ASTM F2054/F2054M-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Burst Testing of Flexible Package Seals Using Internal Air Pressurization Within Restraining Plates
Standard Test Method for Burst Testing of Flexible Package Seals Using Internal Air Pressurization Within Restraining Plates
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test provides a rapid means of evaluating tendencies for package seal failure when the package is exposed to a pressure differential. Pressure differentials may occur during such processes as sterilization and transportation. This test method provides an indicator of the burst strength of a package, where the burst will normally occur in one or more areas of the seal. An indicator of the minimum burst strength may be of importance to the package manufacturer and end user in ensuring adequate package integrity. This test method cannot provide a measure of package seal uniformity. This test method also cannot provide an evaluation of overall package integrity or the burst strength of areas of the package that contact the surface of the restraining plates used. This test method should be combined with other methods of evaluating overall package integrity, uniformity of the package seal, or opening functionality, if so required.
5.2 This test frequently is used to quickly evaluate package seal strength during the manufacturing process and at various stages of the package's life cycle.
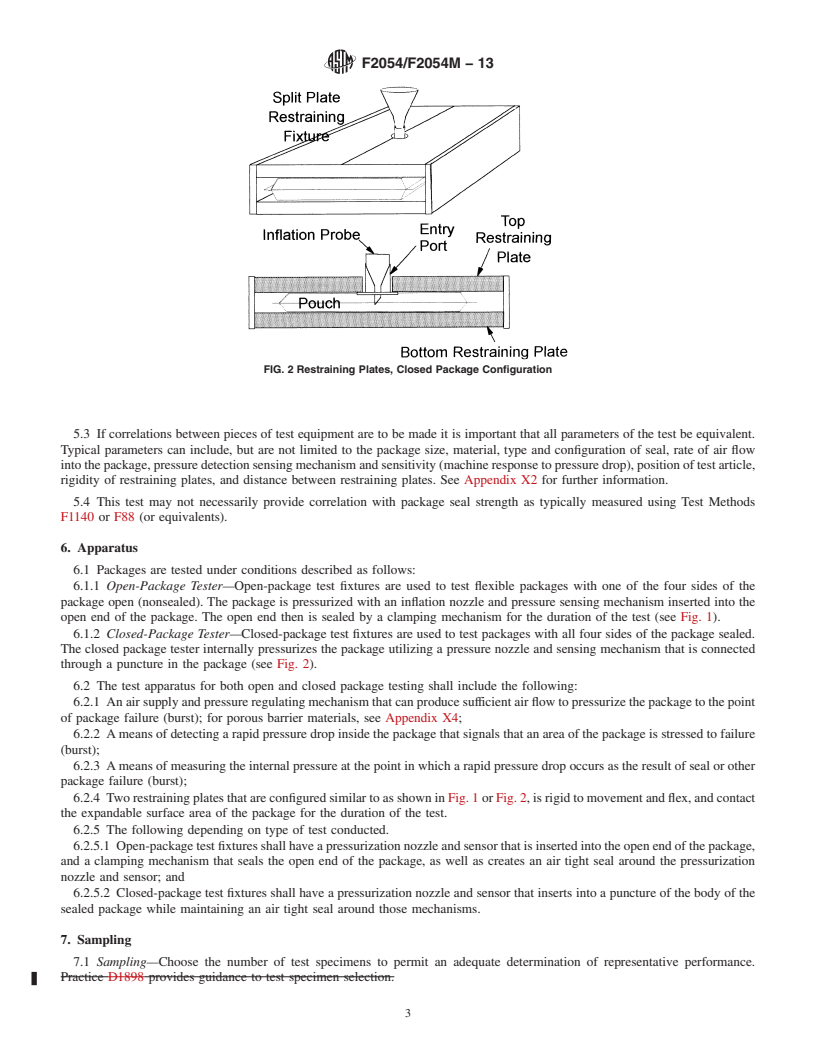
5.3 If correlations between pieces of test equipment are to be made it is important that all parameters of the test be equivalent. Typical parameters can include, but are not limited to the package size, material, type and configuration of seal, rate of air flow into the package, pressure detection sensing mechanism and sensitivity (machine response to pressure drop), position of test article, rigidity of restraining plates, and distance between restraining plates. See Appendix X2 for further information.
5.4 This test may not necessarily provide correlation with package seal strength as typically measured using Test Methods F1140 or F88 (or equivalents).
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the procedure for determining the minimum burst strength of a seal placed around the perimeter of a flexible package as it is internally pressurized and enclosed within restraining plates.
1.2 The test methods described herein are functionally similar to Test Methods F1140 with the exception of the use of restraining plates. Test Methods F1140 describes methods of burst testing that do not include the use of restraining plates and are suitable to determine a packages general ability to withstand pressurization stresses. Under Test Methods F1140 the stresses are not distributed uniformly to all areas of the package seal. Under unrestrained conditions the stress on the package is highest at the middle of the pouch where it inflates to the packages maximum diameter; therefore, Test Methods F1140 may not reliably detect the weakest area of the seal.
1.3 The burst test internally and increasingly pressurizes a package until an area of the package seal around the perimeter “bursts” open in response to pressurization. By placing the package within restraining plates during pressurization, the dimensional stability of the package is maintained in a manner that results in stresses applied more uniformly along the perimeter of the package, where seals are normally placed. This allows the test to have a higher probability of detecting the weakest area of the seal and provide a measurement of the pressure required to “burst” open the package.
1.4 This test only applies to flexible packages with seals placed around the perimeter of a flexible package (often referred to as a pouch). In particular it is intended as applicable to packages with seals that have a peelable seal feature (peeled open by end user to remove contents of package).
1.4.1 Porous barrier materials' failure to reach adequate pressure to burst the package seals may be due to insufficient volume flow. See Appendix X4 for information.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices ...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2054/F2054M −13
Standard Test Method for
Burst Testing of Flexible Package Seals Using Internal Air
1
Pressurization Within Restraining Plates
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF2054/F2054M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
1.1 These test methods cover the procedure for determining
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
the minimum burst strength of a seal placed around the
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
perimeter of a flexible package as it is internally pressurized
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
and enclosed within restraining plates.
with the standard.
1.2 The test methods described herein are functionally
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
similar toTest Methods F1140 with the exception of the use of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
restraining plates. Test Methods F1140 describes methods of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
burst testing that do not include the use of restraining plates
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
and are suitable to determine a packages general ability to
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Particular caution
withstand pressurization stresses. Under Test Methods F1140
is advised where users of this procedure may be required to
the stresses are not distributed uniformly to all areas of the
design and fabricate restraining plate fixtures. Reference Ap-
package seal. Under unrestrained conditions the stress on the
pendix X3 for further information regarding calculation of
package is highest at the middle of the pouch where it inflates
stress factors and structural design considerations.
to the packages maximum diameter; therefore, Test Methods
F1140 may not reliably detect the weakest area of the seal.
2. Referenced Documents
1.3 The burst test internally and increasingly pressurizes a
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
package until an area of the package seal around the perimeter
E171Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier
“bursts” open in response to pressurization. By placing the
Packaging
package within restraining plates during pressurization, the
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
dimensional stability of the package is maintained in a manner
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
that results in stresses applied more uniformly along the
F17Terminology Relating to Flexible Barrier Packaging
perimeter of the package, where seals are normally placed.
F88Test Method for Seal Strength of Flexible Barrier
Thisallowsthetesttohaveahigherprobabilityofdetectingthe
Materials
weakest area of the seal and provide a measurement of the
F1140Test Methods for Internal Pressurization Failure Re-
pressure required to “burst” open the package.
sistance of Unrestrained Packages
1.4 This test only applies to flexible packages with seals
placed around the perimeter of a flexible package (often 3. Terminology
referredtoasapouch).Inparticularitisintendedasapplicable
3.1 Definitions—For definitions and terms used in this test
to packages with seals that have a peelable seal feature (peeled
method, refer to Terminology F17 for standardized terminol-
open by end user to remove contents of package).
ogy for flexible barrier packaging.
1.4.1 Porous barrier materials’ failure to reach adequate
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
pressure to burst the package seals may be due to insufficient
3.2.1 restraining plates, n—refers to plates that are rigid in
volume flow. See Appendix X4 for information.
nature and configured to contact and limit the packages
expandable surface area as the package is pressurized.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF02onFlexible
Barrier Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.20 on
2
Physical Properties. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2013. Published June 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F2054–07 (2012). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/F2054_F2054M-13. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
-----------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F2054 − 07 (Reapproved 2012) F2054/F2054M − 13
Standard Test Method for
Burst Testing of Flexible Package Seals Using Internal Air
1
Pressurization Within Restraining Plates
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2054;F2054/F2054M; the number immediately following the designation indicates
the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the procedure for determining the minimum burst strength of a seal placed around the perimeter
of a flexible package as it is internally pressurized and enclosed within restraining plates.
1.2 The test methods described herein are functionally similar to Test Methods F1140 with the exception of the use of restraining
plates. Test Methods F1140 describes methods of burst testing that do not include the use of restraining plates and are suitable to
determine a packages general ability to withstand pressurization stresses. Under Test Methods F1140 the stresses are not distributed
uniformly to all areas of the package seal. Under unrestrained conditions the stress on the package is highest at the middle of the
pouch where it inflates to the packages maximum diameter; therefore, Test Methods F1140 may not reliably detect the weakest
area of the seal.
1.3 The burst test internally and increasingly pressurizes a package until an area of the package seal around the perimeter
“bursts” open in response to pressurization. By placing the package within restraining plates during pressurization, the dimensional
stability of the package is maintained in a manner that results in stresses applied more uniformly along the perimeter of the
package, where seals are normally placed. This allows the test to have a higher probability of detecting the weakest area of the
seal and provide a measurement of the pressure required to “burst” open the package.
1.4 This test only applies to flexible packages with seals placed around the perimeter of a flexible package (often referred to
as a pouch). In particular it is intended as applicable to packages with seals that have a peelable seal feature (peeled open by end
user to remove contents of package).
1.4.1 Porous barrier materials’ failure to reach adequate pressure to burst the package seals may be due to insufficient volume
flow. See Appendix X4 for information.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Particular caution is advised where users of this procedure may be required to design and fabricate
restraining plate fixtures. Reference Appendix X3 for further information regarding calculation of stress factors and structural
design considerations.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1898E171 Practice for Sampling of PlasticsConditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier Packaging (Withdrawn 1998)
D4332 Practice for Conditioning Containers, Packages, or Packaging Components for Testing
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
F17 Terminology Relating to Flexible Barrier Packaging
F88 Test Method for Seal Strength of Flexible Barrier Materials
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F02 on Flexible Barrier Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F02.20 on Physical
Properties.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012April 1, 2013. Published November 2012June 2013. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20072012 as
F2054 – 07.F2054 – 07 (2012). DOI: 10.1520/F2054-07R12.10.1520/F2054_F2054M-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO B
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.