ASTM F1115-95(2001)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Carbon Dioxide Loss of Beverage Containers
Standard Test Method for Determining the Carbon Dioxide Loss of Beverage Containers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Two procedures, A and B, are outlined in this test method. Procedure A is used most often for development of various beverage container designs to determine the functional characteristics of the package in regard to shelf life. Procedure B is recommended for use in beverage filling operations as a quality control tool in maintaining the desired CO2 fill pressure. A loss of CO2 will affect product taste.
5.1.1 Procedure A involves the use of sensitive pressure and temperature monitoring equipment where a high degree of accuracy is essential, for example, a micro-pressure transducer and thermocouple for measuring pressure and temperature of the package in a closed system. Alternatively, this procedure may also use bottles closed with roll-on aluminum caps containing rubber septums. The septum is pierced with a hypodermic needle attached to a pressure transducer to obtain pressure readings. This procedure should be confined to laboratories that are practiced in this type of analytical testing.
5.1.2 Procedure B is more widely used when measuring the carbonation level of the package due to the simplicity of the technique. A simple Zahm-Nagle pressure assembly or Terris CO2 Analyzer is utilized.
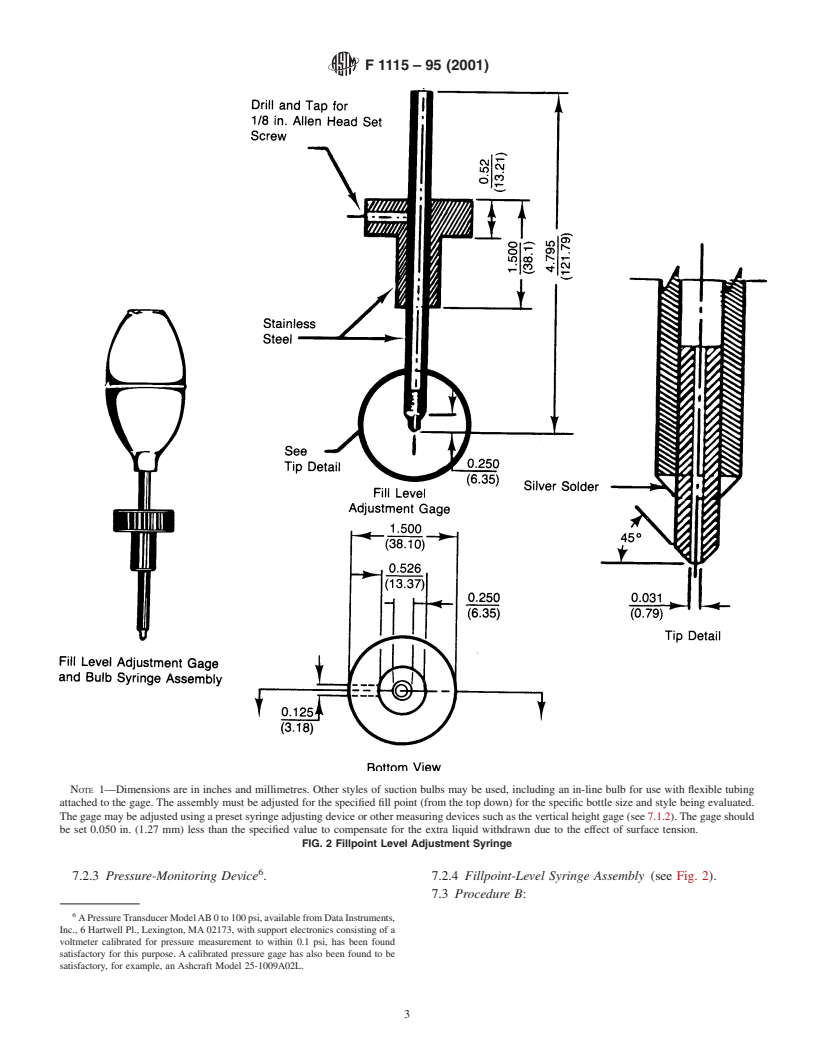
SCOPE
1.1 The objective of this test method is to determine the carbon dioxide (CO2) loss from plastic beverage containers after a specified period of storage time.
1.2 Factors contributing to this pressure loss are volume expansion and the gas transport characteristics of the package including permeation and leakage.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 1115 – 95 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Carbon Dioxide Loss of Beverage
1
Containers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1115; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.1 carbonation volume—the volume of CO (at 0°C, 1
2
atm pressure) that is dissolved in the carbonated water, divided
1.1 The objective of this test method is to determine the
by the volume of the liquid (based on water volume at 3.98°C
carbon dioxide (CO ) loss from plastic beverage containers
2
3
equals1.000g/cm ).Theconversionofpressuretocarbonation
after a specified period of storage time.
volumes should be made using a carbonation volumes table.A
1.2 Factors contributing to this pressure loss are volume
table for carbonated water would not necessarily apply to
expansion and the gas transport characteristics of the package
liquids containing additional substances, such as carbonated
including permeation and leakage.
beverages containing sugar.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.2 initial pressure—the equilibrium pressure in the test
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
bottles as measured at 24 h after filling with carbonated water.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(The filled bottles are allowed to stand for 24 h to obtain
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
temperatureequilibriumwiththetestenvironmentandtoallow
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
time for pressure adjustment and equilibration of the CO in
2
2. Referenced Documents the headspace and liquid.)
2
3.2.3 sample—a set of bottles produced on the same equip-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ment in a single run and using the same material and process
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
conditions. Bottles should represent normal thickness distribu-
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
tion.
E 177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
3.2.4 shelf life—thenumberofweeksasamplesetofbottles
ASTM Test Methods
retain a specified carbonation level, or a percent of the initial
E 380 Practice for the Use of International System of Units
3
level.
(SI) (the Modernized Metric System)
3.2.5 pressure monitoring device—a pressure gage or trans-
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
ducer assembly with support electronics for indicating internal
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
pressure level of the bottle. This device is used with brass
3. Terminology
closure fitting-equipped bottles.
3.2.5.1 temperature monitoring device—a thermocouple
3.1 Units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this test
with support electronics (same equipment as described in
method are those recommended by Practice E 380.
7.2.2). A precision glass thermometer may be used provided a
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
bottle filled with noncarbonated water is used as a control in
each sample set (Procedure A).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F2 on Flexible
3.2.6 Terriss CO Analyzer—an electronic unit that will
2
Barrier Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.10 on
pierce the roll-on closure and automatically read pressure,
Permeation.
temperature, and volume of gas (Procedure B).
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1995. Published March 1996. Originally
published as F 1115 – 87. Last previous edition F 1115 – 87. 3.2.7 Zahm-Nagle Pressure Tester—a unit that manually
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
pierces the closure and measures container pressure; an at-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
tached thermometer is then used to measure temperature
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
(Procedure B).
the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 1115 – 95 (2001)
3.2.8 support ring—a protrusion below the bottle finish
which is used to support or stabilize the bottle during filling
and capping.
3.2.9 finish—the threaded part of the bottle which receives
the cap.
3.3 For other terms used in this test method, refer to
Terminology D 1129.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Test bottles are filled with carbonated water or beverage
and, after closure application, are exposed to test environments
forspecifiedtimeperiods.Byperiodicallymeasuringtheinitial
and final carbonat
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.