ASTM B5-16
(Specification)Standard Specification for High Conductivity Tough-Pitch Copper Refinery Shapes
Standard Specification for High Conductivity Tough-Pitch Copper Refinery Shapes
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for high conductivity, tough-pitch, copper wire bars, cakes, slabs, billets, ingots, and ingot bars. Copper wires under this specification include UNS C113000, C11400, C11500 and C11600, C12000, C12200, C12300, and C14500. The maximum values of mass resistivity for wire bars, cakes, slabs, and billets, for electrical use and for other uses, shall conform to the specified requirements. Samples for the electrical resistivity test of electrolytic copper, electrorefined copper, electrowon copper, and fire-refined copper shall be fabricated into a rod. The external oxide shall be removed, the rod cold drawn into a wire of a specific diameter, and cut into sampling lengths. The resulting specimen shall be annealed and quickly cooled in an inert atmosphere. The mean resistivity shall be determined as the mean of the observations from the test on the wires.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
14.1 Calculated values shall be rounded to the specified number of places in accordance with Practice E29.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for high conductivity, tough-pitch, copper wire bars, cakes, slabs, billets, ingots, and ingot bars.
1.2 Copper under this specification corresponds to the designations “ETP” (UNS C11000) and “FRHC” (UNS C11020) as shown in Classification B224. These coppers may also be used to produce coppers corresponding to the following:
Copper UNS No.
Classification B224 Designation
C11300, C11400, C11500, and C11600
STP
C12000
DLP
C12200
DHP
C12300
DHPS
C14520
DPTE
1.3 Although this specification includes certain UNS designations as described in Practice E527, these designations are for cross reference only and are not specification requirements. Therefore, in case of conflict, this ASTM specification shall govern.
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Electrical resistivity is expressed in SI units.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B5 −16
Standard Specification for
1
High Conductivity Tough-Pitch Copper Refinery Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B5; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* B224 Classification of Coppers
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for high
B950 Guide for Editorial Procedures and Form of Product
conductivity, tough-pitch, copper wire bars, cakes, slabs,
Specifications for Copper and Copper Alloys
billets, ingots, and ingot bars.
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
1.2 Copper under this specification corresponds to the
Determine Conformance with Specifications
designations “ETP” (UNS C11000) and “FRHC” (UNS
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed
C11020) as shown in Classification B224. These coppers may
Copper by Gravimetry
also be used to produce coppers corresponding to the follow-
E255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for
ing:
the Determination of Chemical Composition
Copper UNS No. Classification B224 Designation
E478 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of CopperAlloys
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
C11300, C11400, C11500, and C11600 STP
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
C12000 DLP
C12200 DHP
C12300 DHPS
3. Terminology
C14520 DPTE
3.1 For definitions of terms related to copper and copper
1.3 Although this specification includes certain UNS desig-
alloys, refer to Terminology B846. For definitions of terms
nations as described in Practice E527, these designations are
related to standard classification of coppers, refer to Classifi-
for cross reference only and are not specification requirements.
cation B224.
Therefore, in case of conflict, this ASTM specification shall
govern.
4. Ordering Information
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
4.1 Include the following information, as applicable:
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
4.1.1 ASTM Specification Designation and year of issue;
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
4.1.2 Copper UNS No. Designation;
information only and are not considered standard.
4.1.3 Quantity, shape, and dimension of each piece, and
1.4.1 Exception—Electrical resistivity is expressed in SI
weight;
units.
4.1.4 Should cakes, slabs, or billets be ordered for electrical
use, it must be stated in the contract or purchase order.
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.5 Silver content in silver-bearing shapes, when required,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in troy oz per short ton.
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor
5. Materials and Manufacture
Materials
5.1 Materials:
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper 5.1.1 The material of manufacture shall be a form (copper
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.07 on
wire bar, cake, slabs, billets, ingots, and ingot bars) of Copper
Refined Copper.
Alloy “ETP” (UNS C11000) or “FRHC” (UNS C11020) of
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016. Published November 2016. Originally
such purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing into
approved in 1911. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as B5 – 11. DOI:
10.1520/B0005-16.
the prescribed herein.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
5.1.2 When specified in the contract or purchase order that
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
heat identification or traceability is required, the purchaser
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. shall specify the details desired.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B5−16
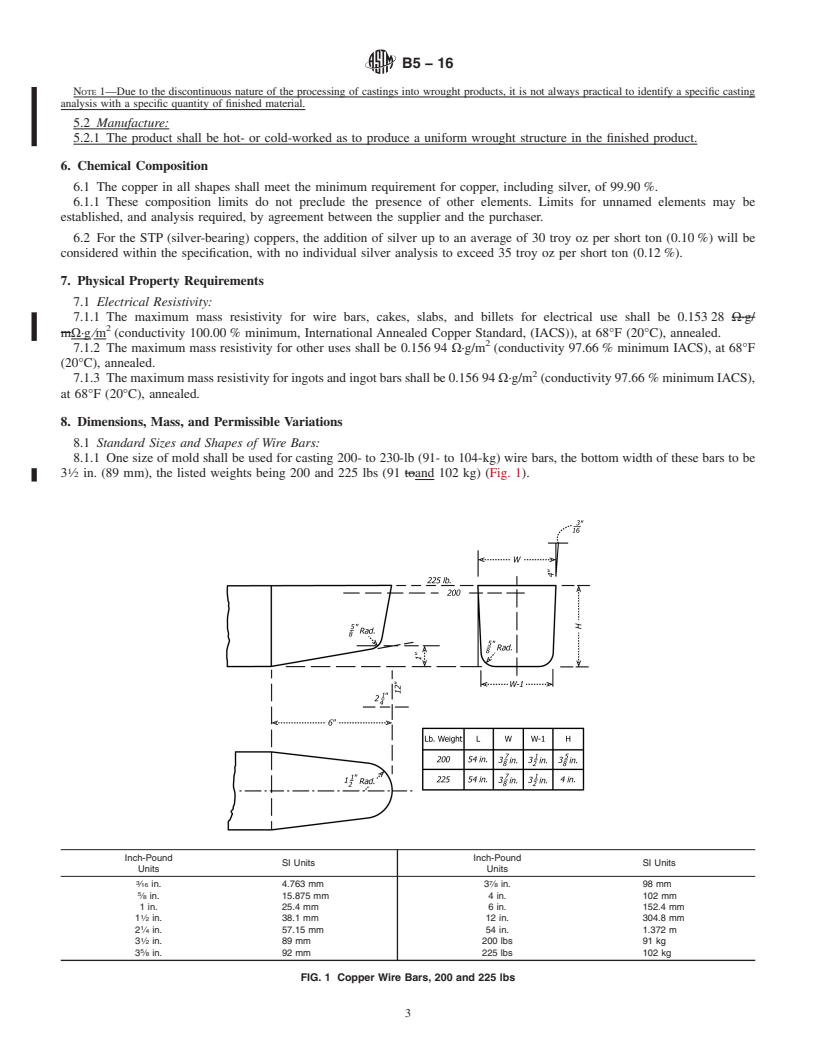
NOTE 1—Due to the discontinuous nature of the processing of castings
7.1.2 The maximum mass resistivity for other uses shall be
2
into wrought products, it is not always practical to identify a specific
0.156 94 Ω·g/m (conductivity 97.66 % minimum IACS), at
casting analysis with a specific quantity of finished material.
68°F (20°C), annealed.
5.2 Manufacture:
7.1.3 The maximum mass resistivity for ingots and ingot
2
5.2.1 Theproductshallbehot-orcold-workedastoproduce
bars shall be 0.156 94Ω·g/m (conductivity 97.66 % minimum
a uniform wrought structure in the finished product.
IACS), at 68°F (20°C), an
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B5 − 11 B5 − 16
Standard Specification for
1
High Conductivity Tough-Pitch Copper Refinery Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B5; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for high conductivity, tough-pitch, copper wire bars, cakes, slabs, billets,
ingots, and ingot bars.
1.2 Copper under this specification corresponds to the designations “ETP” (UNS C11000) and “FRHC” (UNS C11020) as
shown in Classification B224. These coppers may also be used to produce coppers corresponding to the following:
Copper UNS No. Classification B224 Designation
C11300, C11400, C11500, and C11600 STP
C12000 DLP
C12200 DHP
C12300 DHPS
C14520 DPTE
1.3 Although this specification includes certain UNS designations as described in Practice E527, these designations are for cross
reference only and are not specification requirements. Therefore, in case of conflict, this ASTM specification shall govern.
1.4 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Electrical resistivity is expressed in SI units.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
B224 Classification of Coppers
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
B950 Guide for Editorial Procedures and Form of Product Specifications for Copper and Copper Alloys
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E53 Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed Copper by Gravimetry
E255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for the Determination of Chemical Composition
E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms related to copper and copper alloys, refer to Terminology B846. For definitions of terms related to
standard classification of coppers, refer to Classification B224.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Include the following information, as applicable:
4.1.1 ASTM Specification Designation and year of issue,issue;
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.07 on Refined
Copper.
Current edition approved April 1, 2011Oct. 1, 2016. Published May 2011November 2016. Originally approved in 1911. Last previous edition approved in 20052011 as
B5 – 00B5 – 11. (2005). DOI: 10.1520/B0005-11.10.1520/B0005-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B5 − 16
4.1.2 Copper UNS No. Designation,Designation;
4.1.3 Quantity, shape, and dimension of each piece, and weight,weight;
4.1.4 Should cakes, slabs, or billets be ordered for electrical use, it must be stated in the contract or purchase order, andorder.
4.1.5 Silver content in silver-bearing shapes, when required, in troy oz per short ton.
5. Materials and Manufacture
5.1 Materials:
5.1.1 The material of manufacture shall be a form (copper wire bar, cake, slabs, billets, ingots, and ingot bars) of Copper Alloy
“ETP” (UNS C11000) or “FRHC” (UNS C11020) of such purity and soundness as to be suitable for processing into the prescribed
herein.
5.1.2 When specified in the contract or purchase order that heat identification or traceability is required, the purchaser shall
specify the details desired.
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
B5 − 16
NOTE 1—Due to the discontinuous nature of the processing of castings into wrought products, it is not always practical to identify a specific c
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.