ASTM E1343-90(2001)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Molecular Weight Cutoff Evaluation of Flat Sheet Ultrafiltration Membranes (Withdrawn 2010)
Standard Test Method for Molecular Weight Cutoff Evaluation of Flat Sheet Ultrafiltration Membranes (Withdrawn 2010)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a convenient, rapid, reproducible method of comparing the intrinsic properties of ultrafiltration membranes. The use of nonfouling dextrans allows a direct comparison of membranes without interference from materials that may foul one membrane and not affect another. The degree of correlation between this test and actual performance on a commercial feed stream has not been completely established; however, a membrane can be exposed to the fouling solution in question and then the effect of that foulant determined by then running the test and comparing to the results on an appropriate unfouled membrane. It should be made clear that this test method does not substitute for the actual testing of a commercial or experimental membrane on a feed stream of interest. The low transmembrane pressures, lack of adsorption of the test permeants onto the membrane, and low recovery/pass are intended to eliminate interferences such as polarization and fouling that mask the properties of the membrane. It is likely that any system operated in a commercial fashion will experience fouling, adsorption, and polarization to some degree as well as a “compaction” phenomenon over the first several h of operation.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the molecular weight cutoff of flat sheet ultrafiltration membranes with cutoffs between 4500 and 1000000 daltons. The nonadsorbing characteristics of the test penetrant utilized by this test method permit the test to be performed on a wide variety of membrane substrates, excluding those which strongly adsorb dextran, from highly hydrophilic to highly hydrophobic. This test method is not applicable for microfiltration membranes with pore sizes of 0.01 µm or larger, nor for reverse osmosis or dialysis membranes with less than 4500 molecular weight cutoff. (It is possible that this test method could be modified to expand the range from 100 to 2 000 000 daltons.) This test method is not applicable to membrane materials that strongly adsorb dextrans since these materials will potentially change the value of the measured molecular weight cutoff and hence will invalidate the test results.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covers the evaluation of the molecular weight cutoff of flat sheet ultrafiltration membranes with cutoffs between 4500 and 1 000 000 daltons. The nonadsorbing characteristics of the test penetrant utilized by this test method permit the test to be performed on a wide variety of membrane substrates, excluding those which strongly adsorb dextran, from highly hydrophilic to highly hydrophobic. This test method is not applicable for microfiltration membranes with pore sizes of 0.01 μm or larger, nor for reverse osmosis or dialysis membranes with less than 4500 molecular weight cutoff. (It is possible that this test method could be modified to expand the range from 100 to 2 000 000 daltons.) This test method is not applicable to membrane materials that strongly adsorb dextrans since these materials will potentially change the value of the measured molecular weight cutoff and hence will invalidate the test results.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee E48 on Biotechnology, this test method was withdrawn in February 2010 in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: E1343 – 90 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Test Method for
Molecular Weight Cutoff Evaluation of Flat Sheet
Ultrafiltration Membranes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope tration membranes. The use of nonfouling dextrans allows a
direct comparison of membranes without interference from
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the molecular
materials that may foul one membrane and not affect another.
weight cutoff of flat sheet ultrafiltration membranes with
The degree of correlation between this test and actual perfor-
cutoffsbetween4500and1 000 000daltons.Thenonadsorbing
mance on a commercial feed stream has not been completely
characteristics of the test penetrant utilized by this test method
established; however, a membrane can be exposed to the
permit the test to be performed on a wide variety of membrane
fouling solution in question and then the effect of that foulant
substrates, excluding those which strongly adsorb dextran,
determined by then running the test and comparing to the
from highly hydrophilic to highly hydrophobic. This test
results on an appropriate unfouled membrane. It should be
method is not applicable for microfiltration membranes with
made clear that this test method does not substitute for the
pore sizes of 0.01 µm or larger, nor for reverse osmosis or
actual testing of a commercial or experimental membrane on a
dialysis membranes with less than 4500 molecular weight
feed stream of interest.The low transmembrane pressures, lack
cutoff. (It is possible that this test method could be modified to
of adsorption of the test permeants onto the membrane, and
expand the range from 100 to 2 000 000 daltons.) This test
low recovery/pass are intended to eliminate interferences such
method is not applicable to membrane materials that strongly
as polarization and fouling that mask the properties of the
adsorb dextrans since these materials will potentially change
membrane. It is likely that any system operated in a commer-
the value of the measured molecular weight cutoff and hence
cial fashion will experience fouling, adsorption, and polariza-
will invalidate the test results.
tion to some degree as well as a “compaction” phenomenon
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
over the first several h of operation.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 The basic membrane test system consists of the follow-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ing:
2. Summary of Test Method 4.1.1 Standard Flat Membrane, Stirred Ultrafiltration Test
Cell, for 62-mm membrane disc, modified as shown in Fig. 1,
2.1 The membrane is rinsed with purified water and in-
4.1.2 Diaphragm Pump, approximately 0 to 200 mL/min
stalledinthetestcell.TheprecalibrateddextranT-fractionfeed
variable pumping range, 30 psig pressure capability at 100
is pumped through the cell and the flux through the membrane
mL/min, all wetted parts of 316 stainless steel and polyfluo-
is set at the value of 0.0001 cm/s and an ultrafiltrate sample
rocarbon construction,
taken and compared to a sample of the feed for molecular
4.1.3 Back Pressure Regulator and Pressure Gage,0to30
weight distribution. Gel permeation chromatography is used to
psig, 316 stainless steel,
compare the feed to the permeate and the rejection at each 3-s
4.1.4 Electronic Digital Flowmeter, with direct readout of
datasliceiscalculated.Theresultingrejectionisthenplottedas
volumetric flow in the approximate range 0.06 to 5 mL/min,
a function of the molecular mass average of the sample for the
4.1.5 Magnetic Stirplate with Tachometer,
data slice.
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Thistestmethodprovidesaconvenient,rapid,reproduc-
Membrane equipment, model 8200 or equal, available from Amicon Division
of W. R. Grace, 1114-T Avenue of the Americas, New York, NY 10036, has been
ible method of comparing the intrinsic properties of ultrafil-
found suitable for this purpose.
Diaphram pump, model EP-C40 or equal, available from CHEM/TECH
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E48 on International Industries, 1655-T Des Peres P.O. Box 31000, St. Louis, MO 63131,
Biotechnology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E48.03 on Unit has been found suitable for this purpose.
Processes and Validation. Stirplate, model 4650-54, or its equivalent, available from Cole Parmer
Current edition approved May 10, 2001. Published May 1990. DOI: 10.1520/ Spincadet,7427-TN.OakParkAve.,Chicago,IL60648,hasbeenfoundsuitablefor
E1343-90R01. this purpose.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E1343 – 90 (2001)
NOTE 1—The top of a standard stirred ultrafiltration cell was modified by drilling a hole through it and tapping it for ⁄8-in. male pipe thread (MPT).
1 1 1
Anylon fitting ( ⁄8-in. tube to ⁄8-in. MPT) was drilled through to allow the insertion of ⁄8-in. tubing. The fitting was threaded into the top of the test cell.
Astainlesssteelinlettubewaspreparedasshown.Thenylonfittingallowsforthedirectionofflowtobeatanyheight,anddirection,orboth.Theexisting
fitting in the cap is used as an exit of flow. If the cell is equipped with a wrap-around clamp, it is modified to accommodate the extra fitting.
FIG. 1 Flow Through Modification of an Amicon-Stirred Cell
4.1.6 MagneticStirPlate,Stirbar,andContainer,(1000cm 4.2.5 Differential Refractometer HPLC Detector, with 30°C
Erlenmeyer) for test solution, water recirculating in the detector block and associated ther-
4.1.7 Pulse Dampener, 500-Ml, 316 stainless steel, mostatically controlled water source 60.1°C,
4.1.8 Suitable Thermostatically Controlled Bath, capable of 4.2.6 Computing Integrator, with data slicing and BASIC
30 6 0.2°C, programming capabilities and suitable connecting cables for
4.1.9 Highly Reproducible and Stable Peristaltic Pump, the integrator and detector. The integrator should include a
capable of flows in the 0.06 to 5 mL/min range, printer capability to provide on-line output.
4.1.10 Appropriate Silicone Rubber Tubing, for the peristal-
5. Reagents and Materials
tic pump, and
4.1.11 Inline Filters, two, 2 and 15-µm, 316 stainless steel
5.1 Dextran T-fractions—10 000 (T-10); 40 000 (T-40);
construction. 70 000 (T-70); and 500 000 (T-500) average molecular mass,
4.2 The gel chromatography system consists of the follow-
supplied by the manufacturer with calibration curves of instan-
ing: taneous and cumulative distribution versus molecular mass.
4.2.1 Good Quality High-Performance Liquid Chromatog-
5.2 Purified Water—Treated with reverse osmosis, ion ex-
5 11
raphy (HPLC) Pump with Highly Reproducible Flow, change and 0.2-µm filter to 18 MV quality.
4.2.2 HPLC Injection Valve, with 20-mL sample loop and a 5.3 Sodium Azide.
position sensing switch,
6. Hazards
4.2.3 Pair of Gel Permeation Columns, capable of size
exclusion separation of dextran polysaccharides in the 4500 to
6.1 Warning—Sodium azide is toxic and flammable with a
6 7
10 molecular mass range,
tolerance of 1 ppm in air, while the dextran T-fractions are
4.2.4 Precolumn Filter to Protect the Columns (Guard
nontoxic, the pressures utilized are hydraulic and are typically
Column),
less than one atmosphere.
7. Preparation of Apparatus
HPLC pump such as Beckman 110B Solvent Delivery Module, or its
7.1 Assembly of Equipment—Chromatograph:
equivalent, available from Beckman Instruments, Inc., 2500-T Harbor Blvd., L-19
Fullerton, CA, has been found suitable for this purpose.
Injectionvalve,suchas7010HPLC,oritsequivalent,availablefromRheodyne
Inc., 6815-T S. Santa Rosa Ave., P.O. Box 996, Cotati, CA 94928 has been found Refractometer such as a R401 Differential, or its equivalent, available from
suitable for this purpose. Walters Inc., has been found suitable for this purpose.
7 10
Gel permeation columns such as Toyo-Soda G4000PW and G2000PW, with Computing integrator such as model SP.4270, or its equivalent, available from
matching guard column or equivalents, have been found suitable for this purpose. Spectra Physics, 5475-T Kellenberger Dr., Dayton, OH 45425, has been found
Filters such as #84 560, or equivalents, available from Walters Inc., Mausner suitable for this purpose.
Equipment Co. Inc., 1304-T Prospect Ave. East Meadows, NY, have been found System such as a Millipore Milli-Q, or its equivalent, available from Millipore
suitable for this purpose. Inc., 80 Ashby Rd., Bedford, MA, has been found suitable for this purpose.
E1343 – 90 (2001)
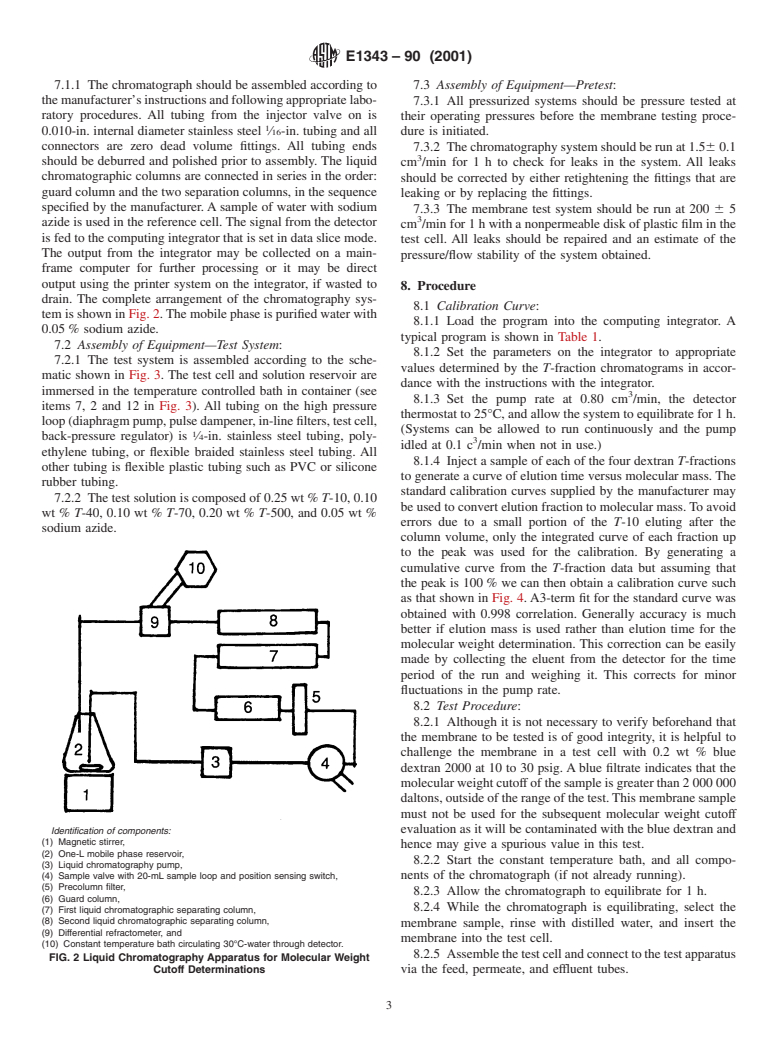
7.1.1 The chromatograph should be assembled according to 7.3 Assembly of Equipment—Pretest:
themanufacturer’sinstructionsandfollowingappropriatelabo- 7.3.1 All pressurized systems should be pressure tested at
ratory procedures. All tubing from the injector valve on is
their operating pressures before the membrane testing proce-
0.010-in. internal diameter stainless steel ⁄16-in. tubing and all dure is initiated.
connectors are zero dead volume fittings. All tubing ends
7.3.2 Thechromatographysystemshouldberunat1.560.1
should be deburred and polished prior to assembly. The liquid
cm /min for1hto check for leaks in the system. All leaks
chromatographic columns are connected in series in the order:
should be corrected by either retightening the fittings that are
guard column and the two separation columns, in the sequence leaking or by replacing the fittings.
specified by the manufacturer. A sample of water with sodium
7.3.3 The membrane test system should be run at 200 6 5
azide is used in the reference cell. The signal from the detector
cm /min for 1 h with a nonpermeable disk of plastic film in the
is fed to the computing integrator that is set in data slice mode.
test cell. All leaks should be repaired and an estimate of the
The output from the integrator may be collected on a main-
pressure/flow stability of the sy
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.