ASTM G201-09
(Practice)Standard Practice for Conducting Exposures in Outdoor Glass-Covered Exposure Apparatus with Air Circulation
Standard Practice for Conducting Exposures in Outdoor Glass-Covered Exposure Apparatus with Air Circulation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
As with any accelerated test, the increase in rate of weathering compared to in-service exposure is material dependent. Results from exposures conducted to this practice may provide good rank correlation to results from actual use conditions for one type of material or product. It should not be assumed that this will be true for other materials or products. It is always best to verify the ability of an accelerated exposure test to properly rank the durability of materials with actual use conditions. Guide G141 provides information about using rank correlation.
Variation in results may be expected when operating conditions are varied within the accepted limits of this practice. Therefore, no reference shall be made to results from the use of this practice unless accompanied by a report detailing the specific operating conditions in conformance with Report Section 8.
The durability of materials in outdoor use can be very different depending on the location of the exposure because of differences in solar radiation, moisture, heat, pollutants, and other factors. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that results from exposure in a single location will be useful for determining durability ranking of materials in a different location.
It is strongly recommended that at least one control material be exposed with each test. The control material should be of similar composition and construction and be chosen so that its failure modes are the same as that of the material being tested. It is preferable to use two control materials, one with relatively good durability, and one with relatively poor durability. If control materials are included as part of the test, they shall be used for the purpose of comparing the performance of the test materials relative to the controls.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the basic principles and operating procedures for using outdoor glass-covered exposure apparatus with air circulation. This practice is limited to the procedures for obtaining, measuring and controlling conditions of exposure. A number of exposure procedures are listed in Appendix X1; however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited for the material to be tested.
1.2 For direct weathering exposures, refer to Practice G7. For exposures behind glass without air circulation, refer to Practice G24.
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to solar radiation filtered through glass under partially controlled environmental test conditions. Different glass types and operating parameters are described.
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific materials. More specific information for determining the change in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described in Practices D5870, D2244 and Test Method D523.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G201 − 09
StandardPractice for
Conducting Exposures in Outdoor Glass-Covered Exposure
Apparatus with Air Circulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G201; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2244 Practice for Calculation of Color Tolerances and
Color Differences from Instrumentally Measured Color
1.1 This practice covers the basic principles and operating
Coordinates
procedures for using outdoor glass-covered exposure apparatus
D5870 Practice for Calculating Property Retention Index of
with air circulation. This practice is limited to the procedures
Plastics
for obtaining, measuring and controlling conditions of expo-
E903 Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and
sure. A number of exposure procedures are listed in Appendix
Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
X1; however, this practice does not specify the exposure
E1084 Test Method for Solar Transmittance (Terrestrial) of
conditions best suited for the material to be tested.
Sheet Materials Using Sunlight
1.2 For direct weathering exposures, refer to Practice G7.
G7 Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Test-
For exposures behind glass without air circulation, refer to
ing of Nonmetallic Materials
Practice G24.
G24 Practice for Conducting Exposures to Daylight Filtered
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to solar radiation filtered Through Glass
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural andArtificial Weath-
through glass under partially controlled environmental test
conditions. Different glass types and operating parameters are ering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
G141 Guide for Addressing Variability in Exposure Testing
described.
of Nonmetallic Materials
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are
G173 TablesforReferenceSolarSpectralIrradiances:Direct
covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific
Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
materials. More specific information for determining the
G177 Tables for Reference Solar Ultraviolet Spectral Distri-
change in properties after exposure and reporting these results
butions: Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
is described in Practices D5870, D2244 and Test Method
G179 Specification for Metal Black Panel and White Panel
D523.
Temperature Devices for Natural Weathering Tests
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
G183 Practice for Field Use of Pyranometers, Pyrheliom-
standard.
eters and UV Radiometers
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the 2.2 Other Document:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the WMO No. 8 Guide to Meteorological Instruments and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- Methods of Observation, Fifth Edition
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
2.3 ISO Standard:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. ISO 9060 Solar energy — Specification and classification of
instruments for measuring hemispherical solar and direct
2. Referenced Documents
solar radiation
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Terminology
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
3.1 The definitions given in Terminology G113 are appli-
cable to this practice.
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee G03 on Weathering
and Durability and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.02 on Natural 3.2 Other Definitions:
and Environmental Exposure Tests.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2009. Published May 2010. DOI: 10.1520/
G0201–09. Available from World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 7bis, avenue de la
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Paix, Case postale 2300, CH-1211 Geneva 2, Switzerland, http://www.wmo.int.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://
the ASTM website. www.iso.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
G201 − 09
3.2.1 limit temperature, n—For enclosures operated in tem-
perature control mode, the specified black panel temperature at
which the circulating fan switches on in order to prevent or
minimize black panel temperature readings above the set
temperature.
4. Summary of Practices
4.1 Specimens are exposed to light, moisture (in the form of
humidity) and heat in an outdoor glass-covered enclosure with
air circulation.
4.2 The exposure conditions may be varied by selection of:
4.2.1 Glass Type:
4.2.2 Operation of the circulating fan (whether constantly
on during daylight hours or only on when a specific limit
temperature is reached).
4.2.3 Temperature level at which the fan operates.
4.2.4 Orientation of the test fixture.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 As with any accelerated test, the increase in rate of
weathering compared to in-service exposure is material depen-
dent. Results from exposures conducted to this practice may
provide good rank correlation to results from actual use
FIG. 1 Diagram of Typical Enclosure with Air Circulation
conditions for one type of material or product. It should not be
assumed that this will be true for other materials or products. It
is always best to verify the ability of an accelerated exposure
test to properly rank the durability of materials with actual use
prevent outside air from circulating over specimens.
conditions. Guide G141 provides information about using rank
Optionally, vents covered with air filter material may be
correlation.
installed in the bottom of the test fixture if required to limit the
black panel temperature to a specified maximum.
5.2 Variation in results may be expected when operating
6.1.2 The enclosure shall be located where it will receive
conditionsarevariedwithintheacceptedlimitsofthispractice.
solar radiation throughout the day with no shadow on any
Therefore,noreferenceshallbemadetoresultsfromtheuseof
specimen when the sun’s angle of elevation is greater than 20
this practice unless accompanied by a report detailing the
degrees. When the enclosure is installed over grass, the
specific operating conditions in conformance with Report
distance between the bottom of the enclosure and the ground
Section 8.
shall be sufficient to prevent contact with plant growth, or to
5.3 The durability of materials in outdoor use can be very
minimize damage that might occur during maintenance.
different depending on the location of the exposure because of
6.1.3 The enclosure shall be equipped with a rack which
differences in solar radiation, moisture, heat, pollutants, and
supports the specimens in a plane parallel to the glass.
other factors. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that results from
Alternately, the specimens can be mounted in an in-service
exposure in a single location will be useful for determining
position. Unless otherwise specified, the distance between the
durability ranking of materials in a different location.
exposed surface of flat specimens shall be 75 6 25 mm from
5.4 It is strongly recommended that at least one control
the back surface of the glass cover.
material be exposed with each test.The control material should
6.1.4 Formed specimens with irregular dimensions may
be of similar composition and construction and be chosen so
require custom mounting with varying distances from the glass
that its failure modes are the same as that of the material being
cover. In such cases, mount the test specimen surface of major
tested. It is preferable to use two control materials, one with
interest parallel to the glass cover at a distance of 75 6 25 mm
relatively good durability, and one with relatively poor dura-
from the glass cover. The mounting frame or plate shall be
bility. If control materials are included as part of the test, they
constructed of a material that is compatible with the test
shall be used for the purpose of comparing the performance of
specimens. In order to minimize shadowing from the top and
the test materials relative to the controls.
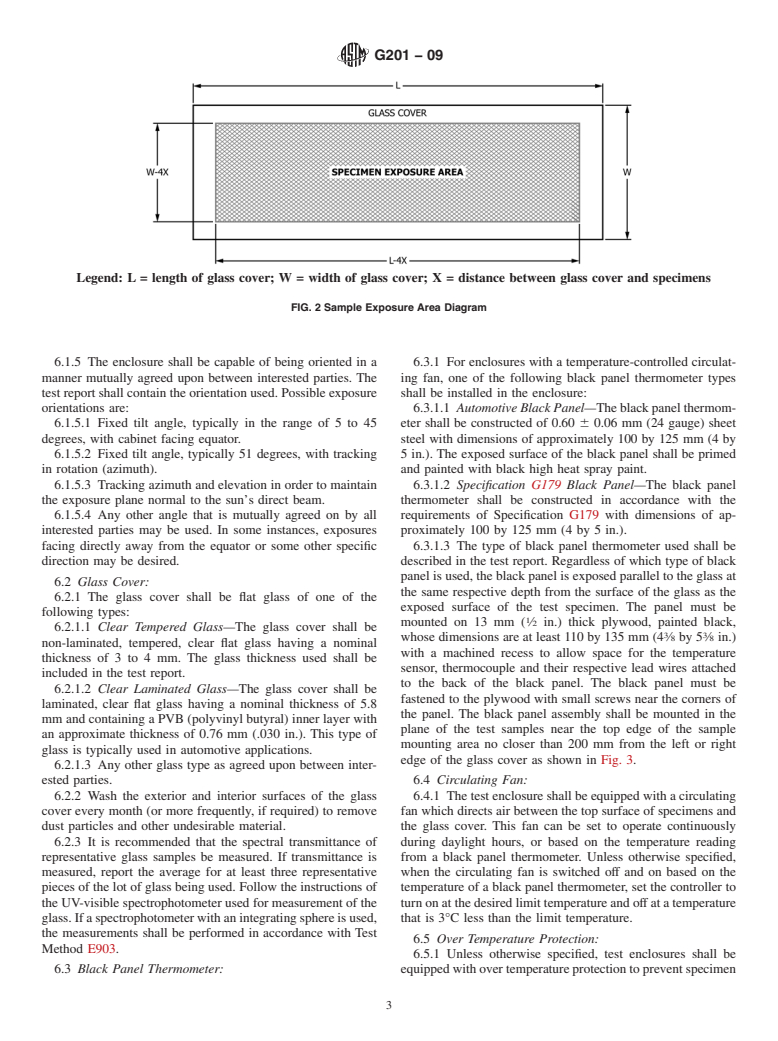
sides of the enclosure, the usable exposure area under the glass
shall be limited to that of the glass cover reduced by twice the
6. Apparatus
distance from the cover to the specimens as shown in Fig. 2.
6.1 Enclosure: TheeffectivewidthofthespecimenmountingareaisL-4Xand
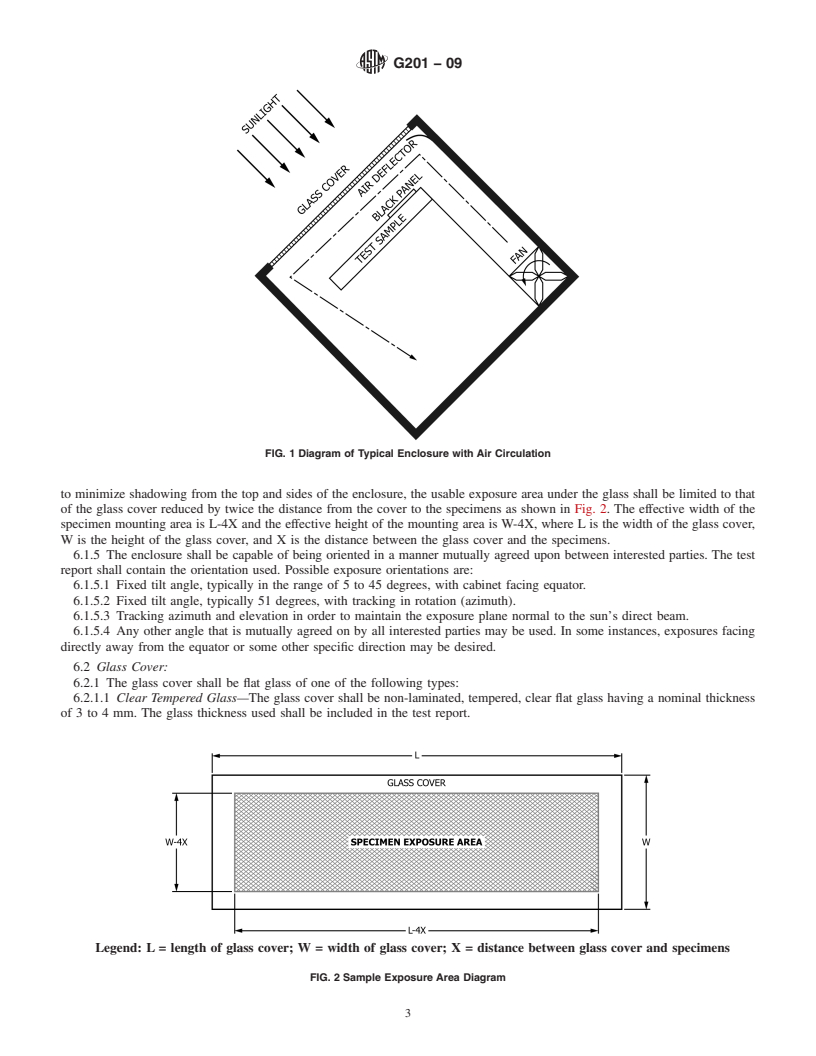
6.1.1 Exposures shall be conducted in a glass-covered the effective height of the mounting area is W-4X, where L is
enclosure of any convenient size (see Fig. 1). The enclosure the width of the glass cover, W is the height of the glass cover,
shall be constructed of a corrosion-resistant metal, such as and X is the distance between the glass cover and the
anodized aluminum or stainless steel, and be designed to specimens.
G201 − 09
Legend: L = length of glass cover; W = width of glass cover; X = distance between glass cover and specimens
FIG. 2 Sample Exposure Area Diagram
6.1.5 The enclosure shall be capable of being oriented in a 6.3.1 For enclosures with a temperature-controlled circulat-
manner mutually agreed upon between interested parties. The ing fan, one of the following black panel thermometer types
test report shall contain the orientation used. Possible exposure shall be installed in the enclosure:
orientations are: 6.3.1.1 Automotive Black Panel—Theblackpanelthermom-
6.1.5.1 Fixed tilt angle, typically in the range of 5 to 45 eter shall be constructed of 0.60 6 0.06 mm (24 gauge) sheet
degrees, with cabinet facing equator. steel with dimensions of approximately 100 by 125 mm (4 by
6.1.5.2 Fixed tilt angle, typically 51 degrees, with tracking 5 in.). The exposed surface of the black panel shall be primed
in rotation (azimuth). and painted with black high heat spray paint.
6.1.5.3 Tracking azimuth and elevation in order to maintain 6.3.1.2 Specification G179 Black Panel—The black panel
the exposure plane normal to the sun’s direct beam. thermometer shall be constructed in accordance with the
6.1.5.4 Any other angle that is mutually agreed on by all requirements of Specification G179 with dimensions of ap-
interested parties may be used. In some instances, exposures proximately 100 by 125 mm (4 by 5 in.).
facing directly away from the equator or some other specific 6.3.1.3 The type of black panel thermometer used shall be
direction may be desired. described in the test report. Regardless of which type of black
panel is used, the black panel is exposed parallel to the glass at
6.2 Glass Cover:
the same respective depth from the surface of the glass as the
6.2.1 The glass cover shall be flat glass of one of the
exposed surface of the test specimen. The panel must be
following types:
mounted on 13 mm ( ⁄2 in.) thick plywood, painted black,
6.2.1.1 Clear Tempered Glass—The glass cover shall be
3 3
whose dimensions are at least 110 by 135 mm (4 ⁄8 by 5 ⁄8 in.)
non-laminated, tempered, clear flat glass having a nominal
with a machined recess to allow space for the temperature
thickness of 3 to 4 mm. The glass thickness used shall be
sensor, thermocouple and their respective lead wires attached
included in the test report.
to the back of the black panel. The black panel must be
6.2.1.2 Clear Laminated Glass—The glass cover shall be
fastened to the plywood with small screws near the corners of
laminated, clear flat glass having a nominal thickness of 5.8
the panel. The black panel assembly shall be mounted in the
mm and containing a PVB (polyvinyl butyral) inner layer with
plane of the test samples near the top edge of the sample
an approximate thickness of 0.76 mm (.030 in.). This type of
mounting area no closer than 200 mm from the left or right
glass is typically used in automotive applications.
edge of the glass cover as shown in Fig. 3.
6.2.1.3 Any other glass type as agreed upon between inter-
ested parties. 6.4 Circulating Fan:
6.2.2 Wash the exterior and interior surfaces of the glass 6.4.1 The test enclosure shall be equipped with a circulating
cover every month (or more frequently, if required) to remove fan which directs air between the top surface of specimens and
dust particles and other undesirable material. the glass cover. This fan can be set to operate continuously
6.2.3 It is recommended that the spectral transmittance of during daylight hours, or based on the temperature reading
representative glass samples be measured. If transmittance is from a black panel thermometer. Unless otherwise specified,
measured, report the average for at least three representative when the circulating fan is switched off and on based on the
pieces of the lot of glass being used. Follow the instructions of temperature of a black panel thermometer, set the controller to
the UV-visible spectrophotometer used for measurement of the turn on at the desired limit temperature and off at a temperature
glass.Ifaspectrophotometerwithanintegratingsphereisused, that is 3°C less than the limit temperature.
the measurements shall be performed in accordance with Test
6.5 Over Temperature Protection:
Method E903.
6.5.1 Unless otherwise specified, test enclosures shall be
6.3 Black Panel Thermometer: equippedwithovertemperatureprotectiontopreventspecimen
G201 − 09
If only one specimen is available, it is recommended to make
at least three measurements in different locations if possible.
Mount test specimens in the test enclosure. For specimens that
come in direct contact with plywood, it is recommended that
plywood be covered with white card stock to shield specimens
from exudation from plywood.
7.5 If test enclosures are used in tracking mode, set the
enclosures to follow the sun between sunrise and sunset. If the
circulating fan is set to non temperature control mode, the fan
shall be switched on at sunrise and switched off at sunset.
Other start and stop times may be used for daylight operations.
If the circulating fan is set to a specified limit temperature, the
control can be set to operate 24 hours per day, or while
enclosures are following the sun.
FIG. 3 Black Panel Location
7.6 Expose the test specimens and control specimens in the
glass-covered test enclosure continuously 24 hours a day and
overheating in the event of a fan failure. The over temperature
remove from the cabinet only for inspection, return of
protection shall be set to operate at a temperature no greater
speci
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: G201 − 09 G201 − 09
Standard Practice for
Conducting Exposures in Outdoor Glass-Covered Exposure
Apparatus with Air Circulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G201; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the basic principles and operating procedures for using outdoor glass-covered exposure apparatus with
air circulation. This practice is limited to the procedures for obtaining, measuring and controlling conditions of exposure. A number
of exposure procedures are listed in Appendix X1; however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited for
the material to be tested.
1.2 For direct weathering exposures, refer to Practice G7. For exposures behind glass without air circulation, refer to Practice
G24.
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to solar radiation filtered through glass under partially controlled environmental test conditions.
Different glass types and operating parameters are described.
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific materials.
More specific information for determining the change in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described in
Practices D5870, D2244 and Test Method D523.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
D2244 Practice for Calculation of Color Tolerances and Color Differences from Instrumentally Measured Color Coordinates
D5870 Practice for Calculating Property Retention Index of Plastics
E903 Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
E1084 Test Method for Solar Transmittance (Terrestrial) of Sheet Materials Using Sunlight
G7 Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Testing of Nonmetallic Materials
G24 Practice for Conducting Exposures to Daylight Filtered Through Glass
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural and Artificial Weathering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
G141 Guide for Addressing Variability in Exposure Testing of Nonmetallic Materials
G173 Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
G177 Tables for Reference Solar Ultraviolet Spectral Distributions: Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface
G179 Specification for Metal Black Panel and White Panel Temperature Devices for Natural Weathering Tests
G183 Practice for Field Use of Pyranometers, Pyrheliometers and UV Radiometers
2.2 Other Document:
WMO No. 8 Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation, Fifth Edition
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G03 on Weathering and Durability and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.02 on Natural and
Environmental Exposure Tests.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2009. Published May 2010. DOI: 10.1520/G0201–09.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 7bis, avenue de la Paix, Case postale 2300, CH-1211 Geneva 2, Switzerland, http://www.wmo.int.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
G201 − 09
2.3 ISO Standard:
ISO 9060 Solar energy — Specification and classification of instruments for measuring hemispherical solar and direct solar
radiation
3. Terminology
3.1 The definitions given in Terminology G113 are applicable to this practice.
3.2 Other Definitions:
3.2.1 limit temperature, n—For enclosures operated in temperature control mode, the specified black panel temperature at which
the circulating fan switches on in order to prevent or minimize black panel temperature readings above the set temperature.
4. Summary of Practices
4.1 Specimens are exposed to light, moisture (in the form of humidity) and heat in an outdoor glass-covered enclosure with air
circulation.
4.2 The exposure conditions may be varied by selection of:
4.2.1 Glass Type:
4.2.2 Operation of the circulating fan (whether constantly on during daylight hours or only on when a specific limit temperature
is reached).
4.2.3 Temperature level at which the fan operates.
4.2.4 Orientation of the test fixture.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 As with any accelerated test, the increase in rate of weathering compared to in-service exposure is material dependent.
Results from exposures conducted to this practice may provide good rank correlation to results from actual use conditions for one
type of material or product. It should not be assumed that this will be true for other materials or products. It is always best to verify
the ability of an accelerated exposure test to properly rank the durability of materials with actual use conditions. Guide G141
provides information about using rank correlation.
5.2 Variation in results may be expected when operating conditions are varied within the accepted limits of this practice.
Therefore, no reference shall be made to results from the use of this practice unless accompanied by a report detailing the specific
operating conditions in conformance with Report Section 8.
5.3 The durability of materials in outdoor use can be very different depending on the location of the exposure because of
differences in solar radiation, moisture, heat, pollutants, and other factors. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that results from
exposure in a single location will be useful for determining durability ranking of materials in a different location.
5.4 It is strongly recommended that at least one control material be exposed with each test. The control material should be of
similar composition and construction and be chosen so that its failure modes are the same as that of the material being tested. It
is preferable to use two control materials, one with relatively good durability, and one with relatively poor durability. If control
materials are included as part of the test, they shall be used for the purpose of comparing the performance of the test materials
relative to the controls.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Enclosure:
6.1.1 Exposures shall be conducted in a glass-covered enclosure of any convenient size (see Fig. 1). The enclosure shall be
constructed of a corrosion-resistant metal, such as anodized aluminum or stainless steel, and be designed to prevent outside air
from circulating over specimens. Optionally, vents covered with air filter material may be installed in the bottom of the test fixture
if required to limit the black panel temperature to a specified maximum.
6.1.2 The enclosure shall be located where it will receive solar radiation throughout the day with no shadow on any specimen
when the sun’s angle of elevation is greater than 20 degrees. When the enclosure is installed over grass, the distance between the
bottom of the enclosure and the ground shall be sufficient to prevent contact with plant growth, or to minimize damage that might
occur during maintenance.
6.1.3 The enclosure shall be equipped with a rack which supports the specimens in a plane parallel to the glass. Alternately, the
specimens can be mounted in an in-service position. Unless otherwise specified, the distance between the exposed surface of flat
specimens shall be 75 6 25 mm from the back surface of the glass cover.
6.1.4 Formed specimens with irregular dimensions may require custom mounting with varying distances from the glass cover.
In such cases, mount the test specimen surface of major interest parallel to the glass cover at a distance of 75 6 25 mm from the
glass cover. The mounting frame or plate shall be constructed of a material that is compatible with the test specimens. In order
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.ch.
G201 − 09
FIG. 1 Diagram of Typical Enclosure with Air Circulation
to minimize shadowing from the top and sides of the enclosure, the usable exposure area under the glass shall be limited to that
of the glass cover reduced by twice the distance from the cover to the specimens as shown in Fig. 2. The effective width of the
specimen mounting area is L-4X and the effective height of the mounting area is W-4X, where L is the width of the glass cover,
W is the height of the glass cover, and X is the distance between the glass cover and the specimens.
6.1.5 The enclosure shall be capable of being oriented in a manner mutually agreed upon between interested parties. The test
report shall contain the orientation used. Possible exposure orientations are:
6.1.5.1 Fixed tilt angle, typically in the range of 5 to 45 degrees, with cabinet facing equator.
6.1.5.2 Fixed tilt angle, typically 51 degrees, with tracking in rotation (azimuth).
6.1.5.3 Tracking azimuth and elevation in order to maintain the exposure plane normal to the sun’s direct beam.
6.1.5.4 Any other angle that is mutually agreed on by all interested parties may be used. In some instances, exposures facing
directly away from the equator or some other specific direction may be desired.
6.2 Glass Cover:
6.2.1 The glass cover shall be flat glass of one of the following types:
6.2.1.1 Clear Tempered Glass—The glass cover shall be non-laminated, tempered, clear flat glass having a nominal thickness
of 3 to 4 mm. The glass thickness used shall be included in the test report.
Legend: L = length of glass cover; W = width of glass cover; X = distance between glass cover and specimens
FIG. 2 Sample Exposure Area Diagram
G201 − 09
6.2.1.2 Clear Laminated Glass—The glass cover shall be laminated, clear flat glass having a nominal thickness of 5.8 mm and
containing a PVB (polyvinyl butyral) inner layer with an approximate thickness of 0.76 mm (.030 in.). This type of glass is
typically used in automotive applications.
6.2.1.3 Any other glass type as agreed upon between interested parties.
6.2.2 Wash the exterior and interior surfaces of the glass cover every month (or more frequently, if required) to remove dust
particles and other undesirable material.
6.2.3 It is recommended that the spectral transmittance of representative glass samples be measured. If transmittance is
measured, report the average for at least three representative pieces of the lot of glass being used. Follow the instructions of the
UV-visible spectrophotometer used for measurement of the glass. If a spectrophotometer with an integrating sphere is used, the
measurements shall be performed in accordance with Test Method E903.
6.3 Black Panel Thermometer:
6.3.1 For enclosures with a temperature-controlled circulating fan, one of the following black panel thermometer types shall be
installed in the enclosure:
6.3.1.1 Automotive Black Panel—The black panel thermometer shall be constructed of 0.60 6 0.06 mm (24 gauge) sheet steel
with dimensions of approximately 100 by 125 mm (4 by 5 in.). The exposed surface of the black panel shall be primed and painted
with black high heat spray paint.
6.3.1.2 Specification G179 Black Panel—The black panel thermometer shall be constructed in accordance with the requirements
of Specification G179 with dimensions of approximately 100 by 125 mm (4 by 5 in.).
6.3.1.3 The type of black panel thermometer used shall be described in the test report. Regardless of which type of black panel
is used, the black panel is exposed parallel to the glass at the same respective depth from the surface of the glass as the exposed
surface of the test specimen. The panel must be mounted on 13 mm ( ⁄2 in.) thick plywood, painted black, whose dimensions are
3 3
at least 110 by 135 mm (4 ⁄8 by 5 ⁄8 in.) with a machined recess to allow space for the temperature sensor, thermocouple and their
respective lead wires attached to the back of the black panel. The black panel must be fastened to the plywood with small screws
near the corners of the panel. The black panel assembly shall be mounted in the plane of the test samples near the top edge of the
sample mounting area no closer than 200 mm from the left or right edge of the glass cover as shown in Fig. 3.
6.4 Circulating Fan:
6.4.1 The test enclosure shall be equipped with a circulating fan which directs air between the top surface of specimens and the
glass cover. This fan can be set to operate continuously during daylight hours, or based on the temperature reading from a black
panel thermometer. Unless otherwise specified, when the circulating fan is switched off and on based on the temperature of a black
panel thermometer, set the controller to turn on at the desired limit temperature and off at a temperature that is 3°C less than the
limit temperature.
6.5 Over Temperature Protection:
6.5.1 Unless otherwise specified, test enclosures shall be equipped with over temperature protection to prevent specimen
overheating in the event of a fan failure. The over temperature protection shall be set to operate at a temperature no greater than
6°C above the limit temperature. The over temperature protection shall cover the test enclosure or change the enclosure orientation
in order to prevent damage to specimens being exposed.
6.6 Climatological Instruments:
6.6.1 Within 1000 m of test enclosures shall be an area designated for measuring climatological conditions such as ambient
temperature, relative humidity, and solar radiation.
6.6.2 Optionally, ambient air temperature and relative humidity can be measured in a shielded, elevated location.
6.6.3 Solar Radiation:
FIG. 3 Black Panel Location
G201 − 09
6.6.3.1 Instrumental means of measuring full-spectrum solar rad
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.