ASTM F2158-01
(Specification)Standard Specification for Residential Central-Vacuum Tube and Fittings
Standard Specification for Residential Central-Vacuum Tube and Fittings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions and tolerances, flattening resistance and impact resistance of plastic tubing for use in central-vacuum systems for residential buildings.
1.2 All notes and footnotes shall be considered as non-mandatory requirements of the specification.
1.3 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units, which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 2158 – 01
Standard Specification for
Residential Central-Vacuum Tube and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2158; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F 402 Practice for Safe Handling of Solvent Cements,
Primers, and Cleaners Used for JoiningThermoplastic Pipe
1.1 This specification establishes requirements and test
and Fittings
methods for materials, dimensions and tolerances, flattening
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
resistance and impact resistance of plastic tubing for use in
central-vacuum systems for residential buildings.
3. Terminology
1.2 All notes and footnotes shall be considered as non-
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412,
mandatory requirements of the specification.
abbreviations are in accordance withTerminology D 1600, and
1.3 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
dimension symbols are in accordance with Specification
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
D 2749.
mathematical conversions to SI units, which are provided for
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
information only and are not considered standard.
3.2.1 central-vacuum tubing, n—piping used for central-
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
vacuum systems, that is O.D controlled.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.2 unaided eye, n—observable without enhancement be-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
yond correction for normal vision.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory requirements prior to use.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The requirements of this specification are intended to
2. Referenced Documents
provide tube and fittings for central-vacuum cleaning systems,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2 used to convey debris from the vacuum inlets to the central-
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
vacuum power units.
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
Plastics
5. Materials
D 1784 Specification for Rigid Poly (Vinyl Chloride)
5.1 Basic Materials—The tube and fittings shall be made of
(PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly (Vinyl Chloride)
2 virgin plastic having a cell classification of equivalent to or
(CPVC) Compounds
greater than that for poly (vinyl chloride) (PVC) 12454, 13354,
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
3 and 12223, as defined in Specification D 1784. Compounds
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
that have different cell classifications, because one or more
D 2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Re-
properties are superior to those of the specified compounds, are
sistance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
also acceptable.
Tup (Falling Weight)
5.2 Recycled Material—The use of recycled materials as
D 2564 Specification for Solvent Cements for Poly (Vinyl
defined in Guide D 5033 is acceptable as long as the material
Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping Systems
meets the cell classification requirements in 5.1.
D 2749 Specification for Dimensions of Plastic Pipe Fit-
3 5.3 Solvent Cement—Where solvent cement is used to join
tings
PVC tube and fittings, it shall meet the requirements of
D 5033 Guide for Development of ASTM Standards Relat-
4 Specification D 2564.
ing to Recycling and Use of Recycled Plastic
6. Requirements
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
6.1 General—The tube and fittings shall be homogeneous
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on
throughout and free of visible cracks, holes, foreign inclusions,
Vinyl-Based Pipe.
or other defects. They shall be as uniform as commercially
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2001. Published February 2002.
practicable in color, opacity, density, and other physical prop-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
erties.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2158–01
TABLE 2 Fitting Dimensions
6.1.1 Tube Flattening—There shall be no evidence of split-
ting, cracking, or breaking when the tube is tested in accor- Socket Socket Wall
Socket
Nominal Entrance-Diameter Bottom-Diameter Thick-
dance with 7.4.
Depth,
Size ness,
A A A A
min
6.1.2 Tube Impact Strength—The impact strength of the min max OOR min max OOR A
min
tube at the time of manufacture shall not be less than 20ft·lbf 2 2.005 2.015 +0.015 1.990 2.000 +0.015 0.730 0.085
(50.93) (51.18) (0.38) (50.54) (50.8) (0.38) (18.54) (2.16)
(27 J), when tested in accordance with 7.5.
A
The wall thickness is a minimum value except that a 610 % variation resulting
6.2 Dimensions and Tolerances:
from core shift is allowed. In such case, the average of the two opposite wall
6.2.1 Tube Dimensions—The tube dimensions shall meet
thicknesses shall equal or exceed the value shown in the table.
the requirements given in Table 1, when measured in accor-
dance with Test Method D 2122.
6.2.1.1 Tube Length—The tolerance on the tube length shall 8. Retest and Rejection
be 6 ⁄2 in. (612.5 mm).
8.1 If the results of any test(s) do not meet the requirements
6.2.2 Fitting Dimensions—The dimensions of fittings shall
of this specification, the tests shall be conducted again in
meet the requirements of Table 2, when measured in accor-
accordance with an agreement between the purchase and the
dance with Test Method D 2122.
seller. There shall be no agreement to lower the minimum
requirements of this specification by such means as omitting
7. Test Methods
tests that are a part of this specification, substituting or
7.1 Sampling—The selection of tube samples shall be as
modifying a test method, or by changing the specification
agreed upon between the purchaser and seller. In case of no
limits. In retesting, the product requirements of this specifica-
prior agreement, samples selected by a testing laboratory shall
tion shall be met, and the test methods designated in the
be deemed adequate.
specification shall be followed. If, upon retest, failure occurs,
7.2 Test Specimens—For testing in accordance with 7.4 and
the quantity of product represented by the test(s) does not meet
7.5, cut each test specimen from the selected tube to a
the requirements of this specification.
minimumof6 6 ⁄8in.(152 63.175mm)inlength.Deburrthe
edges of each specimen on the inner and outer diameter.
9. Product Marking
7.3 Conditioning—For time-of-manufacture testing, condi-
9.1 Tube Marking—The markings shall be applied to the
tioning shall be permitted at the ambient temperature and
tube in such a manner that they remain legible after installa-
humidity of the manufacturer’s facility. For referee purposes,
tion.
conditioning shall be in accordance with procedure A of
9.2 Content of Marking—The tube shall be marked at least
Practice D 618.
every 5 ft (1.5 m) in letters not less than ⁄16 in. (5 mm) high,
7.4 Tube Flattening—Flatten three test specimens between
in a contrasting color, with the following information.
parallel plates in a press until the distance between the plates is
9.2.1 The manufacturer’s name (or trademark).
40 % of the outside diameter of the tube. The rate of loading
9.2.2 The designation “ASTM F 2158.”
shall be uniform and such that the flattening is completed
9.2.3 Nominal Pipe Size (for example, 2 in. (50 mm).
within 2 to 5 min. On the removal of the load, the specimen
9.2.4 The material identification for example “PVCVacuum
shall pass if no splitting, cracking, or breaking is observed
Tubing.”
under normal light with the unaided eye.
9.3 Fitting Markings:
7.5 Impact Resistance—Determine the impact resistance of
9.3.1 Manufacturer’s name (or trademark).
the tube in accordance withAppendix X3.5 “Procedure–Speci-
9.3.2 The designation ASTM F 2158.
fication Requirement” of D 2444. Use either a 6lb (2.7kg) or a
9.3.3 Nominal tube size.
20-lb (9.1-kg) B tup and the flat plate (holder B). Test six
9.3.4 The material identification symbol, for example, PVC.
specimens at an impact of 20 ft ·lbf (27 joules). If all six
specimens pass, accept the lot. If one specimen fails, test
10. Quality Assurance
another six specimens. If eleven of twelve specimens pass,
10.1 When the product is marked with this designation,
accept the lot. If two or more specimens fail, reject the lot.
ASTM D 2158, the manufacturer affirms that the product was
manufactured, inspected, sampled, and tested in accordance
TABLE 1 Outside Diameters and Tolerances for Vacuum Tubing,
with this standard and has been found to meet the requirements
in. (mm)
of this specification.
Nominal Wall Thickness
Tube Size max min min max
2 2.005 1.995 0.060 0.070
11. Keywords
(50.93) (50.67) (1.52) (1.78)
11.1 central vacuum; fittings; PVC; tube
F2158–01
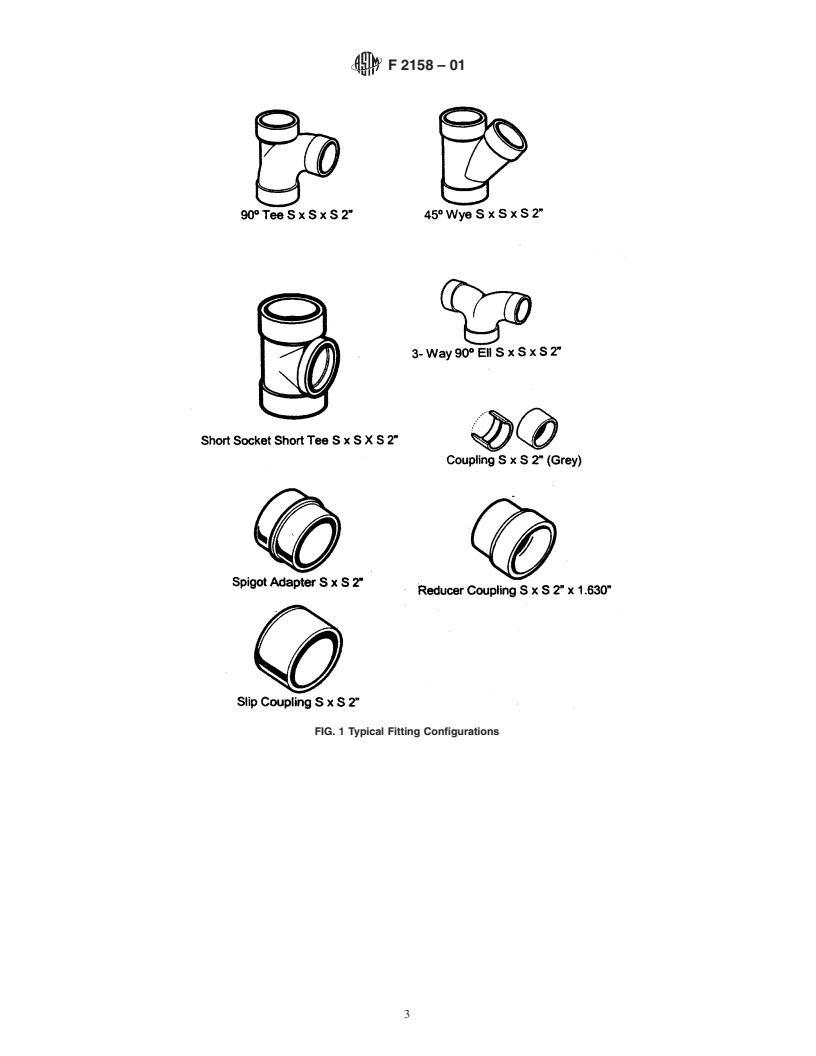
FIG. 1 Typical Fitting Configurations
F2158–01
FIG. 1 Typical Fitting Configurations (continued)
F2158–01
FIG. 1 Typical Fitting Configurations (continued)
APPENDIXES
(Nonmandatory Information)
X1. STORAGE
X1.1 Outside Storage—Plastic tube should be stored on a the temperature exceeds 100°F (38°C).
flat surface or supported in a manner that will prevent sagging
or bending. Do not store tube in direct sunlight for long X1.2 Inventoriesofplastictubeshouldbeusedonafirst-in,
periods.Topreventdamage,fittingsshouldnotbestoredwhere first-out basis.
F2158–01
X2. JOINTS AND CONNECTIONS
X2.1 PVC tubing and fittings shall be joined by the
solvent-cement method.
X3. SOLVENT CEMENT JOINTS
X
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.