ASTM D402-97
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Distillation of Cut-Back Asphaltic (Bituminous) Products
Standard Test Method for Distillation of Cut-Back Asphaltic (Bituminous) Products
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a distillation test for cut-back asphaltic (bituminous) products.
1.2 The values given in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 402 – 97 American Association State
Highway and Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No.: T78
27/74 (88)
Standard Test Method for
Distillation of Cut-Back Asphaltic (Bituminous) Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 402; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense. This method was adopted as a joint ASTM-IP
standard in 1961.
1. Scope distillation, and also the distillate, may be tested as required.
1.1 This test method covers a distillation test for cut-back
4. Significance and Use
asphaltic (bituminous) products.
4.1 This procedure measures the amount of the more vola-
1.2 The values given in SI units are to be regarded as the
tile constituents in cut-back asphaltic products. The properties
standard.
of the residue after distillation are not necessarily characteristic
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
of the bitumen used in the original mixture nor of the residue
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
which may be left at any particular time after application of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
cut-back asphaltic product. The presence of silicone in the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
cut-back may affect the distillation residue by retarding the loss
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of volatile material after the residue has been poured into the
2. Referenced Documents residue container.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Apparatus
D 86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products
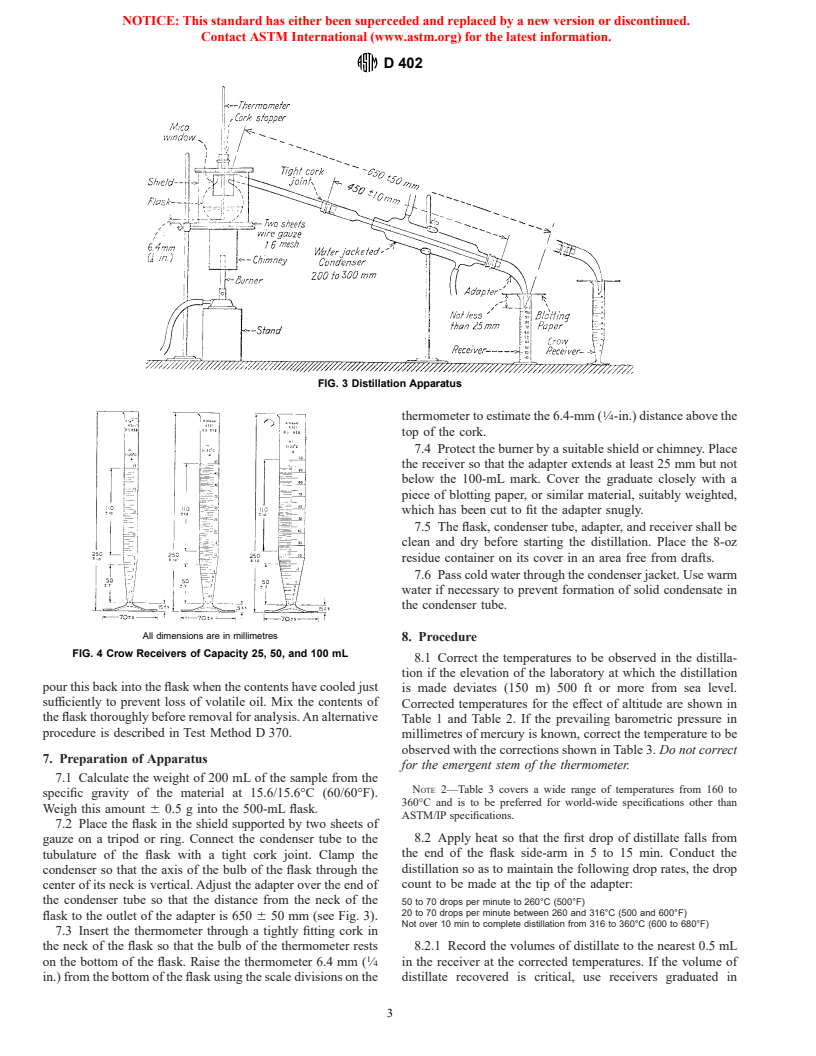
5.1 Distillation Flask, 500-mL side-arm, having the dimen-
D 370 Test Method for Dehydration of Oil-Type Preserva-
sions shown in Fig. 1.
tives
4 5.2 Condenser, standard glass-jacketed, of nominal jacket
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
length from 200 to 300 mm and overall tube length of 450 6
E 133 Specification for Distillation Equipment
10 mm (see Fig. 3).
2.2 IP Standards:
5.3 Adapter, heavy-wall (1-mm) glass, with reinforced top,
IP 123/ASTM D 86, Distillation of Petroleum Products
having an angle of approximately 105°. The inside diameter at
Thermometers as specified in IP Standards
the large end shall be approximately 18 mm, and at the small
Crow Receiver as specified in British Standards 658:1962
end, not less than 5 mm. The lower surface of the adapter shall
C.O.3—Standard Methods for Testing Tar and its Products
be on a smooth descending curve from the larger end to the
(Published by the U.K. Standardization of Tar Products
smaller. The inside line of the outlet end shall be vertical, and
Tests Committee)
the outlet shall be cut or ground (not fire-polished) at an angle
3. Summary of Method of 45 6 5° to the inside line.
5.4 Shield, steel, lined with 3-mm fire proof insulation and
3.1 Two hundred millilitres of the sample are distilled in a
fitted with transparent mica windows, of the form and dimen-
500-mL flask at a controlled rate to a temperature in the liquid
sions shown in Fig. 2, used to protect the flask from air currents
of 360°C (680°F) and the volumes of distillate obtained at
and to reduce radiation. The cover (top) shall be made in two
specified temperatures are measured. The residue from the
parts of 6.4-mm ( ⁄4-in.) fire proof insulation.
5.5 Shield and Flask Support—Two 15-cm sheets of 16-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-4 on Road
mesh Chromel wire gauze on a tripod or ring.
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.46on
5.6 Heat Source—
Durability Tests.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1997. Published February 1998. Originally
5.6.1 Adjustable Tirrill-type gas burner or equivalent.
published as D 402 – 34 T. Last previous edition D 402 – 94.
5.6.2 An electric heater equipped with a transformer ca-
In the IP, this method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization Committee.
2 pable of controlling from 0 to 750 W. The shield and support
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3 1
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.09. shall be a refractory with an opening of 3 ⁄8in. (79 mm), with
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
the upper surface beleveled to 3 ⁄8 in. (86 mm) to accommodate
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 402
FIG. 1 Distillation Flask
FIG. 2 Shield
the specified 500-mL flask. When the flask is placed on the 5.9 Thermometer— ASTM Thermometers 8C (8F) con-
refractory, there should be a distance of approximately ⁄8 in. (3 forming to Specification E 1, or IP Thermometer 6C conform-
mm) between the bottom of the flask and the heating elements. ing to IP Specifications for Standard Thermometers.
5.7 Receiver—A standard 100-mL graduated cylinder con-
forming to dimensions of Fig. 4 of Specification E 133, or
6. Sampling
a 100-mL crow receiver as shown in Fig. 4 of this test method.
6.1 Stir the sample thoroughly, warming if necessary, to
NOTE 1—Receivers of smaller capacity having 0.1-mL divisions may ensure homogeneity before removal of a portion for analysis.
be used when low volumes of total distillate are expected and the added
6.2 If sufficient water is present to cause foaming or
accuracy required.
bumping, dehydrate a sample of not less than 250 mL by
5.8 Residue Container—An 8-oz seamless metal container heating in a distillation flask sufficiently large to prevent
with slip on cover of 75 6 5 mm in diameter, and 55 6 5mm foaming over into the side arm. When foaming has ceased, stop
in height. the distillation. If any light oil has distilled over, separate and
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 402
FIG. 3 Distillation Apparatus
thermometer to estimate the 6.4-mm ( ⁄4-in.) distance above the
top of the cork.
7.4 Protect the burner by a suitable shield or chimney. Place
the receiver so that the adapter extends at least 25 mm but not
below the 100-mL mark. Cover the graduate closely with a
piece of blotting paper, or similar material, suitably weighted,
which has been cut to fit the adapter snugly.
7.5 The flask, condenser tube, adapter, and receiver shall be
clean and dry before starting the distillation. Place the 8-oz
residue container on its cover in an area free from drafts.
7.6 Pass cold water through the condenser jacket. Use warm
water if necessary to prevent formation of solid condensate in
the condenser tube.
All dimensions are in millimetres
8. Procedure
FIG. 4 Crow Receivers of Capacity 25, 50, and 100 mL
8.1 Correct the temperatures to be observed in the distilla-
tion if the elevation of the laboratory at which the distillation
pour this back into the flask when the contents have cooled just
is made deviates (150 m) 500 ft or more from sea level.
sufficiently to prevent loss of volatile oil. Mix the contents of
Corrected temperatures for the effect of altitude are shown in
the flask thoroughly before removal for analysis. An alternative
Table 1 and Table 2. If the prevailing barometric pressure in
procedure is described in Test Method D 370.
millimetres of mercury is known, correct the temperature to be
observed with the corrections shown in Table 3. Do not correct
7. Preparation of Apparatus
for the emergent stem of the thermometer.
7.1 Calculate the weight of 200 mL of the sample from the
NOTE 2—Table 3 covers a wide range of temperatures from 160 to
specific gravity of the material at 15.6/15.6°C (60/60°F).
360°C and is to be preferred for world-wide specifications other than
Weigh this amount 6 0.5 g into the 500-mL flask.
ASTM/IP specifications.
7.2 Place the flask in the shield supported by two sheets of
8.2 Apply heat so that the first drop of distillate falls from
gauze on a tripod or ring. Connect the condenser tube to the
tubulature of the flask with a tight cork joint. Clamp the the end of the flask side-arm in 5 to 15 min. Conduct the
distillation so as to maintain the following drop rates, the drop
condenser so that the axis of the bulb of the flask through the
count to be made at the tip o
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.