ASTM D4989-90a(2004)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for the Apparent Viscosity (Flow) of Roofing Bitumens Using the Parallel Plate Plastometer
Standard Test Method for the Apparent Viscosity (Flow) of Roofing Bitumens Using the Parallel Plate Plastometer
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of apparent viscosity of roofing bitumen by means of a parallel plate plastometer. This test method is applicable for a viscosity range from 102 to 10 9 Pas (103 to 1010 poises). See . Note 1This relatively simple test method of measuring viscosity uses pre-determined arbitrary shear stress levels. Since roofing bitumens are non-Newtonian, other viscosity test methods may give different results.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are regarded as standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 4989 – 90a (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Test Method for
Apparent Viscosity (Flow) of Roofing Bitumens Using the
Parallel Plate Plastometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4989; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of apparent 4.1 The sample is molded into a disc of specified dimen-
viscosity of roofing bitumen by means of a parallel plate sions, heated to the selected temperature, placed between the
plastometer.Thistestmethodisapplicableforaviscosityrange plates of the pre-heated apparatus and pressed under standard
2 9 3 10
from 10 to 10 Pa·s (10 to 10 poises). See Note 1. conditions for a measured time. The apparent viscosity is
calculatedfromthefinaldiameterofthepressedspecimendisc.
NOTE 1—Thisrelativelysimpletestmethodofmeasuringviscosityuses
pre-determined arbitrary shear stress levels. Since roofing bitumens are
5. Apparatus
non-Newtonian, other viscosity test methods may give different results.
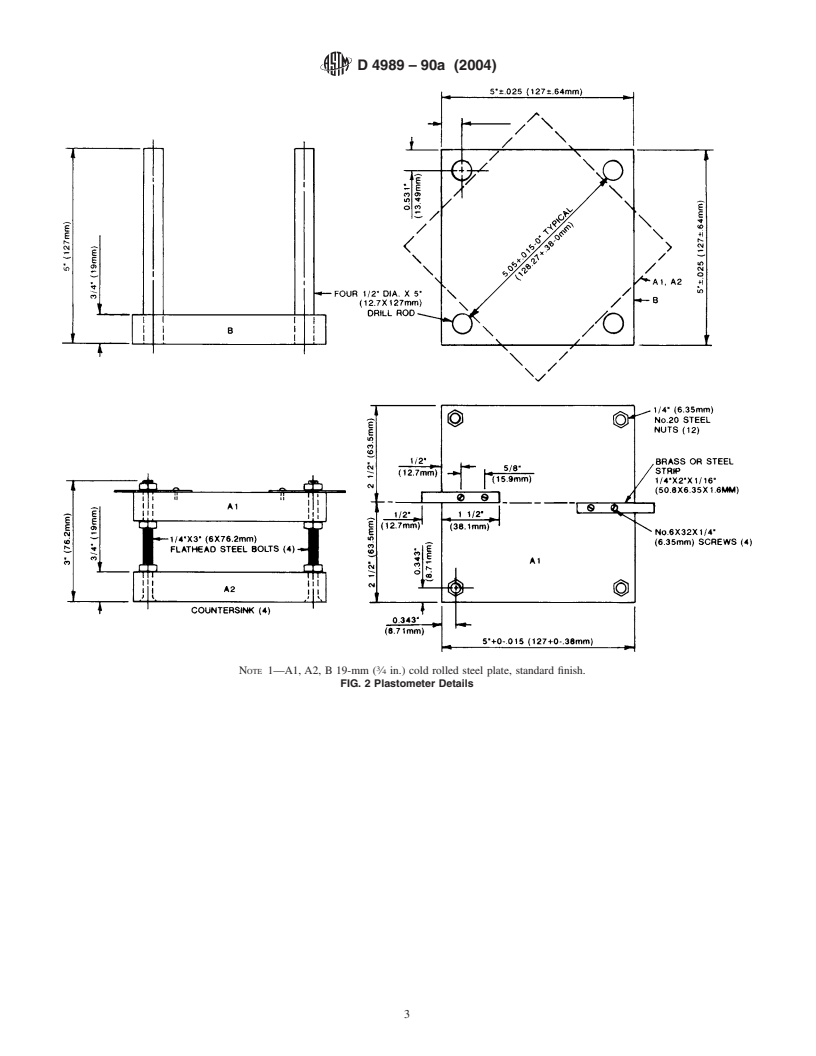
5.1 Parallel Plate Plastometer—A modified form of Will-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are regarded as standard.
iams’plastometerasshowninFig.1andFig.2.MassofPlaten
The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information
A is 5000 6 50 g (11.02 6 0.11 lb).
only.
5.2 Ring Molds, with an inside diameter of 25.40 6 0.01
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mm (1.0000 6 0.0025 in.) and a height of 12.70 6 0.01 mm
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
(0.5000 6 0.0025 in.) cut from copper or brass tubing.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.3 Constant Temperature Oven, capable of maintaining test
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
temperature within 60.1°C (60.2°F).
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.4 Scale, linearly graduated in millimetres over at least 150
mm (6 in.) and accurate to 60.5 mm (60.02 in.).
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6. Sampling
D 140 Practice for Sampling Bituminous Materials
6.1 Sample the material to be tested in accordance with
D 312 Specification for Asphalt Used in Roofing
Practice D 140.
D 450 Specification for Coal-Tar Pitch Used in Roofing,
Dampproofing and Waterproofing
7. Test Specimens
D 2171 Test Method for Viscosity of Asphalts by Vacuum
7.1 Prepare two molds by coating with a pasty mixture of
Capillary Viscometer
talc in glycerine as a mold release agent. Coat all surfaces of
D 3205 TestMethodforViscosityofAsphaltwithConeand
each mold by brushing or applying the paste with a finger tip.
Plate Viscometer
Place the rings on a brass or aluminum plate coated with the
release agent.
3. Terminology
7.2 Bring the sample to pouring temperature by heating in
3.1 Definitions—See definitions of viscosity given in Test
an oven for not more than 30 min. Heat the sample with care
Methods D 2171 and D 3205.
to prevent local overheating, stirring until it has become
sufficiently fluid to pour readily. Avoid incorporating air
1 bubbles in the sample. Pour the heated sample into the ring
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D08 on Roofing
and Waterproofing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D08.03 on moldsuntilaslightoverflowisachieved.Allowtocoolatroom
Surfacing and Bituminous Materials for Membrane Waterproofing and Built-up
temperature overnight, and then cut the excess material off
Roofing.
cleanly with a slightly heated knife or spatula. Trim the excess
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published May 2004. Originally
e1
material off not more than 1 h before testing.
approvedin1990.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin1999asD 4989 – 90a(1999) .
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
7.3 Just prior to testing, carefully remove each specimen
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
from its mold by holding it under a stream of cool tap water
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and pressing the specimen from the ring with the fingers.Wash
the ASTM website.
Withdrawn.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 4989 – 90a (2004)
9. Calculation
9.1 Calculate the average final diameter of the specimen
disc from the five measurements recorded.
9.2 Calculate the average apparent viscosity as follows:
18 10
3.60 3 10 t 2.08 3 10 t
Pa·s 5 ; viscosity, cps 5 (1)
8 S 8 D
~d! d
where:
t = time interval of the test in minutes, and
d = final average diameter of the specimen in inches
(millimetres) (see Note 3).
FIG. 1 Plastometer With Platens in Open and Closed Positions
NOTE 3—National Institute of Standards and Technology, NBS Report
10950, Appendix
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.