ASTM A814/A814M-15
(Specification)Standard Specification for Cold-Worked Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
Standard Specification for Cold-Worked Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
ABSTRACT
This specification covers two classes of flanged and cold-bending quality cold-worked straight-beam single or double welded austenitic steel pipe intended for high-temperature and general corrosive services. Pipes of Class SW shall be single-welded with no addition of filler metal and Class DW pipes shall be double-welded with no addition of filler metal. The pipes shall be made by machine-welding or an automatic-welding process, welding from one or both sides and producing full penetration welds with no addition of filler metal in the welding operation. Prior to final heat treatment, the weld bead must be cold-worked by methods such as forging, planishing, drawing, swaging or bead rolling so as to obtain a flush condition on the inside and outside of the pipe. All specimens shall be subjected to transverse or longitudinal tension test, flattening test, and hydrostatic test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers two classes of flanged and cold-bending quality cold-worked straight-seam single or double welded austenitic steel pipe intended for high-temperature and general corrosive services.
Note 1: When the impact test criterion for a low-temperature service would be 15 ft·lbf [20 J] energy absorption or 15 mils [0.38 mm] lateral expansion, some of the austenitic stainless steel grades covered by this specification are accepted by certain pressure vessel or piping codes without the necessity of making the actual test. For example, Grades 304, 304L, and 347 are accepted by the ASME Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII Division 1, and by the Chemical Plant and Refinery Piping Code, ANSI B31.3 for service at temperatures as low as −425 °F [−250 °C] without qualification by impact tests. Other AISI stainless steel grades are usually accepted for service temperatures as low as −325 °F [−200 °C] without impact testing. Impact testing may, under certain circumstances, be required. For example, materials with chromium or nickel content outside the AISI ranges, and for material with carbon content exceeding 0.10 %, are required to be impact tested under the rules of ASME Section VIII Division 1 when service temperatures are lower than −50 °F [−45 °C].
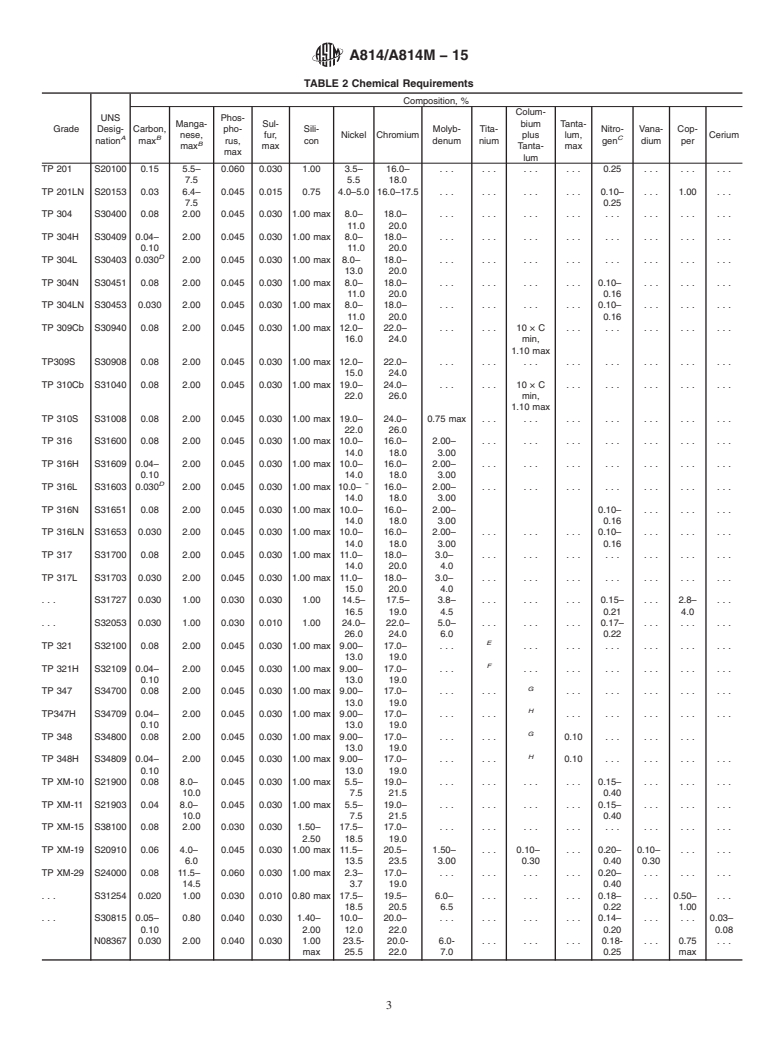
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP304N, TP316H, TP316N, TP321H, TP347H, and TP348H are modifications of Grades TP304, TP316, TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended for high-temperature service.
1.3 Two classes of pipe are covered as follows:
1.3.1 Class SW—Pipe, single-welded with no addition of filler metal and
1.3.2 Class DW—Pipe, double-welded with no addition of filler metal.
1.4 Optional supplementary requirements are provided for pipe where a greater degree of testing is desired. These supplementary requirements call for additional tests to be made and, when desired, one or more of these may be specified in the order.
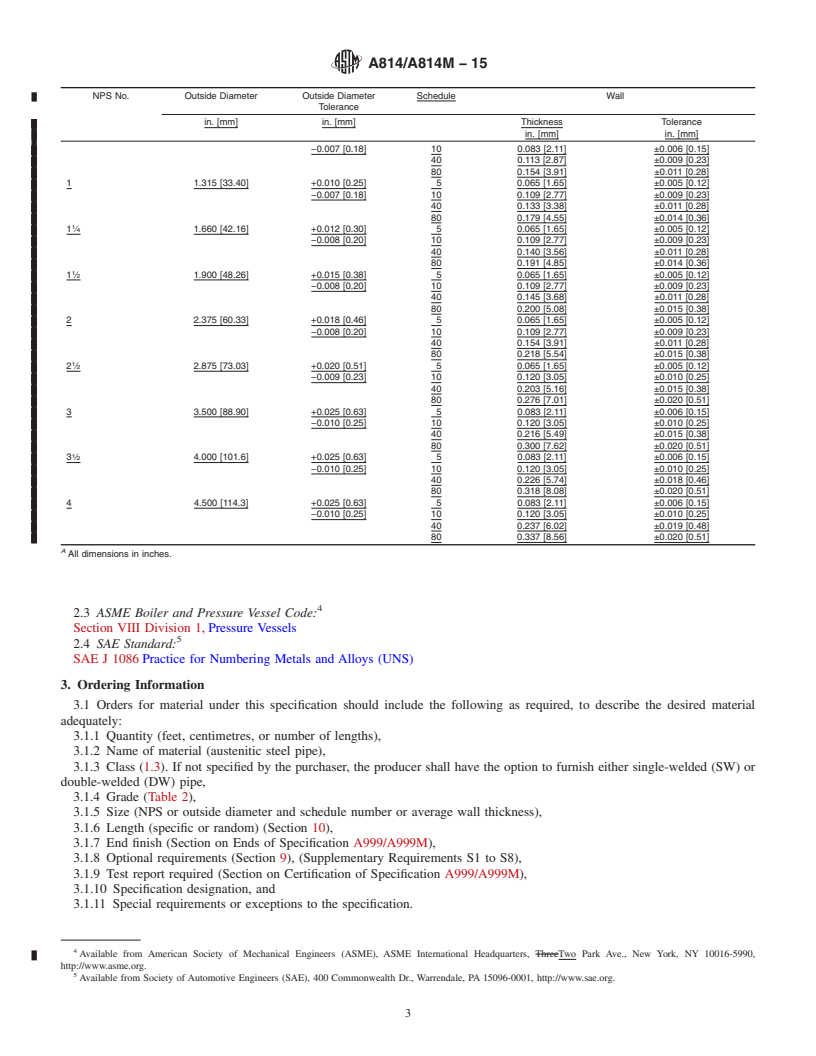
1.5 Table 1 lists the dimensions of cold-worked single- or double-welded stainless steel pipe. Pipe having other dimensions may be furnished provided such pipe complies with all other requirements of this specification. (A) All dimensions in inches.
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A814/A814M −15
StandardSpecification for
1
Cold-Worked Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA814/A814M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* sions may be furnished provided such pipe complies with all
other requirements of this specification.
1.1 This specification covers two classes of flanged and
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
cold-bending quality cold-worked straight-seam single or
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
double welded austenitic steel pipe intended for high-
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
temperature and general corrosive services.
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must
NOTE 1—When the impact test criterion for a low-temperature service
beusedindependentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthe
would be 15 ft·lbf [20 J] energy absorption or 15 mils [0.38 mm] lateral
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
expansion, some of the austenitic stainless steel grades covered by this
specification are accepted by certain pressure vessel or piping codes cation. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M”
without the necessity of making the actual test. For example, Grades 304,
designation of this specification is specified in the order.
304L, and 347 are accepted by theASME Pressure Vessel Code, Section
VIII Division 1, and by the Chemical Plant and Refinery Piping Code,
2. Referenced Documents
ANSI B31.3 for service at temperatures as low as −425 °F [−250 °C]
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
without qualification by impact tests. OtherAISI stainless steel grades are
usually accepted for service temperatures as low as −325 °F [−200 °C] A262Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
without impact testing. Impact testing may, under certain circumstances,
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
be required. For example, materials with chromium or nickel content
A370Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
outside the AISI ranges, and for material with carbon content exceeding
of Steel Products
0.10%, are required to be impact tested under the rules ofASME Section
A480/A480MSpecification for General Requirements for
VIII Division 1 when service temperatures are lower than −50 °F [−45
°C]. Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate,
Sheet, and Strip
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP304N, TP316H, TP316N, TP321H,
A999/A999MSpecification for General Requirements for
TP347H, and TP348H are modifications of Grades TP304,
Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe
TP316, TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended for
E112Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
high-temperature service.
E381Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets,
1.3 Two classes of pipe are covered as follows:
Blooms, and Forgings
1.3.1 Class SW—Pipe, single-welded with no addition of
E527Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
filler metal and
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
3
1.3.2 Class DW—Pipe, double-welded with no addition of
2.2 ANSI Standards:
filler metal.
B31.3Process Piping
4
2.3 ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code:
1.4 Optional supplementary requirements are provided for
Section VIII Division 1,Pressure Vessels
pipe where a greater degree of testing is desired. These
5
2.4 SAE Standard:
supplementaryrequirementscallforadditionalteststobemade
SAE J 1086Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys
and,whendesired,oneormoreofthesemaybespecifiedinthe
(UNS)
order.
1.5 Table 1 lists the dimensions of cold-worked single- or
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
double-welded stainless steel pipe. Pipe having other dimen-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel, 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
A01.10 on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products. International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
Current edition approved March 1, 2015. Published March 2015. Originally www.asme.org.
5
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A814/A814M–08. Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 C
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A814/A814M − 08 A814/A814M − 15
Standard Specification for
1
Cold-Worked Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A814/A814M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers two classes of flanged and cold-bending quality cold-worked straight-seam single or double
welded austenitic steel pipe intended for high-temperature and general corrosive services.
NOTE 1—When the impact test criterion for a low-temperature service would be 15 ft·lbf [20 J] energy absorption or 15 mils [0.38 mm] lateral
expansion, some of the austenitic stainless steel grades covered by this specification are accepted by certain pressure vessel or piping codes without the
necessity of making the actual test. For example, Grades 304, 304L, and 347 are accepted by the ASME Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII Division 1,
and by the Chemical Plant and Refinery Piping Code, ANSI B31.3 for service at temperatures as low as −425 °F [−250 °C] without qualification by impact
tests. Other AISI stainless steel grades are usually accepted for service temperatures as low as −325 °F [−200 °C] without impact testing. Impact testing
may, under certain circumstances, be required. For example, materials with chromium or nickel content outside the AISI ranges, and for material with
carbon content exceeding 0.10 %, are required to be impact tested under the rules of ASME Section VIII Division 1 when service temperatures are lower
than −50 °F [−45 °C].
1.2 Grades TP304H, TP304N, TP316H, TP316N, TP321H, TP347H, and TP348H are modifications of Grades TP304, TP316,
TP321, TP347, and TP348, and are intended for high-temperature service.
1.3 Two classes of pipe are covered as follows:
1.3.1 Class SW—Pipe, single-welded with no addition of filler metal and
1.3.2 Class DW—Pipe, double-welded with no addition of filler metal.
1.4 Optional supplementary requirements are provided for pipe where a greater degree of testing is desired. These
supplementary requirements call for additional tests to be made and, when desired, one or more of these may be specified in the
order.
1.5 Table 1 lists the dimensions of cold-worked single- or double-welded stainless steel pipe. Pipe having other dimensions may
be furnished provided such pipe complies with all other requirements of this specification.
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. The
inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
A999/A999M Specification for General Requirements for Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
3
2.2 ANSI Standards:
B31.3 Process Piping
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.10
on Stainless and Alloy Steel Tubular Products.
Current edition approved March 1, 2008March 1, 2015. Published April 2008March 2015. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 20072008 as
A814/A814M – 07.A814/A814M – 08. DOI: 10.1520/A0814_A0814M-08.10.1520/A0814_A0814M-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.