ASTM F1914-18(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Short-Term Indentation and Residual Indentation of Resilient Floor Covering
Standard Test Methods for Short-Term Indentation and Residual Indentation of Resilient Floor Covering
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
11.1 The indentation and the residual indentation of resilient floor covering is important since the resistance and recovery from indentation reflects on the ability of the resilient floor covering to perform properly after installation.
11.2 The indentation of a resilient floor covering shall be measured using a specified type of indentor, flat or spherical, under a specified load and time.
11.3 The residual indentation of a resilient floor covering shall be measured after a specified recovery time.
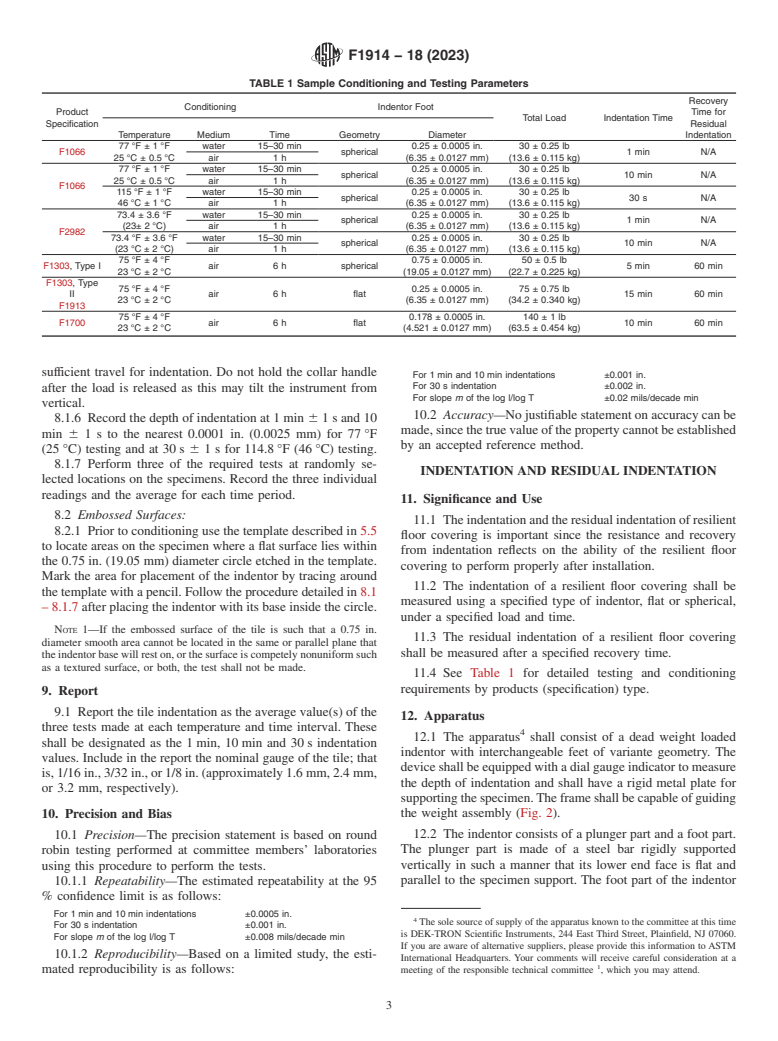
11.4 See Table 1 for detailed testing and conditioning requirements by products (specification) type.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers procedures to determine short-term indentation and residual indentation of resilient flooring, when subjected to concentrated loads.
1.2 The test methods appear in the following order:
Section
Indentation by McBurney2 Test
4 to 10
Indentation and Residual Indentation
11 to 15
1.3 There are two procedures with their respective apparatus. The first (McBurney Test) is described in Sections 4 to 10 and is restricted to a spherical foot. It is only used for initial indentation measurements of VCT. The second is described in Sections 11 to 15 and has interchangeable feet with variable geometry. It is used to measure initial and residual indentation.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1914 − 18 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Methods for
Short-Term Indentation and Residual Indentation of
Resilient Floor Covering
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1914; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers procedures to determine short-
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
term indentation and residual indentation of resilient flooring,
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
when subjected to concentrated loads.
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
1.2 The test methods appear in the following order:
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
F141 Terminology Relating to Resilient Floor Coverings
Section
F1066 Specification for Vinyl Composition Floor Tile
Indentation by McBurney Test 4 to 10
Indentation and Residual Indentation 11 to 15 F1303 Specification for Sheet Vinyl Floor Covering with
Backing
1.3 There are two procedures with their respective appara-
F1700 Specification for Solid Vinyl Floor Tile
tus. The first (McBurney Test) is described in Sections 4 to 10
F1913 Specification for Vinyl Sheet Floor Covering Without
and is restricted to a spherical foot. It is only used for initial
Backing
indentation measurements of VCT. The second is described in
F2982 Specification for Polyester Composition Floor Tile
Sections 11 to 15 and has interchangeable feet with variable
geometry. It is used to measure initial and residual indentation.
3. Terminology
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
method, refer to Terminology F141.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard. INITIAL INDENTATION MEASUREMENTS OF VCT
(MCBURNEY TEST)
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 This test method measures short-term indentation of
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
resilient flooring and is useful as a predictor of performance in
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
actual installations over time.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.2 The slope, m, of a log-log plot indentation (I) versus
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the time (T), is related to the indentation of tile in service. The
115 °F (46 °C) indentation is a measure of the tendency of the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical tile to indent at temperatures above 77 °F (25 °C).
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Apparatus —The indentation tester is a spherical foot
1 device consisting essentially of a rigidly mounted indentor
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F06 on Resilient
Floor Coverings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F06.20 on Test acting under an initial load of 2.00 lbf 6 0.02 lbf (8.90 N 6
Methods.
0.09 N) and a total deadweight load of 30.00 lbf 6 0.25 lbf
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2023. Published January 2024. Originally
(133.45 N 6 1.11 N) with a suitable dial indicator, calibrated in
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as F1914 – 18. DOI:
10.1520/F1914-18R23.
The sole source of supply of the McBurney Indentation Tester known to the
committee at this time is Frazier Precision Co, Gaithersburg, MD. If you are aware For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
responsible technical committee , which you may attend. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1914 − 18 (2023)
0.0005 in. (0.01 mm) increments. The spherical foot shall be 7.3 Condition the indentation tester and glass plate in the
0.250 in. 6 0.0005 in. (6.35 mm 6 0.01 mm) in diameter. A same medium and for at least the same time period as the
suitable apparatus is shown in Fig. 1.
specimen(s).
5.2 Flat Glass Plate, of 0.25 in. (6.35 mm) minimum
8. Procedures
thickness for supporting the specimen and tester during test.
5.3 Timing Device that will indicate the time in seconds. 8.1 Nonembossed Surfaces:
8.1.1 Place the specimen on the glass plate with the wearing
5.4 Thermometer, calibrated as in Specification E2251.
surface up.
5.5 Circular Plexiglas Template, 3.50 in. (88.9 mm) in
8.1.2 Place the indentor on the specimen. Be sure the
diameter, 0.25 in. (6.35 mm) thick and having a 0.3125 in.
indentor tip is retracted into the base when the instrument is
(7.94 mm) diameter hole drilled in the center and a 0.75 in.
placed on the specimen and when being moved to another test
(19.05 mm) diameter concentric circle etched on the face.
location.
5.6 Water Baths, or air atmosphere maintained at 77 °F 6
8.1.3 Apply the initial 2 lbf (8.9 N) load (shaft assembly) to
0.9 °F (25 °C 6 0.5 °C) or 115 °F 6 1 °F (46 °C 6 0.5 °C).
the specimen surface.
6. Test Specimens
8.1.3.1 Position the 28 lbf (124.5 N) load on the specimen
by holding down with the thumb the 2 lbf (8.9 N) shaft cross
6.1 The test specimen shall be a full tile, usually 12 in. by 12
bar to proper load.
in. (approximately 305 mm by 305 mm) or 9 in. by 9 in.
(approximately 230 mm by 230 mm). Larger tiles shall be cut 8.1.3.2 Gently lower the load to force the shaft cross bar
to one of the above sizes. upward until there is no clearance between the shaft and the
upper wear plate. This will ensure proper 2 lbf (8.9 N) loading
7. Conditioning
and positioning of the 28 lbf (124.5 N) load.
7.1 For testing in air, condition the specimen(s) for 1 h at the
8.1.4 Set the dial gauge at zero.
test temperature.
8.1.5 Release the 28 lbf (124.5 N) load and start the timing
device. (Steps 8.1.3 – 8.1.5 should not exceed a total of 5 s.)
7.2 For testing in water, condition the specimen(s) at the test
temperature for 15 min minimum and 30 min maximum (see Load release should be smooth and as mechanical as possible.
Table 1). Turn the collar at least one-half turn beyond release to allow
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Measuring Indentation: McBurney
F1914 − 18 (2023)
TABLE 1 Sample Conditioning and Testing Parameters
Recovery
Conditioning Indentor Foot
Product Time for
Total Load Indentation Time
Specification Residual
Temperature Medium Time Geometry Diameter Indentation
77 °F ± 1 °F water 15–30 min 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 30 ± 0.25 lb
F1066 spherical 1 min N/A
25 °C ± 0.5 °C air 1 h (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (13.6 ± 0.115 kg)
77 °F ± 1 °F water 15–30 min 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 30 ± 0.25 lb
spherical 10 min N/A
25 °C ± 0.5 °C (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (13.6 ± 0.115 kg)
air 1 h
F1066
115 °F ± 1 °F water 15–30 min 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 30 ± 0.25 lb
spherical 30 s N/A
46 °C ± 1 °C air 1 h (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (13.6 ± 0.115 kg)
73.4 ± 3.6 °F water 15–30 min 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 30 ± 0.25 lb
spherical 1 min N/A
(23± 2 °C) air 1 h (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (13.6 ± 0.115 kg)
F2982
73.4 °F ± 3.6 °F water 15–30 min 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 30 ± 0.25 lb
spherical 10 min N/A
(23 °C ± 2 °C) air 1 h (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (13.6 ± 0.115 kg)
75 °F ± 4 °F 0.75 ± 0.0005 in. 50 ± 0.5 lb
F1303, Type I air 6 h spherical 5 min 60 min
23 °C ± 2 °C (19.05 ± 0.0127 mm) (22.7 ± 0.225 kg)
F1303, Type
75 °F ± 4 °F 0.25 ± 0.0005 in. 75 ± 0.75 lb
II air 6 h flat 15 min 60 min
23 °C ± 2 °C (6.35 ± 0.0127 mm) (34.2 ± 0.340 kg)
F1913
75 °F ± 4 °F 0.178 ± 0.0005 in. 140 ± 1 lb
F1700 air 6 h flat 10 min 60 min
23 °C ± 2 °C (4.521 ± 0.0127 mm) (63.5 ± 0.454 kg)
sufficient travel for indentation. Do not hold the collar handle
For 1 min and 10 min indentations ±0.001 in.
For 30 s indentation ±0.002 in.
after the load is released as this may tilt the instrument from
For slope m of the log l/log T ±0.02 mils/decade min
vertical.
10.2 Accuracy—No justifiable statement on accuracy can be
8.1.6 Record the depth of indentation at 1 min 6 1 s and 10
made, since the true value of the property cannot be established
min 6 1 s to the nearest 0.0001 in. (0.0025 mm) for 77 °F
by an accepted reference method.
(25 °C) testing and at 30 s 6 1 s for 114.8 °F (46 °C) testing.
8.1.7 Perform three of the required tests at randomly se-
INDENTATION AND RESIDUAL INDENTATION
lected locations on the specimens. Record the three individual
readings and the average for each time period.
11. Significance and Use
8.2 Embossed Surfaces:
11.1 The indentation and the residual indentation of resilient
8.2.1 Prior to conditioning use the template described in 5.5
floor covering is important since the resistance and recovery
to locate areas on the specimen where a flat surface lies within
from indentatio
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.