ASTM D5197-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Formaldehyde and Other Carbonyl Compounds in Air (Active Sampler Methodology)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Formaldehyde and Other Carbonyl Compounds in Air (Active Sampler Methodology)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
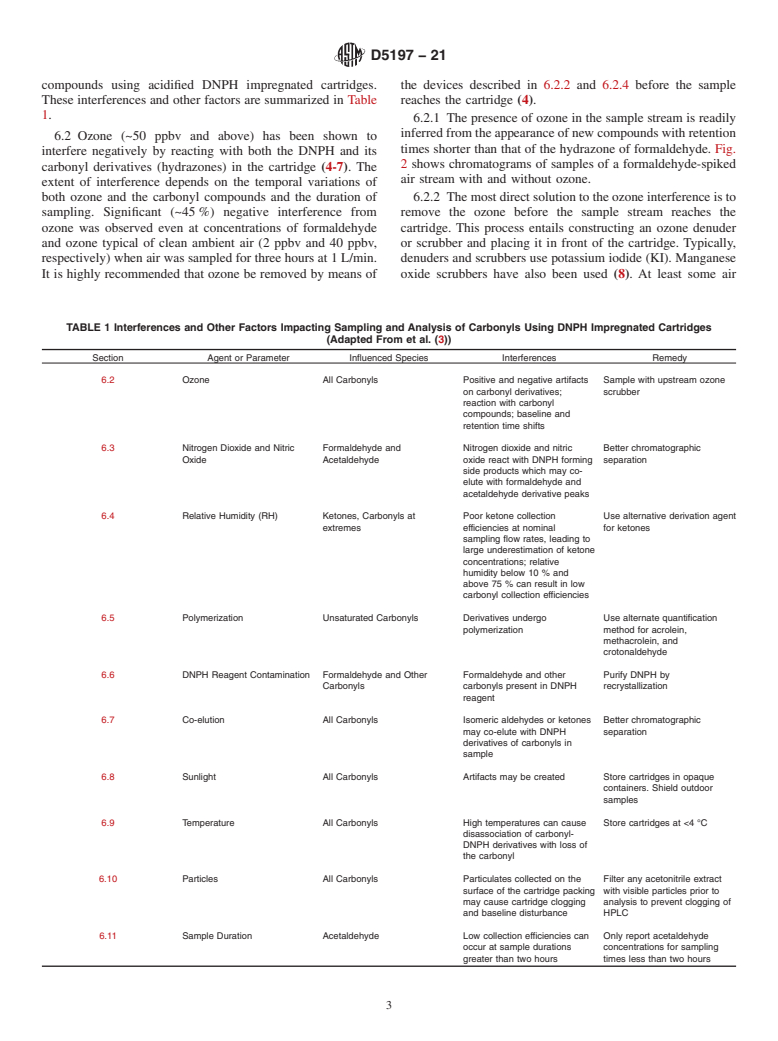
5.1 This test method provides an analytical procedure for measuring formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds in indoor, workplace, ambient air or for emission testing.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method presents a procedure for the determination of formaldehyde (HCHO) and other carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) in air. Other carbonyl compounds that have been successfully quantified by this method include acetaldehyde, acetone, propanal (propionaldehyde), 2-butanone (methyl ethyl ketone), butyraldehyde, benzaldehyde, isovaleraldehyde, valeraldehyde, o-tolualdehyde, m-tolualdehyde, p-tolualdehyde, hexanal, and 2,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde.
1.2 This test method involves drawing air through a cartridge containing silica gel coated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) reagent. Carbonyl compounds readily form stable derivatives with the acidified DNPH reagent. The DNPH derivatives are analyzed for parent aldehydes and ketones using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). UHPLC systems use higher pressures and smaller particle sizes in columns compared to HPLC systems. The sampling procedure is a modification of U.S. EPA Method TO-11A (see 2.2).
1.3 This test method is based on the reaction of carbonyl compounds with DNPH in the presence of an acid to form stable derivatives according to the reaction shown in Fig. 1, (where: both R and R1 are alkyl or aromatic groups (ketones), or either, or both R or R1 is a hydrogen atom (aldehydes)). The determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds, as DNPH derivatives, is similar to that of U.S. EPA Method TO-11A in that it uses HPLC or UHPLC for separation of carbonyl compounds followed by UV adsorption or photodiode array detection. This test method exceeds the stated applicability of TO-11A to include other carbonyl compounds that can be determined as stated in 10.2.4. This test method is suitable for determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds in the airborne concentration range from approximately 10 ppbv/v (12 μg/m3), requires sampling for 1 h at 1 L/min) to 1 ppmv/v (1.2 mg/m3). Lower concentrations in air may be determined using higher sampling volume and with control of contamination, appropriate selection of flow rate and sampling duration.
FIG. 1 Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds
1.4 The sampling method gives a time-weighted average (TWA) sample. It can be used for long-term (1 to 24 h) or short-term (5 to 60 min) sampling of air for formaldehyde. Shorter sampling times or low flow rates will result in higher detection limits and may result in greater variation in co-located sampler results. Tests should be performed over a duration and a flow rate that allows the data quality objective of the project to be achieved. Sample times for other carbonyls, such as acetaldehyde, may be limited to short term (1).2 The data provides total concentrations of carbonyl compounds from which time weighted average concentrations can be calculated.
1.5 This test method instructs the user on how to prepare sampling cartridges from commercially available chromatographic grade silica gel cartridges3 by the application of acidified DNPH to each cartridge.
1.6 The sampling flow rate, as described in this test method, has been validated for sampling rates up to 1.5 L/min for formaldehyde. This flow rate limitation is principally due to the high pressure drop (>8 kPa at 1.0 L/min) across user prepared silica gel cartridges which have a particle size of 55 to 105 µm. These cartridges are not generally compatible with battery-powered pumps used in personal sampling equipment (for example, those used by industrial hygienists).
1.7 Alternatively, pre-coated DNPH silica gel cartridges are commercially available and may be substituted provided they can be demonstrated to meet blank and analyte trapping acceptance criteria (2). Some of these use silica gel of a larger parti...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5197 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Formaldehyde and Other Carbonyl
1
Compounds in Air (Active Sampler Methodology)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5197; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
3
1. Scope 1ppm (1.2mg⁄m ). Lower concentrations in air may be
v/v
determined using higher sampling volume and with control of
1.1 This test method presents a procedure for the determi-
contamination, appropriate selection of flow rate and sampling
nation of formaldehyde (HCHO) and other carbonyl com-
duration.
pounds (aldehydes and ketones) in air. Other carbonyl com-
pounds that have been successfully quantified by this method 1.4 The sampling method gives a time-weighted average
include acetaldehyde, acetone, propanal (propionaldehyde), (TWA) sample. It can be used for long-term (1 to 24 h) or
2-butanone (methyl ethyl ketone), butyraldehyde, short-term (5 to 60 min) sampling of air for formaldehyde.
benzaldehyde, isovaleraldehyde, valeraldehyde, Shorter sampling times or low flow rates will result in higher
o-tolualdehyde, m-tolualdehyde, p-tolualdehyde, hexanal, and detection limits and may result in greater variation in co-
2,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde. located sampler results. Tests should be performed over a
duration and a flow rate that allows the data quality objective
1.2 This test method involves drawing air through a car-
oftheprojecttobeachieved.Sampletimesforothercarbonyls,
tridge containing silica gel coated with 2,4-
2
such as acetaldehyde, may be limited to short term (1). The
dinitrophenylhydrazine(DNPH)reagent.Carbonylcompounds
dataprovidestotalconcentrationsofcarbonylcompoundsfrom
readily form stable derivatives with the acidified DNPH
whichtimeweightedaverageconcentrationscanbecalculated.
reagent. The DNPH derivatives are analyzed for parent alde-
hydes and ketones using high performance liquid chromatog- 1.5 This test method instructs the user on how to prepare
raphy (HPLC) or ultra-high performance liquid chromatogra- sampling cartridges from commercially available chromato-
3
phy (UHPLC). UHPLC systems use higher pressures and graphic grade silica gel cartridges by the application of
smaller particle sizes in columns compared to HPLC systems. acidified DNPH to each cartridge.
The sampling procedure is a modification of U.S. EPAMethod
1.6 Thesamplingflowrate,asdescribedinthistestmethod,
TO-11A (see 2.2).
has been validated for sampling rates up to 1.5 L/min for
1.3 This test method is based on the reaction of carbonyl formaldehyde.Thisflowratelimitationisprincipallyduetothe
compounds with DNPH in the presence of an acid to form
high pressure drop (>8 kPa at 1.0 L/min) across user prepared
stable derivatives according to the reaction shown in Fig. 1, silicagelcartridgeswhichhaveaparticlesizeof55to105µm.
1
(where: both R and R are alkyl or aromatic groups (ketones),
These cartridges are not generally compatible with battery-
1
or either, or both R or R is a hydrogen atom (aldehydes)).The powered pumps used in personal sampling equipment (for
determinationofformaldehydeandothercarbonylcompounds,
example, those used by industrial hygienists).
as DNPH derivatives, is similar to that of U.S. EPA Method
1.7 Alternatively, pre-coated DNPH silica gel cartridges are
TO-11A in that it uses HPLC or UHPLC for separation of
commercially available and may be substituted provided they
carbonylcompoundsfollowedbyUVadsorptionorphotodiode
can be demonstrated to meet blank and analyte trapping
array detection. This test method exceeds the stated applica-
acceptance criteria (2). Some of these use silica gel of a larger
bilityofTO-11Atoincludeothercarbonylcompoundsthatcan
particle size that results in a lower pressure drop across the
be determined as stated in 10.2.4. This test method is suitable
cartridge. These low pressure drop cartridges may be more
for determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl com-
suitable for sampling air using battery-powered personal sam-
poundsintheairborneconcentrationrangefromapproximately
pling pumps.
3
10ppb (12 µg/m ), requires sampling for 1h at 1L⁄min) to
v/v
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air. this standard.
3
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2021. Published May 2022. Orig
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5197 − 16 D5197 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Formaldehyde and Other Carbonyl
1
Compounds in Air (Active Sampler Methodology)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5197; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method presents a procedure for the determination of formaldehyde (HCHO) and other carbonyl compounds
(aldehydes and ketones) in air. Other carbonyl compounds that have been successfully quantified by this method include
acetaldehyde, acetone, propanal (propionaldehyde), 2-butanone (methyl ethyl ketone), butyraldehyde, benzaldehyde,
isovaleraldehyde, valeraldehyde, o-tolualdehyde, m-tolualdehyde, p-tolualdehyde, hexanal, and 2,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde.
1.2 This test method involves drawing air through a cartridge containing silica gel coated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
(DNPH) reagent. Carbonyl compounds readily form stable derivatives with the acidified DNPH reagent. The DNPH derivatives
are analyzed for parent aldehydes and ketones utilizingusing high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). (HPLC) or
ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). UHPLC systems use higher pressures and smaller particle sizes in
columns compared to HPLC systems. The sampling procedure is a modification of U.S. EPA Method TO-11A (see 2.2).
1.3 This test method is based on the specific reaction of carbonyl compounds with DNPH in the presence of an acid to form stable
1
derivatives according to the reaction shown in Fig. 1, (where: both R and R are alkyl or aromatic groups (ketones), or either, or
1
both R or R is a hydrogen atom (aldehydes)). The determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds, as DNPH
derivatives, is similar to that of U.S. EPA Method TO-11A in that it utilizes HPLC with UV detection as the analytical finish. The
applicability of this test method is extended beyond uses HPLC or UHPLC for separation of carbonyl compounds followed by UV
adsorption or photodiode array detection. This test method exceeds the stated applicability of TO-11A to include other carbonyl
compounds that can be determined as stated in 10.2.4. This test method is suitable for determination of formaldehyde and other
3
carbonyl compounds in the airborne concentration range from approximately 1010 ppb ppb (12 μg/m ), requires sampling for
v/v
3
1 h at 1 L ⁄min) to 11 ppm ppm(1.2 mg ⁄m (v/v). ). Lower concentrations in air may be determined with careful using higher
v/v
sampling volume and with control of contamination, appropriate selection of flow rate and sampling duration.
1.4 The sampling method gives a time-weighted average (TWA) sample. It can be used for long-term (1 to 24 h) or short-term
(5 to 60 min) sampling of air for formaldehyde. Shorter sampling times or low flow rates will result in higher detection limits and
may result in greater variation in co-located sampler results. Tests should be performed over a duration and a flow rate that allows
the data quality objective of the project to be achieved. Sample times for other carbonyls, such as acetaldehyde, may be limited
2
to short term (1). The data provides total concentrations of carbonyl compounds from which time weighted average concentrations
can be calculated.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016Sept. 1, 2021. Published November 2016May 2022. Originally approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 20092016 as
ɛ1
D5197 – 09D5197 – 16. . DOI: 10.1520/D5197-16.10.1520/D5197-22.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5197 − 21
FIG. 1 Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds
1.5 This test method instructs the user on how to prepare sampling cartridges from commercially available chromatographic grade
3
silica gel cartridges by the application of acidified DNPH to each cartridge.
1.6 The sampling flow rate, as described in this test method, has been validated for sampling rates up to 1.5 L/min for
formaldehyde. This flow rate
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.