as the standard. The metric equivalents may be approximate.
5.1 The weighing cup shall conform to the requirements
NOTE 1—ThisspecificationwasoriginallydevelopedbytheCommittee
shown in Fig. 11, and shall be made of platinum-rhodium alloy
on MicrochemicalApparatus, Division ofAnalytical Chemistry,American
containing 3.5 % rhodium. The cup is designed to be used as a
Chemical Society.
sample container to fit into the weighing bottle shown in Fig.
2. Referenced Documents
5, and is useful for weighing hygroscopic materials.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6. Weighing Tubes
E671 Specification for Maximum Permissible Thermal Re-
6.1 Weighing tubes of three types shall conform to the
sidual Stress in Annealed Glass Laboratory Apparatus
requirements shown in Fig. 12, Fig. 13, and Fig. 14. These
E920 Specification for Commercially Packaged Laboratory
tubes should preferably be made of soda-lime glass.
Apparatus
E921 Specification for Export Packaged Laboratory Appa-
7. Spatulas
ratus
7.1 Spatulas of four types, and preferably made of stainless
E1133 Practice for Performance Testing of Packaged Labo-
steel, shall conform to the following requirements:
ratory Apparatus for United States Government Procure-
7.1.1 TypeA(Fig.15)—Thisspatulaisgenerallyuseful.The
ments
top can be used for crushing crystals and the bent blade for
E1157 Specification for Sampling and Testing of Reusable
scraping containers.
Laboratory Glassware
7.1.2 Type B (Fig. 16)—This spatula has a flat bent portion
3. Combustion Boats
at one end and a V-shaped scoop at the other end. It is
particularly useful for weighing samples.
3.1 Combustion boats of three sizes shall conform to the
7.1.3TypeC(Fig. 17)—This spatula is suitable for the
requirements in Table 1 and Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3. These
larger samples commonly encountered in semimicro and pre-
boats shall be made of platinum-rhodium alloy containing
parative work. It has a U-shaped scoop at one end and a
3.5 % rhodium.
V-shapedscoopattheotherend.Thespatulacanbeusedtoadd
shot or beads to tare flasks and for measuring and introducing
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E41 on
solid reagent into combustion tubes.
Laboratory Apparatus and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E41.01 on
7.1.4TypeD(Fig. 18)—This spatula is useful in many
Apparatus.
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published May 2005. Originally microchemical applications.
approved in 1956. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as E124 – 94 (1999).
DOI: 10.1520/E0124-94R05.
8. Forceps
See the “1949 Report on Recommended Specifications for Microchemical
8.1 Forceps of two types, made of nickel-plated steel, shall
Apparatus, Carbon-Hydrogen, Dumas Nitrogen, Sulfur and Halogen,” Analytical
Chemistry, Vol 21, December 1949, p. 1555; and the “1953 Report on Recom- conform to the following requirements:
mended Specifications for Microchemical Apparatus, Weighing and Drying,”
8.1.1 Forceps with Platinum—5% Ruthenium Tips (Fig.
Analytical Chemistry, Vol 26, July 1954, p. 1186.
19) The pin serves as a stop to prevent the forceps from being
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
depressed to such an extent that the tips can open, allowing the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E124 – 94 (2005)
held object to drop. When pressed together, the tips make desiccator with cover and an aluminum insert which shall hold
1 1
contact for a distance of ⁄4 to ⁄2 in. (6.4 to 12.7 mm). securely the metal cooling block, Fig. 24. This combination
serves the same purpose as that described in Section 11, but
NOTE 2—Depending upon the intended use, other materials may be
permits the additional use of drying agents of other chemicals
substituted for the platinum alloy. Thec construction and over-all dimen-
in the bottom container.
sions should be identical with those shown in Fig. 19.
8.1.2 Forceps with Conical Tapered Holders (Fig. 20)—
13. Drying Apparatus
These forceps shall be made of spring steel.They are useful for
handling weighing tubes, absorption tubes, filter tubes, etc. 13.1 The drying apparatus shall be of theAbderhalden type
and shall conform to the requirements shown in Fig. 27.
9. Tare Flasks
NOTE 3—The shape of the tube attached to the ball joint, in the
9.1 Tare flasks of three types, made of soda-lime glass, shall
desiccator bulb, is intended to prevent desiccant from being carried over
conformtotherequirementsshowninFig.21,Fig.22,andFig.
into the sample when the vacuum is broken. A cap for the ball joint and
23. The serial numbers shall be etched on the flasks.
stopper for the standard taper 40/50 joint may be used to protect the
desiccant when the bulb is disconnected and stands alone. The upward
10. Metal Cooling Block
indentation in the vapor tube prevents cooling of the drying chamber by
10.1 The metal cooling block shall conform to the require-
cold condensate.
ments shown in Fig. 24, and shall be made of a metal or alloy
14. Maximum Permissible Thermal Residual Stress
w
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.