ASTM B505-96
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Base Alloy Continuous Castings
Standard Specification for Copper-Base Alloy Continuous Castings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for continuously cast rod, bar, tube, and shapes produced from copper-base alloys with nominal compositions as listed in Table 1.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. SI values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 505 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Copper-Base Alloy Continuous Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 505; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * 3.1.5 ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code requirements
(Section 7),
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for continu-
3.1.6 When castings are purchased for agencies of the U.S.
ously cast rod, bar, tube, and shapes produced from copperbase
Government, the Supplementary Requirements of Specifica-
alloys with nominal compositions as listed in Table 1.
tion B 824 may be specified.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are the standard.
3.2 The following requirements are optional and should be
SI values given in parentheses are provided for information
specified in the purchase order when required.
purposes only.
3.2.1 Chemical analysis of residual elements (Section 5),
2. Referenced Documents
3.2.2 Mechanical requirements, (Section 6),
3.2.3 Witness inspection (Specification B 824),
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the
3.2.4 Certification (Specification B 824),
Book of Standards form a part of this specification to the extent
3.2.5 Foundry test report (Specification B 824),
referenced herein:
3.2.6 Product marking (Specification B 824),
2.2 ASTM Standards:
3.2.7 Castings for seawater service (Section 4),
B 208 Practice for Preparing Tension Test Specimens for
3.2.8 Approval of weld repair and records of repair (Section
Copper-Base Alloys for Sand, Permanent Mold, Centrifu-
9).
gal and Continuous Castings
B 824 Specification for General Requirements for Copper
4. Materials and Manufacture
Alloy Castings
4 4.1 For better corrosion resistance in sea water applications,
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
castings in Copper Alloy C95800 shall be given a temperature
E 10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materi-
anneal heat treatment at 1250 6 50°F (675 6 10°C) for 6 h
als
minimum. Cooling shall be by the fastest means possible that
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
will not cause excessive distortion or cracking. Propeller
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials
castings shall be exempt from this requirement.
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
4.2 Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C95300, C95400, C95410, and
3. Ordering Information
C95500 may be supplied in the heat-treated condition to obtain
the higher mechanical properties shown in Table 9. Suggested
3.1 Orders for continuous castings under this specification
heat treatments for these alloys and Copper Alloy UNS No.
should include the following information:
C95520 are given in Table 2. Actual practice may vary by
3.1.1 Specification title, number, and year of issue,
manufacturer.
3.1.2 Quantity, dimensions, and temper,
4.3 Copper Alloy UNS No. C95520 is used only in the
3.1.3 Copper Alloy UNS Number,
quench-hardened and tempered (TQ30) condition.
3.1.4 Tolerances, if different from Section 8 and Tables 2-8,
4.4 Copper Alloy UNS No. C96900 is normally supplied
heat treated at 1520°F (825°C) for 1 h followed by a water
quench, then aged at 800°F (425°C) for 4 h followed by a water
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-5 on Copper quench.
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.05 on
4.5 If test bar coupons representing castings made in Copper
Castings and Ingots for Remelting.
Alloy UNS Nos. C94700HT, C95300HT, C95400HT,
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1996. Published November 1996. Originally
C95410HT, C95500HT, C95520HT, C95800 temper annealed,
published as B 505 – 70. Last previous edition B 505 – 95.
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple
C95900 annealed and C96900 are removed from the continu-
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition
ous castings before heat treatment, the coupons shall be heat
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00”. The suffix can be used to accommodate
composition variations of the base alloy.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Available from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, United Engi-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01. neering Center, 345 East 47th St., New York, NY 10017.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 505
TABLE 1 Nominal Composition
Composition, %
Copper Alloy UNS
Designation
No.
Copper Tin Lead Zinc Nickel Aluminum Iron Manganese
C83600 leaded red brass 85 5 5 5 . . . .
C83800 leaded red brass 83 4 6 7 . . . .
C84200 leaded semi-red brass 80 5 2 13 . . . .
C84400 leaded semi-red brass 81 3 7 9 . . . .
C84800 leaded semi-red brass 76 3 6 15 . . . .
C85700 leaded naval brass 61 1 1 37 . . . .
C86200 high-strength yellow brass 66 . . 23 . 5 3 3
C86300 high-strength yellow brass 62 . . 26 . 6 3 3
C86500 high-strength yellow brass 58 . . 39 . 1 1 1
A
C89320 bismuth tin bronze 89 6 . . . . . .
C90300 tin bronze 88 8 . 4 . . . .
C90500 tin bronze 88 10 . 2 . . . .
C90700 tin bronze 89 11 . . . . . .
C91000 tin bronze 85 15 . . . . . .
C91300 tin bronze 81 19 . . . . . .
C92200 leaded tin bronze 88 6 2 4 . . . .
C92300 leaded tin bronze 87 8 1 4 . . . .
C92500 nickel-phosphor bronze 86.5 11 1 . 1.5 . . .
C92700 leaded tin bronze 88 10 2 . . . . .
C92800 leaded tin bronze 79 16 5 . . . . .
C92900 leaded nickel-tin bronze 84 10 2.5 . 3.5 . . .
C93200 high-leaded tin bronze 83 7 7 3 . . . .
C93400 high-leaded tin bronze 84 8 8 . . . . .
C93500 high-leaded tin bronze 85 5 9 1 . . . .
C93600 high-leaded tin bronze 81 7 12 . . . . .
C93700 high-leaded tin bronze 80 10 10 . . . . .
C93800 high-leaded tin bronze 78 7 15 . . . . .
C93900 high-leaded tin bronze 78 6 16 . . . . .
C94000 high-leaded tin bronze 72 13 15 . . . . .
C94100 high-leaded tin bronze 75 5 20 . . . . .
C94300 high-leaded tin bronze 70 5 25 . . . . .
C94700 nickel-tin bronze 88 5 0 2 5 . . .
C94800 leaded nickel-tin bronze 87 5 1 2 5 . . .
C95200 aluminum bronze 88 . . . . 9 3 .
C95300 aluminum bronze 89 . . . . 10 1 .
C95400 aluminum bronze 85 . . . . 11 4 .
C95410 aluminum bronze 84 . . . 2 10 4 .
C95500 nickel-aluminum bronze 81 . . . 4 11 4 .
C95520 nickel-aluminum bronze 78.5 . . . 5.5 11 5.0 .
C95700 manganese nickel aluminum 75 . . . 2 8 3 12
bronze
C95800 nickel-aluminum bronze 81.3 . . . 4.5 9 4 1.2
C95900 aluminum bronze 82.5 . . . . 13 4.5 .
C96400 copper-nickel 70 . . . 30 . . .
C96900 copper-nickel 76.6 8 . . 15 . . 0.4
C97300 leaded nickel bronze 57 2 9 20 12 . . .
C97600 leaded nickel bronze 64 4 4 8 20 . . .
C97800 leaded nickel bronze 66 5 2 2 25 . . .
B
C99500 special alloy 87 . . 1.5 4.5 1.7 4.0 .
A
Bismuth 5.0
B
Silicon 1.3
TABLE 2 Suggested Heat Treatments TABLE 3 Finishing Allowances for Tube (Round Only)
Annealing Treatment Finish Allowances Added to Finished or
Solution Treatment (not less than
Copper Alloy (not less than 2 h Finished Outside Diameter, Print
1 h followed by water quench),
UNS No. followed by air cool), in. (mm) Dimensions of the Part, in. (mm)
°F(°C)
°F(°C) Inside Diameter Outside Diameter
All Alloys Except as Noted Below
C95300 1585–1635 1150–1225
Up to 4 (102), excl −0.031 (−0.79) + 0.031 (0.79)
(860–890) (620–660)
4 (102)–5 (127), incl −0.063 (−1.6) + 0.063 (1.6)
Over 5 (127) −0.094 (−2.4) + 0.094 (2.4)
C95400,
Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, C95400,
C95410, 1600–1675 1150–1225
C95500, C95800, C95900, and C96400
C95500 (870–910) (620–660)
Up to 3 (76.2), incl −0.125 (−3.2) + 0.063 (1.6)
Over 3 (76.2)–4 (102), incl −0.125 (−3.2) + 0.094 (2.4)
C95520 (2 h followed by water quench) 925–1000
Over 4 (102)–5 ⁄2 (140), incl −0.188 (−4.8) + 0.125 (3.2)
1600–1700 (870–925) (495–540)
Over 5 ⁄2 (140) −0.250 (−6.4) + 0.188 (4.8)
treated with the continuous castings.
ments for major elements shown in Table 10.
5. Chemical Composition
5.2 These specification limits do not preclude the presence
5.1 The continuous castings shall conform to the require- of other elements. Limits may be established and analysis
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B 505
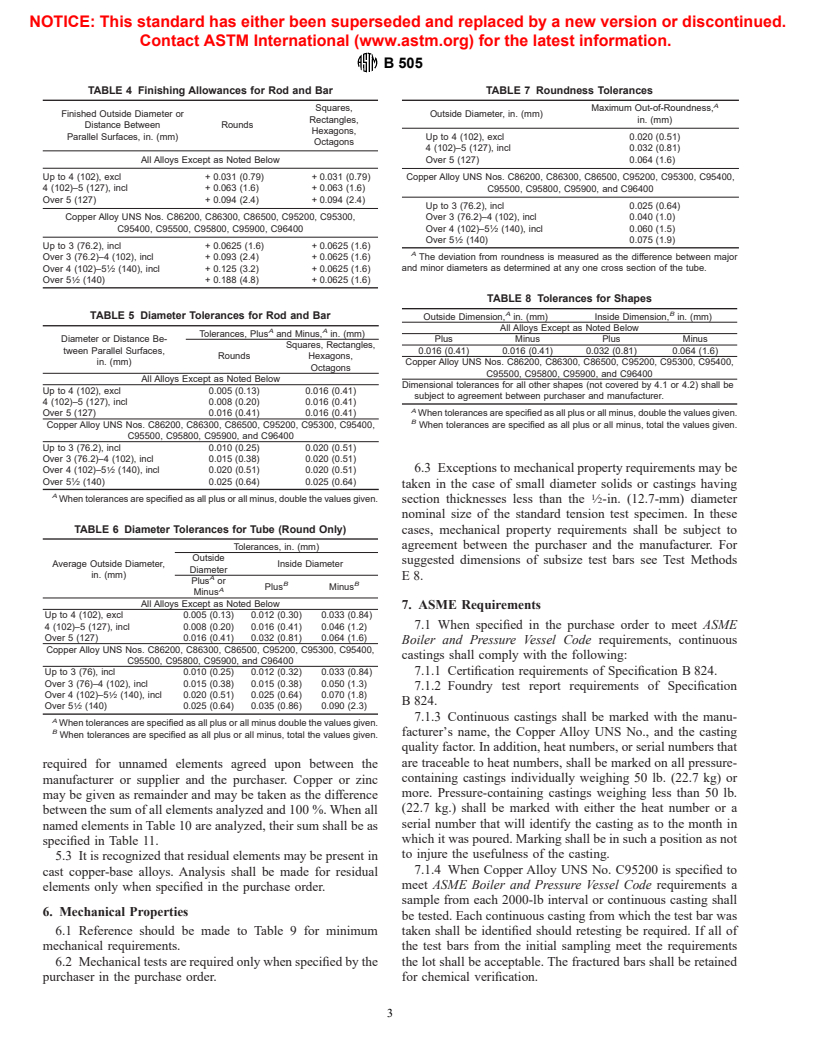
TABLE 4 Finishing Allowances for Rod and Bar TABLE 7 Roundness Tolerances
A
Squares, Maximum Out-of-Roundness,
Finished Outside Diameter or Outside Diameter, in. (mm)
Rectangles, in. (mm)
Distance Between Rounds
Hexagons,
Parallel Surfaces, in. (mm) Up to 4 (102), excl 0.020 (0.51)
Octagons
4 (102)–5 (127), incl 0.032 (0.81)
All Alloys Except as Noted Below
Over 5 (127) 0.064 (1.6)
Up to 4 (102), excl + 0.031 (0.79) + 0.031 (0.79) Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, C95400,
4 (102)–5 (127), incl + 0.063 (1.6) + 0.063 (1.6) C95500, C95800, C95900, and C96400
Over 5 (127) + 0.094 (2.4) + 0.094 (2.4)
Up to 3 (76.2), incl 0.025 (0.64)
Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, Over 3 (76.2)–4 (102), incl 0.040 (1.0)
C95400, C95500, C95800, C95900, C96400 Over 4 (102)–5 ⁄2 (140), incl 0.060 (1.5)
Over 5 ⁄2 (140) 0.075 (1.9)
Up to 3 (76.2), incl + 0.0625 (1.6) + 0.0625 (1.6)
A
Over 3 (76.2)–4 (102), incl + 0.093 (2.4) + 0.0625 (1.6) The deviation from roundness is measured as the difference between major
Over 4 (102)–5 ⁄2 (140), incl + 0.125 (3.2) + 0.0625 (1.6) and minor diameters as determined at any one cross section of the tube.
Over 5 ⁄2 (140) + 0.188 (4.8) + 0.0625 (1.6)
TABLE 8 Tolerances for Shapes
A B
TABLE 5 Diameter Tolerances for Rod and Bar Outside Dimension, in. (mm) Inside Dimension, in. (mm)
All Alloys Except as Noted Below
A A
Tolerances, Plus and Minus, in. (mm)
Diameter or Distance Be- Plus Minus Plus Minus
Squares, Rectangles,
tween Parallel Surfaces, 0.016 (0.41) 0.016 (0.41) 0.032 (0.81) 0.064 (1.6)
Rounds Hexagons,
in. (mm) Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, C95400,
Octagons
C95500, C95800, C95900, and C96400
All Alloys Except as Noted Below
Dimensional tolerances for all other shapes (not covered by 4.1 or 4.2) shall be
Up to 4 (102), excl 0.005 (0.13) 0.016 (0.41)
subject to agreement between purchaser and manufacturer.
4 (102)–5 (127), incl 0.008 (0.20) 0.016 (0.41)
A
Over 5 (127) 0.016 (0.41) 0.016 (0.41) When tolerances are specified as all plus or all minus, double the values given.
B
Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, C95400, When tolerances are specified as all plus or all minus, total the values given.
C95500, C95800, C95900, and C96400
Up to 3 (76.2), incl 0.010 (0.25) 0.020 (0.51)
Over 3 (76.2)–4 (102), incl 0.015 (0.38) 0.020 (0.51)
6.3 Exceptions to mechanical property requirements may be
Over 4 (102)–5 ⁄2 (140), incl 0.020 (0.51) 0.020 (0.51)
Over 5 ⁄2 (140) 0.025 (0.64) 0.025 (0.64)
taken in the case of small diameter solids or castings having
A
When tolerances are specified as all plus or all minus, double the values given.
section thicknesses less than the ⁄2-in. (12.7-mm) diameter
nominal size of the standard tension test specimen. In these
TABLE 6 Diameter Tolerances for Tube (Round Only)
cases, mechanical property requirements shall be subject to
agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer. For
Tolerances, in. (mm)
Outside
suggested dimensions of subsize test bars see Test Methods
Average Outside Diameter, Inside Diameter
Diameter
in. (mm)
E8.
A
Plus or
B B
Plus Minus
A
Minus
All Alloys Except as Noted Below
7. ASME Requirements
Up to 4 (102), excl 0.005 (0.13) 0.012 (0.30) 0.033 (0.84)
7.1 When specified in the purchase order to meet ASME
4 (102)–5 (127), incl 0.008 (0.20) 0.016 (0.41) 0.046 (1.2)
Over 5 (127) 0.016 (0.41) 0.032 (0.81) 0.064 (1.6)
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code requirements, continuous
Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C86200, C86300, C86500, C95200, C95300, C95400,
castings shall comply with the following:
C95500, C95800, C95900, and C96400
7.1.1 Certification requirements of Specification B 824.
Up to 3 (76), incl 0.010 (0.25) 0.012 (0.32) 0.033 (0.84)
Over 3 (76)–4 (102), incl 0.015 (0.38) 0.015 (0.38) 0.050 (1.3)
7.1.2 Foundry test report requirements of Specification
Over 4 (102)–5 ⁄2 (140), incl 0.020 (0.51) 0.025 (0.64) 0.070 (1.8)
B 824.
Over 5 ⁄2 (140) 0.025 (0.64) 0.035 (0.86) 0.090 (2.3)
7.1.3 Continuous castings shall be marked with the manu-
A
When tolerances are specified as all plus or all minus double the values given.
B
facturer’s name, the Copper Alloy UNS No., and the casting
When tolerances are specified as all plus or all minus, total the values given.
quality factor. In addition, heat numbers, or serial numbers that
are traceable to heat numbers, shall be marked on all pressure-
required for unnamed elements agreed upon between the
containing castings individually weighing 50 lb. (22.7 kg) or
manufacturer or supplier and the purchaser. Copper or zinc
more. Pressure-containing castings weighing less than 50 lb.
may be given as remainder and may be taken as the difference
(22.7 kg.) shall be marked with either the heat number or a
between the sum of all elements analyzed and 100 %. When all
serial number that will identify the casting as to the month in
named elements in Table 10 are analyzed, their sum shall be as
which it was poured. Marking shall be in such a position as not
specified in Table 11.
to injure the usefulness of the casting.
5.3 It is recognized that residual elements may be present in
7.1.4 When Copper Alloy UNS No. C95200 is specified to
cast copper-base alloys. Analysis shall be made for residual
meet ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code requirements a
elements only when spec
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.