ASTM E514-90(1996)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Water Penetration and Leakage Through Masonry
Standard Test Method for Water Penetration and Leakage Through Masonry
SCOPE
1.1 This laboratory test method provides a procedure for determining the resistance to water penetration and leakage through unit masonry subjected to wind-driven rain.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement see Section 5.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
e1
Designation:E514–90(Reapproved 1996)
Standard Test Method for
Water Penetration and Leakage Through Masonry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 514; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
e NOTE—Keywords were added editorially in June 1996.
1. Scope mance will also depend on the rigidity of supporting structure
2 andontheresistanceofcomponentstodeteriorationbyvarious
1.1 This laboratory test method provides a procedure for
causes, such as corrosion, vibration, thermal expansion and
determining the resistance to water penetration and leakage
contraction, curing, and others. It is impossible to simulate the
through unit masonry subjected to wind-driven rain.
complex conditions encountered in service, such as variations
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in wind velocity, negative pressure, and lateral or upward
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
moving air and water. Factors such as geographical location,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
topographic exposure, and wall openings should be fully
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
considered also.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
3.4 Given the complexity of variables noted above, this test
hazard statement see Section 5.
method is of primary use to establish comparative behavior
2. Referenced Documents between various masonry wall constructions in a given labo-
ratory.
2.1 American Concrete Institute Standard:
3.5 In fact, even when two laboratories test the same wall
ACI 531 Building Code Requirements for Concrete Ma-
design utilizing the same wall materials and the same construc-
sonry Structures
tion practices, variables such as the level of skill of the mason
2.2 Brick Institute of America Standard:
building the specimen, the temperature and humidity in the
Construction of Brick Masonry, Building Code Require-
laboratory at the time of construction and curing of the
ments for Engineered Brick Masonry
specimen, the moisture contents of the materials used to build
3. Significance and Use
the specimen and even the use or lack of use of a lime and
water wash on the back of the specimen can affect the results
3.1 This test method allows obtaining information that aids
of the test making reliable comparisons between laboratories
in evaluating the effect of four principal variables: the quality
dubious. For these reasons and the multi-variables listed in 3.1,
of materials, coatings, wall design, and workmanship.
3.2, and 3.3, a meaningful, useful, absolute wall leakage rating
3.2 Water penetration and leakage through masonry is
standard is impractical and discouraged by this test method.
significantly affected by air pressure in the test chamber. Data
from tests made at different pressures are not comparable.
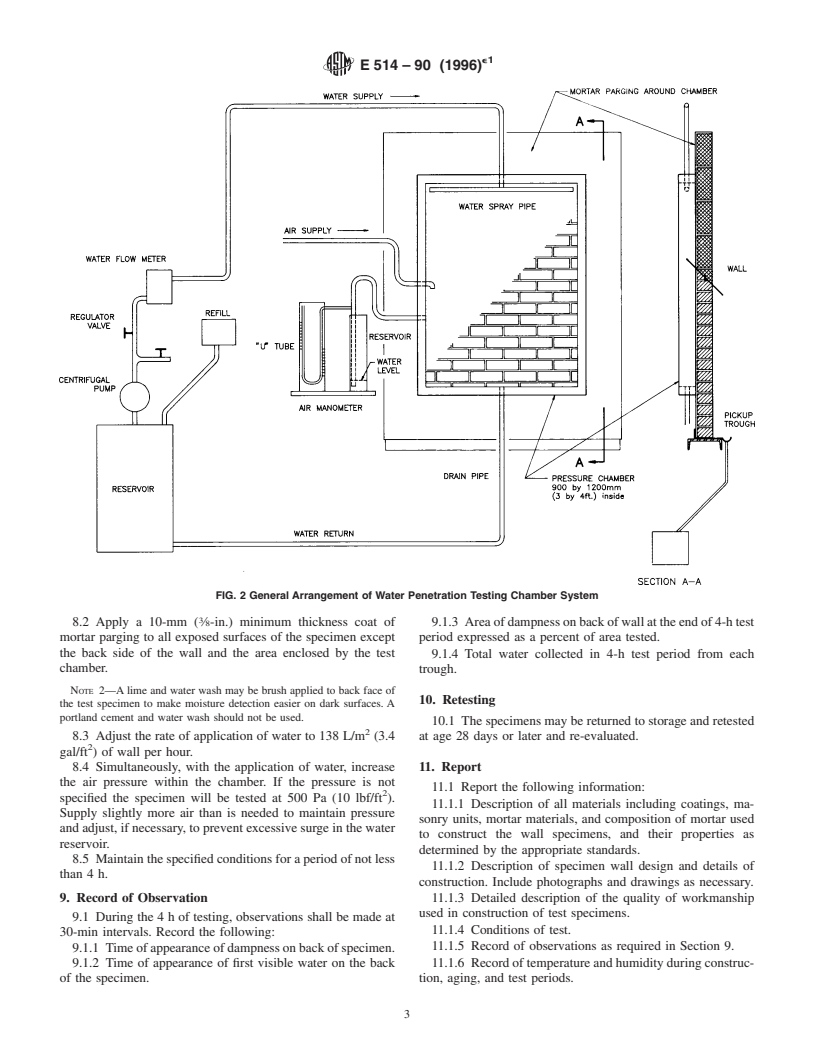
4. Apparatus
3.3 In applying the test method results, it should be noted
4.1 TestChamber—The test chamber shall be similar to that
that the performance of a masonry wall is the function of
shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 and may be constructed of metal,
materials, construction, and wall design. In service the perfor-
wood, or plastic. It shall provide an opening with a minimum
2 2
areaof1.08m (12ft ).Forexample,900mm(36in.)wideand
1200 mm (48 in.) high is suitable. Edges of the chamber in
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-15 on
contact with the specimen shall be lined with a closed-cell
Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
C15.04 on Research. compressible gasket material. An observation port shall be
Current edition approved July 27, 1990. Published September 1990. Originally 3
provided in the face of the chamber. The 19.0-mm ( ⁄4-in.)
published as E 514 – 74. Last previous edition E 514 – 86.
diameter corrosion-resistant spray pipe shall have a single line
This test method is based upon those used by the National Bureau of Standards
of 1.0-mm (0.04-in.) diameter holes spaced 25.0 mm (1 in.)
and described in NBS Report BMS7, “Water Permeability of Masonry Walls,” 1933,
and NBS Report BMS82, “Water Permeability of Walls Built of Masonry Units,”
apart.
1942.
4.2 Fixtures and Appurtenances to Chamber—Fixtures and
Available from American Concrete Inst., P. O. Box 19150, Detroit, MI 48219.
appurtenances to the chamber shall consist of an air line with
Available from Brick Institute of America, 11490 Commerce Park Dr., Suite
300, Reston, VA 22091. manometer, a water line with valves, an orifice meter and
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
e1
E514–90 (1996)
FIG. 1 Isometric Projection of Testing Chamber
manometer and a water drain pipe at the bottom of the to the test, plus at least a 200-mm (8-in.) overlap on all edges.
chamber. The water spray pipe shall be positioned so that the The minimum height or length of the specimen shall be 1.22 m
water impinges the specimen not more than 75.0 mm (3.00 in.) (4 ft).The length of the specimen shall be such that at least one
below the top of the test chamber. The drain pipe may head joint in each course of masonry is exposed to the test.
discharge into a container equipped with an adjustable depth 7.3 Building Wall Specimens—Methods and workmanship
air outlet pipe and top baffles to reduce surge. used in the construction of the specimen shall be representative
4.3 Other equipment shall consist of devices for handling of the construction (Note 1). Build the wall specimen on an
the specimen and measuring tim
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.