ASTM D5801-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
Standard Test Method for Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is useful in confirming that an asphalt cement has been modified with a material that provides a significant elastomeric component. Elastomer modified asphalts can be characterized by their ability to be stretched to a large elongation while at the same time resisting further stretching. Toughness and tenacity are two parameters for measuring this ability.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for measuring the toughness and tenacity of bituminous materials. Typically, the test method has been used to characterize elastomer modified asphalts, although values for toughness and tenacity may be obtained for any type of polymer-modified or non-modified asphalt.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exception—Sample mass is given only in SI units. Sample mass as given in SI units should be regarded as standard. No other units of sample mass are included in this standard.
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency and many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s website – http://www.epa.gov/mercury/index.htm - for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state may be prohibited by state law.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5801 − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5801; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for measuring 2.1 ASTM Standards:
the toughness and tenacity of bituminous materials. Typically, D5 Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials
the test method has been used to characterize elastomer D1754 Test Method for Effects of Heat andAir onAsphaltic
modified asphalts, although values for toughness and tenacity Materials (Thin-Film Oven Test)
may be obtained for any type of polymer-modified or non- D2872 Test Method for Effect of Heat and Air on a Moving
modified asphalt. Film of Asphalt (Rolling Thin-Film Oven Test)
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
mometers
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
E644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Ther-
and are not considered standard.
mometers
1.2.1 Exception—Sample mass is given only in SI units.
E1137/E1137M Specification for Industrial Platinum Resis-
Sample mass as given in SI units should be regarded as
tance Thermometers
standard. No other units of sample mass are included in this
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
standard.
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by the United
3. Summary of Test Method
States Environmental ProtectionAgency and many state agen-
cies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous
3.1 Atensionheadofspecifiedsizeandshapeispulledfrom
system,kidneyandliverdamage.Mercury,oritsvapor,maybe
an asphalt sample at a rate of 20 in./min (508 mm/min). A
hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should
continuous record of the force versus elongation curve is made
be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing
and used to calculate the toughness and the tenacity of the
products. See the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet
sample. The test is run at room temperature 77 6 5°F (25 6
(MSDS) for details and EPA’s website – http://www.epa.gov/
3°C), after the sample has been subjected to a specified
mercury/index.htm - for additional information. Users should
temperature history.
be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing
3.2 Toughness is defined in this procedure as the total work
products into your state may be prohibited by state law.
required to completely separate the tension head from the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sample under the specified test conditions. Tenacity is a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
measure of the increasing force as the sample is stretched past
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the initial peak, and may indicate the type and amount of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
polymer used to modify the asphalt. It is defined as the work
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
required to stretch the material after the initial resistance is
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
overcome.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 4. Significance and Use
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 This test method is useful in confirming that an asphalt
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
cement has been modified with a material that provides a
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
significant elastomeric component. Elastomer modified as-
phalts can be characterized by their ability to be stretched to a
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.44 on
2
Rheological Tests. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2012. Published May 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved as Proposal P 243 in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ε1
D5801 – 95 (2006) . DOI: 10.1520/D5801-12. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D5801 − 95 (Reapproved 2006) D5801 − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5801; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Added Note 3 editorially in December 2006.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for measuring the toughness and tenacity of bituminous materials. Typically, the
test method has been used to characterize elastomer modified asphalts, although values for toughness and tenacity may be obtained
for any type of polymer-modified or non-modified asphalt.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Exception—Sample mass is given only in SI units. Sample mass as given in SI units should be regarded as standard. No
other units of sample mass are included in this standard.
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency and many state agencies
as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous
to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the
applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s website – http://www.epa.gov/mercury/index.htm - for
additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state may be
prohibited by state law.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values given in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in inch-pound units in parentheses are for
informational purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D5 Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials
D1754 Test Method for Effects of Heat and Air on Asphaltic Materials (Thin-Film Oven Test)
D2872 Test Method for Effect of Heat and Air on a Moving Film of Asphalt (Rolling Thin-Film Oven Test)
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Thermometers
E644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Thermometers
E1137/E1137M Specification for Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermometers with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.44 on Rheological
Tests.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2006Dec. 1, 2012. Published December 2006May 2013. Originally approved as Proposal P 243 in 1994. Last previous edition approved
ε1
in 20012006 as D5801 – 95 (2001).(2006) . DOI: 10.1520/D5801-95R06E01.10.1520/D5801-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5801 − 12
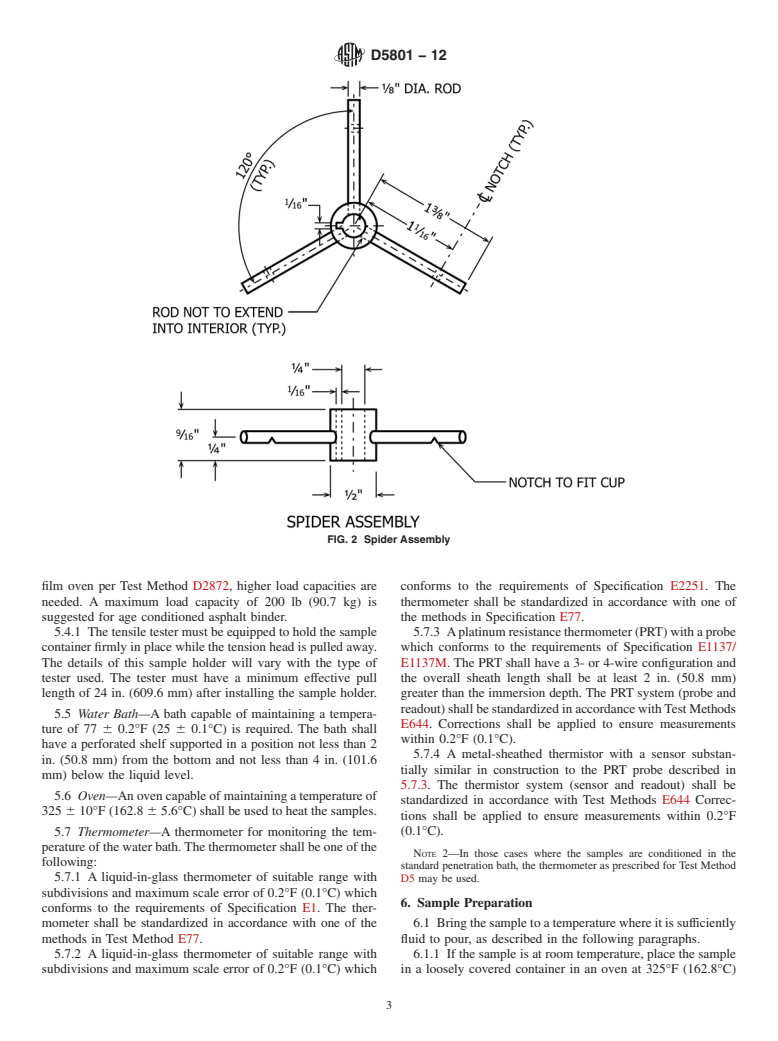
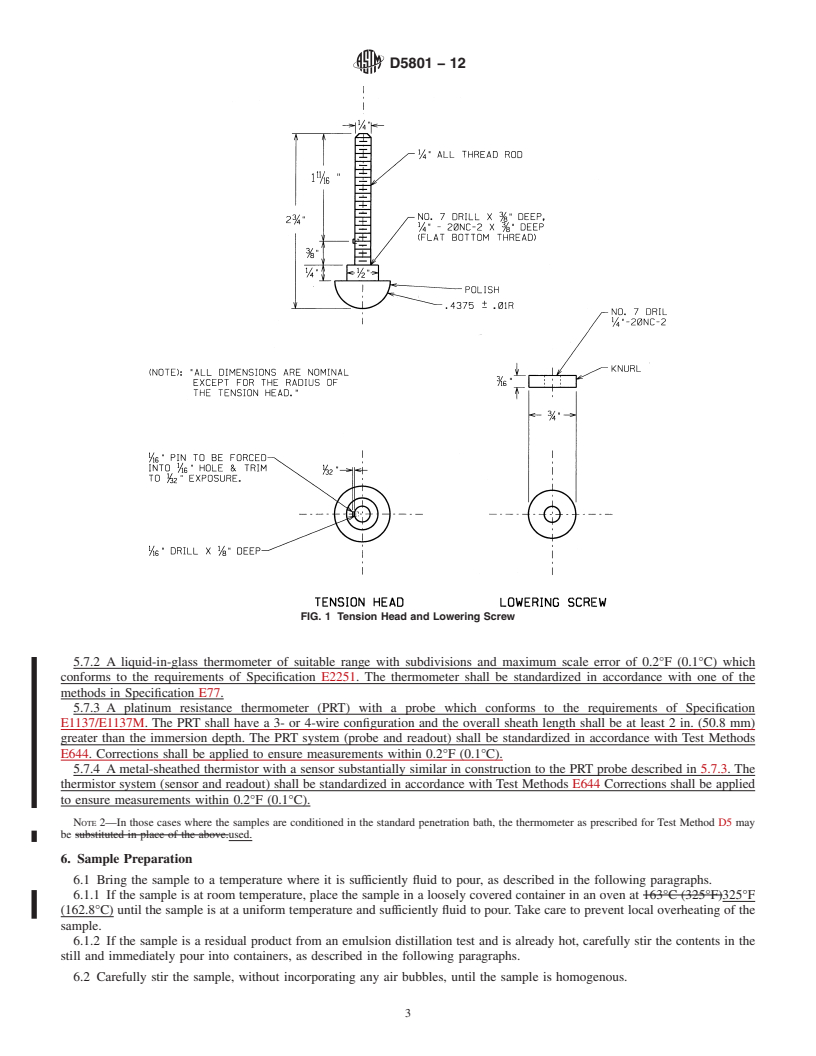
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A tension head of specified size and shape is pulled from an asphalt sample at a rate of 50 cm/min (20 in./min).20 in./min
(508 mm/min). A continuous record of the force versus elongation curve is made and used to calculate the toughness and the
tenacity of the sample. The test is run at room temperature 77 6 5°F (25 6 3°C [77 6 5°F]),3°C), after the sample has been
subjected to a specified t
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.