ASTM D322-97(2012)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Gasoline Diluent in Used Gasoline Engine Oils by Distillation
Standard Test Method for Gasoline Diluent in Used Gasoline Engine Oils by Distillation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Some fuel dilution of the engine oil may take place during normal operation. However, excessive fuel dilution is of concern in terms of possible performance problems.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the amount of dilution in crankcase oils of engines when gasoline has been used as the fuel.Note 1—There may be cases in dispute, therefore, the user of this test method is advised to establish whether this method will be accepted. There may be cases where Test Method D3525 results will be set as the referee value.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statement, see 6.4, 7.1, and 9.3.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D322 − 97(Reapproved 2012)
Designation: 23/2000
Standard Test Method for
Gasoline Diluent in Used Gasoline Engine Oils by
Distillation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D322; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products
1.1 This test method covers determination of the amount of
dilution in crankcase oils of engines when gasoline has been 2.2 IP Methods for Analyses and Testing, Vol II, Part I
used as the fuel.
NOTE 1—There may be cases in dispute, therefore, the user of this test
3. Terminology
methodisadvisedtoestablishwhetherthismethodwillbeaccepted.There
may be cases where Test Method D3525 results will be set as the referee
3.1 Definitions:
value.
3.1.1 fuel diluent, n—in used oil analysis, unburnt fuel
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be
components that enter the engine crankcase causing dilution of
regarded as the standard.
the oil.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In this test method, the fuel diluent
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
components being determined are from gasoline.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.2 used oil, n—any oil that has been in a piece of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
equipment (for example, an engine, gearbox, transformer, or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
turbine) whether operated or not. D4175
precautionary statement, see 6.4, 7.1, and 9.3.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In this test method, used oil is from a
gasoline engine.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Summary of Test Method
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits)
4.1 The sample, mixed with water, is placed in a glass still
(Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
provided with a reflux condenser discharging into a graduated
D3525 Test Method for Gasoline Diluent in Used Gasoline
trap connected to the still. Heat is applied, and the contents of
Engine Oils by Gas Chromatography
the still are brought to boiling. The diluent in the sample is
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
vaporized with the water and then liquefied in the condenser.
Petroleum Products
The diluent collects at the top of the trap, and the excess water
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
runs back to the still where it is again vaporized, carrying over
Products, and Lubricants
an additional quantity of diluent. The boiling is continued until
all the diluent has been boiled out and recovered in the trap.
The volume is recorded.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
5. Significance and Use
Subcommittee D02.06 on Analysis of Lubricants.
This test method was adopted as a jointASTM-IPstandard in 1964. In the IP, this
5.1 Some fuel dilution of the engine oil may take place
method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization Committee.
duringnormaloperation.However,excessivefueldilutionisof
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012. Published November 2012. Originally
concern in terms of possible performance problems.
approved in 1930. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D322 – 97 (2012).
DOI: 10.1520/D0322-97R12.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR,
the ASTM website. U.K., http://www.energyinst.org.uk.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D322 − 97 (2012)
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Determining Diluent in Gasoline Engine Crankcase Oil
6. Apparatus flask. Wash the graduated cylinder with successive portions of
hot water until only a negligible amount of oil is left in the
6.1 Flask, round-bottom type (see Fig. 1 and A1.1).
cylinder. Add additional water to the flask to make a total of
6.2 Condenser, Liebig straight-tube type (see A1.2).
approximately 500 mL of water. Fill the trap with cold water
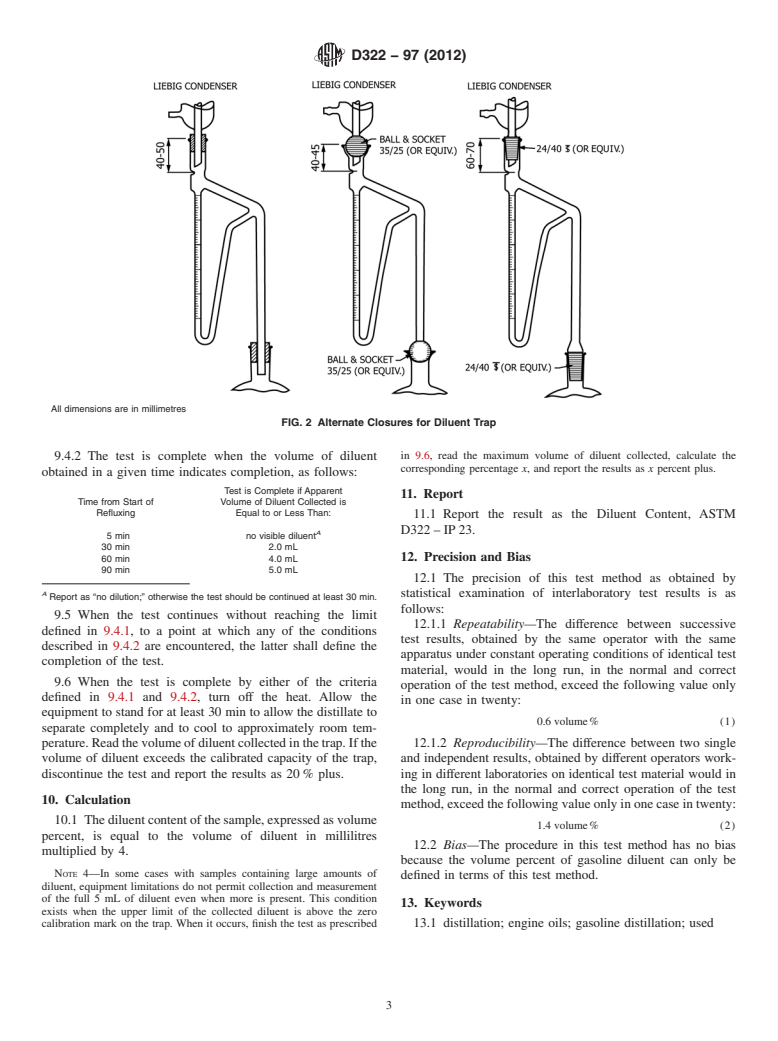
6.3 Trap, 5 mL, graduated in 0.1-mL increments (see Fig. 1 and add 1 6 0.1 mL of denatured ethanol to the water in the
and Fig. 2 and A1.3). trap.
6.4 Heater—Any suitable gas burner or electric heater may
9.2 Assemble the apparatus as shown in Fig. 1, so that the
be used with the glass flask. (Warning—Hot exposed surface.
tip of the condenser is directly over the indentation in the trap.
Avoid contact by wearing protective equipment as required.)
9.3 Apply heat to the flask at such a rate that refluxing starts
within 7 to 10 min after heat is applied, with the water and
7. Reagents and Materials
sample being at 21 to 38°C prior to application of heat. After
7.1 Ethanol, Denatured , conforming to either Formula No.
boiling and condensation has commenced, adjust the rate of
30 or 3A of the US Bureau of Internal Revenue. (Warning—
boiling so that condensed distillate is discharged from the
Flammable. Denatured. Cannot be made non-toxic.)
condenser at a rate of 1 to 3 drops per s. (Warning— Hot
7.2 Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits), conforming to
exposed surface. Avoid contact by wearing protective equip-
Specification D235.
ment as required. )
NOTE 2—In Annex A1.3, the use of reagent grade heptane may be the
NOTE 3—Bumping with a tendency to froth over is often experienced
preferred solvent because the use of commerical grade heptane or mineral
with dirty oils. The use of boiling stones, steel wool, or about 5 mL of
spirits can cause complications of container disposal that may not be
co
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.