ASTM D6777-02(2010)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Relative Rigidity of Poly(Vinyl Chloride)(PVC) Siding
Standard Test Method for Relative Rigidity of Poly(Vinyl Chloride)(PVC) Siding
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Vinyl siding with higher rigidity is often easier to install and expected to provide a straighter appearance when installed on walls having an uneven surface.
The rigidity of vinyl siding is believed to be controlled primarily its characteristic configuration and is not believed to be significantly influenced by manufacturing variables. Siding weight has little influence on this test.
SCOPE
1.1 This procedure describes a method to determine a numerical value indicating the relative rigidity or stiffness of vinyl siding panels. This procedure is not intended for routine quality control inspection during the manufacture of vinyl siding. The rigidity of vinyl siding is believed to be controlled primarily by its configuration and is not believed to be significantly influenced by manufacturing variables.
1.2 Vinyl siding with higher rigidity is often easier to handle and install. It is expected to provide a straighter appearance when installed on walls having an uneven surface.
1.3 All other vinyl siding requirements and test methods can be identified through Specification D3679.
1.4 There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D6777 − 02(Reapproved 2010) An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Relative Rigidity of Poly(Vinyl Chloride)(PVC) Siding
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6777; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—Reapproved with editorial changes throughout in November 2010.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This procedure describes a method to determine a
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
numerical value indicating the relative rigidity or stiffness of
nology D883 and D1600 unless otherwise indicated.
vinyl siding panels. This procedure is not intended for routine
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
quality control inspection during the manufacture of vinyl
3.2.1 relative rigidity (of PVC siding)—stiffness of a piece
siding. The rigidity of vinyl siding is believed to be controlled
of vinyl siding.
primarily by its configuration and is not believed to be
3.2.2 rigidity index (of PVC siding)—amount of sample sag
significantly influenced by manufacturing variables.
or deflection relative to sample length. The “rigidity index” is
1.2 Vinyl siding with higher rigidity is often easier to handle
defined as 100 minus the deflection value, divided by the
and install. It is expected to provide a straighter appearance
sample length, expressed as a percentage.
when installed on walls having an uneven surface.
1.3 All other vinyl siding requirements and test methods can
4. Summary of Test Method
be identified through Specification D3679.
4.1 In this procedure the test specimen is a piece of vinyl
1.4 There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
siding 100 in. long. This specimen is placed on top of a level
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the table with 50 in. of the specimen extending unsupported past
the edge of the table, allowing the specimen to sag under its
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- own weight. The amount of sag that occurs is used to calculate
a rigidity index for the sample.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 Vinyl siding with higher rigidity is often easier to install
2.1 ASTM Standards: and expected to provide a straighter appearance when installed
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing on walls having an uneven surface.
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
5.2 The rigidity of vinyl siding is believed to be controlled
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
primarily its characteristic configuration and is not believed to
tics
be significantly influenced by manufacturing variables. Siding
D3679 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
weight has little influence on this test.
Siding
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
6. Interferences
Plastics Specimens
6.1 The supporting table and floor must be parallel and level
with each other. Calibrations of flatness and levelness, as
describedin9.2-9.4shallbeperformedbeforerunningthistest.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.24 on Plastic Building
Products.
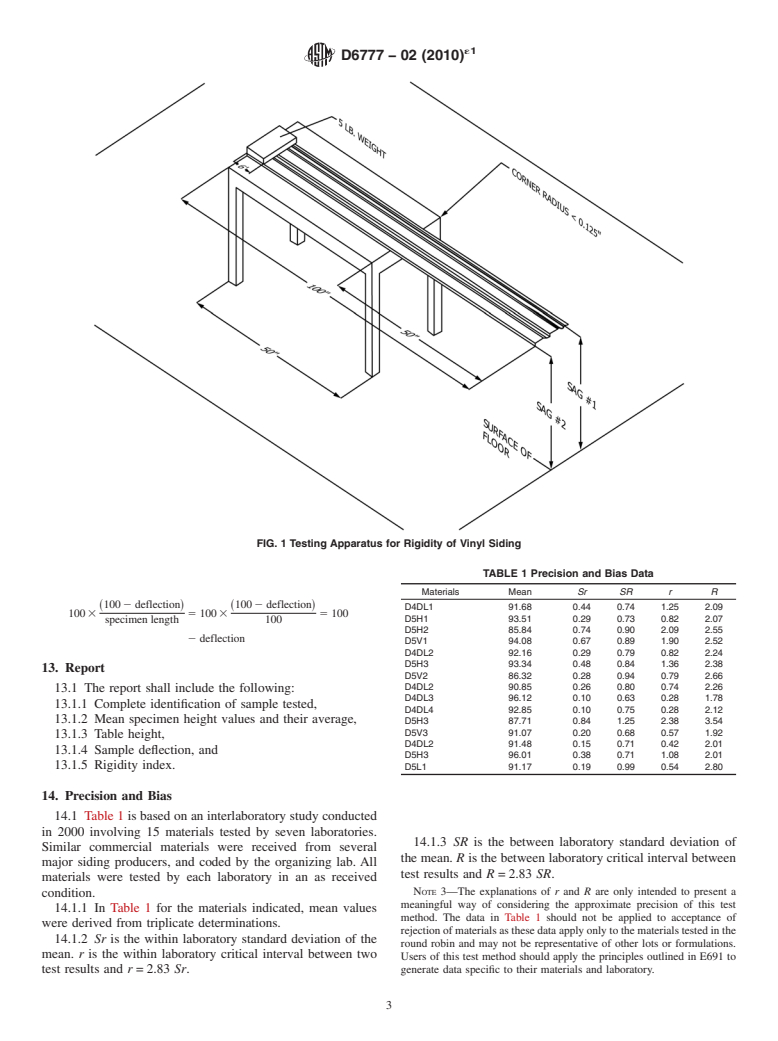
7. Apparatus
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2010. Published March 2011. Originally
7.1 This procedure requires a table that is flat and level. The
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D6777 - 02.
DOI:10.1520/D6777-02R10E01.
table must be at least 50 in. long and at least as wide as the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
widest test specimen to be measured. The height of the table is
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
not critical.The edge of the table over which the specimen will
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. extend shall not have a radius more than 0.125 in. The table
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
D6777 − 02 (2010)
must be positioned on a hard surface or floor (no carpet) that is 9.5 If necessary to correct the level of the table, shims can
also flat and level over a length extending at least 50 in. from be permanently attached to the bottom of the table legs.
the edge of the table.
10. Conditioning
7.2 Aweightconsistingofa5lbsandbagisusedtoholdthe
end of the siding specimen firmly against the table top. The
10.1 Prior to testing, condition the test specimen for a
weight shall be as wide as the widest siding specimen to be
minimum of 24 h at a temperature of 73.4°F 6 3.6 (20°C 6 2).
tested.
During conditioning the specimen shall rest on a flat surface
that supports the specimen over its entire length.
7.3 A line shall be drawn on the table to ensuring that the
specimensarepositionedperpendiculartotheedgeofthetable.
11. Procedure
This line shall be drawn as a perpendicular to the edge using a
large framing square at least 10 in. on each side.
11.1 Select one (unnotched) end of the specimen to be the
7.4 Arigid ruler (such as a folding carpenter’s ruler or large end that will extend off the table. Label this end of the
metal framing square) is used to measure the distance from the specimen to avoid subsequent confusion about which end is to
floor to the table top and the suspended end of the siding
be unsupported. Using a tape measure, make a mark 50 6 ⁄16
specimen. This ruler needs to be at least one inch longer than in. from this unsupported end.
the height of the table, and shall be scribed to allow measure-
11.2 Place the specimen face up (the face is the side that is
ments to the nearest ⁄16 in.
exposed after installation) on the table so that the specimen is
NOTE 1—It is recommended that the end of the ruler being placed
perpendicular to the edge of the table (parallel to the perpen-
against the floor be protected with a cap to prevent abrasive wear.
dicular line drawn on the table) and with the 50 in. mark
7.5 A tape measure is used to measure the length of the directly over the table edge.
siding specimen. This tape measure needs to be at least 101 in.
11.3 Place the weight described in 7.2 on the supported end
long, and shall be scribed to allow measurements to the nearest
of the specimen (the end on the table). The edge of the weight
⁄16 in.
furthest from the supported end shall be 6 6 0.5 in. from the
supported end (see Fig. 1). The weight shall cover the entire
8. Sampling, Test Specimens, and Test Units
width of the specimen.After positioning the weight verify once
8.1 The test specimen shall be taken from a vinyl siding
again that the position of the specimen is as described in 11.2.
panelcomplyingwithSpecificationD3679.Thesidingpanelas
The panel shall be allowed to bow upwa
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.